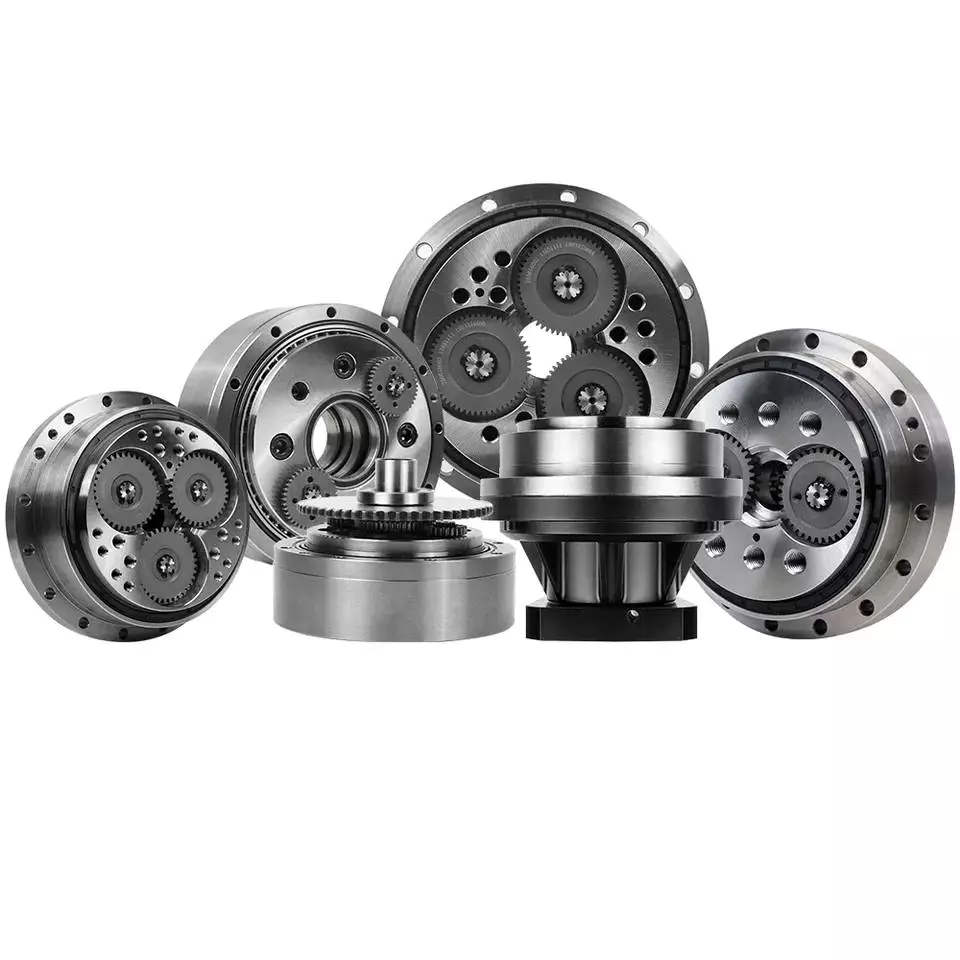
Product Description
Technical Features
The high degree of modularity is a design feature of SRC helical gearboxes range. It can be connected respectively with motors such as normal motor, brake motor, explosion-proof motor, frequency conversion motor, servo motor, IEC motor and so on. This kind of product is widely used in drive fields such as textile, foodstuff, ceramics packing, logistics, plastics and so on. It is possible to set up the version required using flanges or feet.
Products characteristics
SRC series helical gear units has more than 4 types. Power 0.12-4kw; Ratio 3.66-54; Torque max 120-500Nm. It can be connected (foot or flange) discretionary and use multi-mounting positions according to customers requirements.
Ground-hardened helical gears;
Modularity,can be combined in many forms;
Aluminium casing, light weight;
Gears in carbonize hard, durable;
Universal mounting;
Refined design,space effective and low noise
Structure feature
Model illuminate
|
1 |
Code for gear units series |
|
2 |
No F code means foot mounted.With F code B5 flange mounted.With Z code B14 flange mounted |
|
3 |
Specification code of gear units 01 |
|
4 |
I,II,III,B5 Output flange specification,default I not to write out is ok |
|
5 |
IEC: Input flange HS: shaft input |
|
6 |
Transmission ratio of gear units |
|
7 |
M1:Mounting position, default mounting position M1 not to write out is ok |
|
8 |
Position diagram for motor terminal box,default position o°(R) not to write out is ok |
|
9 |
No mark means without motor Model motor(poles of power) |
|
10 |
Voltage – frequency |
|
11 |
Coil in position for motor, default position S not to write out is ok |
4.2 Rotation speed n
n1 Gear units input speed
n2 Gear units output speed
If driven by the external gearing,1400r/min or lower rotation speed is suggested so as to optimize the working conditions and prolong the service life.Higher input rotation speed is permitted, but in this situation,the rated torque M2 will be reduced
4.5 Service factor fs
The effect of the driven machine on the gear unit is taken into account to a sufficient level of accuracy using the service factor fs. The service factor is determined according to the daily operation time and the starting frequency Z. Three load classifications are considered depending on the mass acceleration factor. You can read off the service factor applicable to your application in following figure. The service factor selected using this diagram must be less than or equal to the service factor as given in the performance parameter table.
* starting frequency Z: The cycles include all starting and braking procedures as well as change overs from low to high speed
SRC02..(HS) Performance parameter
|
kw |
Output speed |
Torque |
Speed ratio |
fs |
Model |
IEC |
|
0.37 |
16.7rpm |
204N.M |
54 |
1.0 |
SRC02 |
80B5/B14
|
Helical gearbox outline dimension heet
| Foot Code | U | V | V1 | V2 | V3 | W | X | X1 | Y | Z |
| B02 | 18 | 107.5 | 60 | – | 130 | 11 | 136 | 155 | 100 | 17 |
| M02 | 25 | 85 | – | 110 | 120 | 9 | 112 | 145 | 80 | 15 |
| M01 | 18 | 80 | – | 110 | 120 | 9 | 118 | 145 | 80 | 15 |
| B01 | 18 | 87 | 50 | 110 | – | 9 | 118 | 130 | 90 | 15 |
SRC helical gearbox with motor mounting position and terminal box orientation
Package
1 pc / carton,several cartons / wooden pallet
| Application: | Motor |
|---|---|
| Layout: | Cycloidal |
| Hardness: | Soft Tooth Surface |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How to Calculate Transmission Ratio for a Cycloidal Gearbox
Using a cycloidal gearbox can be very useful in a wide variety of situations. However, it’s important to understand how to use it properly before implementing it. This article discusses the benefits of using a cycloidal gearbox, how to calculate the transmission ratio, and how to determine the effects of dynamic and inertial forces on the gearbox.
Dynamic and inertial effects
Various studies have been done to study the dynamic and inertial effects of cycloidal gearboxes. These studies have been performed using numerical, analytical and experimental methods. Depending on the nature of the load and its distribution along the gear, a variety of models have been developed. These models use finite element method to determine accurate contact stresses. Some of these models have been developed to address the nonlinear elasticity of contacts.
Inertial imbalance in a cycloidal gearbox causes vibration and can affect the efficiency of the device. This can increase mechanical losses and increase wear and tear. The efficiency of the device also depends on the torque applied to the cycloidal disk. The effectiveness of the device increases as the load increases. Similarly, the nonlinear contact dynamics are also associated with an increase in efficiency.
A new model of a cycloidal reducer has been developed to predict the effects of several operational conditions. The model is based on rigid body dynamics and uses a non-linear stiffness coefficient. The model has been validated through numerical and analytical methods. The model offers drastic reduction in computational costs. The model allows for a quick analysis of several operational conditions.
The main contribution of the paper is the investigation of the load distribution on the cycloidal disc. The study of this aspect is important because it allows for an analysis of the rotating parts and stresses. It also provides an indication of which gear profiles are best suited for optimizing torque transmission. The study has been conducted with a variety of cycloidal gearboxes and is useful in determining the performance of different types of cycloidal gearboxes.
To study the load distribution on the cycloidal disc, the authors investigated the relationship between contact force, cycloidal gearboxes and different gear profiles. They found that the non-linear contact dynamics have a large impact on the efficiency of a cycloidal gearbox. The cycloidal gearbox is an ideal solution for applications that involve highly dynamic servos. It can also be used in machine tool applications and food processing industries.
The study found that there are three common design principles of cycloidal reducers. These are the contact force distribution, the speed reduction and the trochoidal profile of the cycloidal disc. The trochoidal profile has to be defined carefully to ensure correct mating of the rotating parts. The trochoidal profile provides an indication of which gear profiles are best for optimizing torque transmission. The contact force distribution can be improved by refining the mesh along the disc’s width.
As the input speed increases, the efficiency of the reducer increases. This is because contact forces are constantly changing in magnitude and orientation. A cycloidal reducer with a one tooth difference can reduce input speed by up to 87:1 in a single stage. It also has the ability to handle high-cycle moves without backlash.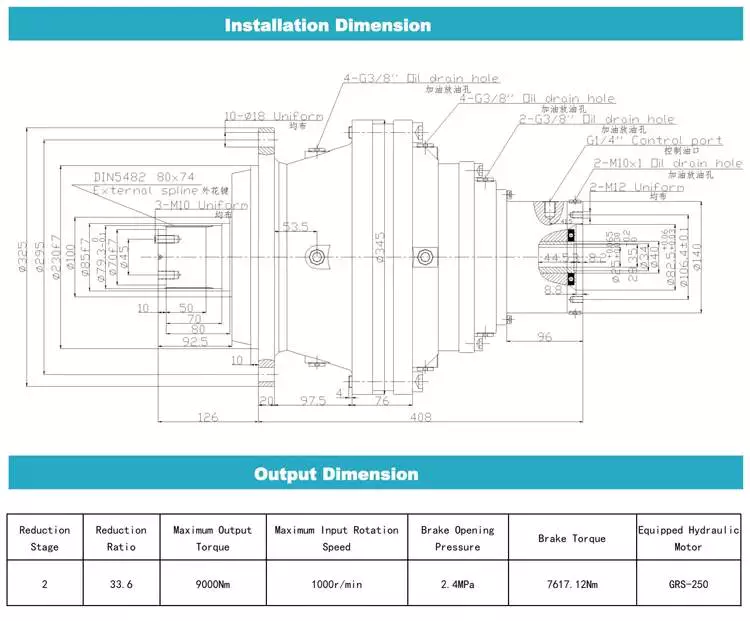
Transmission ratio calculation
Getting the correct transmission ratio calculation for a cycloidal gearbox requires a good understanding of what a gearbox is, as well as the product that it is being used for. The correct ratio is calculated by dividing the output speed of the output gear by the input speed of the input gear. This is usually accomplished by using a stopwatch. In some cases, a catalog or product specification may be required. The correct ratio is determined by a combination of factors, such as the amount of torque applied to the mechanism, as well as the size of the gears involved.
A cycloidal gear is a type of gear tooth profile that can be represented using a spline. It is also possible to model a gear with a cycloidal profile by using a spline to connect points against the beginning of a coordinate system. This is important in the design and functionality of a gear.
There are many different gears used in machines and devices. These include the herringbone gear, the helical gear and the spiral bevel gear. The best transmission ratios are typically obtained with a cycloidal gearbox. In addition to ensuring the accuracy of positioning, a cycloidal gearbox provides excellent backlash. Cycloid gears have a high degree of mechanical efficiency, low friction, and minimal moment of inertia.
A cycloidal gearbox is often referred to as a planetary gearbox, though it is technically a single-stage gearbox. In addition to having a ring gear, the gearbox has an eccentric bearing that drives the cycloidal disc in an eccentric rotation. This makes the cycloidal gearbox a good choice for high gear ratios in compact designs.
The cycloid disc is the key element of a cycloidal gearbox. The cycloid disc has n=9 lobes, and each lobe of the disc moves by a lobe for every revolution of the drive shaft. The cycloid disc is then geared to a stationary ring gear. The cycloidal disc’s lobes act like teeth on the stationary ring gear.
There are many different gears that are classified by the profile of the gear teeth. The most common gears are the involute and helical gears. Most motion control gears include spur designs. However, there are many other types of gears that are used in various applications. The cycloidal gear is one of the more complicated gears to design. The cycloid disc’s outline can be represented using markers or smooth lines, though a scatter chart will also do.
The cycloid disc’s lobes rotate on a reference pitch circle of pins. These pins rotate 40 deg during the eccentric rotation of the drive shaft. The pins rotate around the disc to achieve a steady rotation of the output shaft.
The cycloid disc’s other obvious, and possibly more important, feature is the’magic’ number of pins. This is the number of pins that protrude through the face of the disc. The disc has holes that are larger than the pins. This allows the pins to protrude through the disc and attach to the output shaft.
Application
Whether you’re building a robot drive or you’re simply looking for a gearbox to reduce the speed of your vehicle, a cycloidal gearbox is a great way to achieve a high reduction ratio. Cycloidal gearboxes are a low-friction, lightweight design that has an extremely stable transmission. They are suitable for industrial robots and can be used in many applications, including positioning robots.
Cycloidal gearboxes reduce speed by using eccentric motion. The eccentric motion enables the entire internal gear to rotate in wobbly cycloidal motion, which is then translated back into circular rotation. This eliminates the need for stacking gear stages. Cycloidal gearboxes also have less friction, higher strength, and greater durability than conventional gearboxes.
The cycloidal gearbox is also used in a number of applications, including marine propulsion systems, and robot drives. Cycloidal gearboxes reduce vibration by using offset gearing to cancel out vibrations.
Cycloidal gears have lower friction, higher strength, and better torsional stiffness than involute gears. They also have a reduced Hertzian contact stress, making them better than involute gears for use with shock loads. They also have a smaller size and weight than conventional gearboxes, and they have a higher reduction ratio than involute gears.
Cycloidal gears are typically used to reduce the speed of motors, but they also offer a number of other advantages. Cycloidal gearboxes have a smaller footprint than other gearboxes, allowing them to fit into confined spaces. They also have low backlash, allowing for precise movement. Cycloidal gears have a higher efficiency, resulting in lower power requirements and lower wear.
The cycloidal disc is one of the most important components of the gearbox. Cycloidal discs are normally designed with a short cycloid, which minimizes the eccentricity of the disc. They are also designed with a shortened flank, resulting in better strength and less stress concentration. Cycloidal discs are typically geared to a stationary ring gear. The cycloid is designed to roll around the stationary ring pins, which push against the circular holes in the disc. Cycloidal gearboxes typically employ two degrees of shift.
Cycloidal drives are ideal for heavy load applications. They also have high torsional stiffness, which makes them highly resistant to shock loads. Cycloidal drives also offer a high reduction ratio, which can be achieved without the need for a large input shaft. They are also compact and have a high service life.
The output shaft of a cycloidal gearbox always has two degrees of shifting, which ensures that the input and output shafts always rotate at a different speed. The output shaft would be a pin casing around the drive disks, which would also allow for easy maintenance.
Cycloidal gearboxes are also very compact and lightweight, so they are ideal for use in industrial robots. The cycloidal gearbox reducer is the most stable, low-vibration reducer in industrial robots, and it has a wide transmission ratio range.

editor by CX 2023-10-20
China wholesaler Gear Ratio 25: 1 Lost Motion Less Than 1 Arc. Min Transmission Gearboxes for Trunnion Table with Good quality
Product Description
Product Description
Gear Ratio 25: 1 Lost motion less than 1 arc.min transmission gearboxes for Trunnion Table
high-precision corner reducer for 5 axis machining center developed and manufactured by WEITENSTAN together with German and ZheJiang technicians for many years.
This high-precision corner reducer has high precision (backlash less than 1arcmin), low noise (68dB), and can replace the harmonic drive reducer. The life and rigidity are 3 times longer than the harmonic.
high-precision corner reducer has the characteristics of smaller, ultra-thin, lightweight and high rigidity, anti-overload and high torque. With good deceleration performance, smooth operation and accurate positioning can be achieved. Integrated design, can be directly connected with the motor, to achieve high precision, high rigidity, high durability and other advantages. It is designed for high speed ratio, high geometric accuracy, low motion loss, large torque capacity and high stiffness applications. The compact design (minimum OD ≈40mm, currently the world’s smallest precision cycloidal pin-wheel reducer) allows it to be installed in limited Spaces.
Reducer drawings
Detailed Photos
Product Advantage
Gear Ratio 25: 1 Lost motion less than 1 arc.min transmission gearboxes for Trunnion Table
advantages:
1, fine precision cycloidal structure
Ultra flat shape is achieved through differential reduction mechanism and thin cross roller bearing, contributing to the compact size of the equipment. The combination of small size and unmatched superior parameters achieves the best combination of performance, price and size (high cost performance).
2. Excellent accuracy (transmission loss ≤1 arcmin)
Through the complex meshing of precision cycloid gear and high precision roller pin, higher transmission accuracy is achieved while maintaining small size and high speed ratio.
3, high rigidity
Increase the mesh rate to disperse the load, so the rigidity is high.
4. High overload capacity
It maintains trouble-free operation under abnormally low noise and vibration conditions while ensuring excellent overturning and torsional stiffness parameters. Integrated axial radial cross roller bearings, high load capacity and overload capacity of the reducer, can ensure users to provide a variety of temperature range of applications.
5, the motor installation is simple
Electromechanical integration design, can be directly connected with the motor, any brand of motor can be installed directly, without adding any device.
6. Maintenance free
Seal grease to achieve maintenance free. No refueling, no mounting direction restrictions.
7, stable performance
The manufacturing process of high wear-resistant materials and high precision parts has been certified by ISO9000 quality system, which guarantees the reliable operation of the reducer.
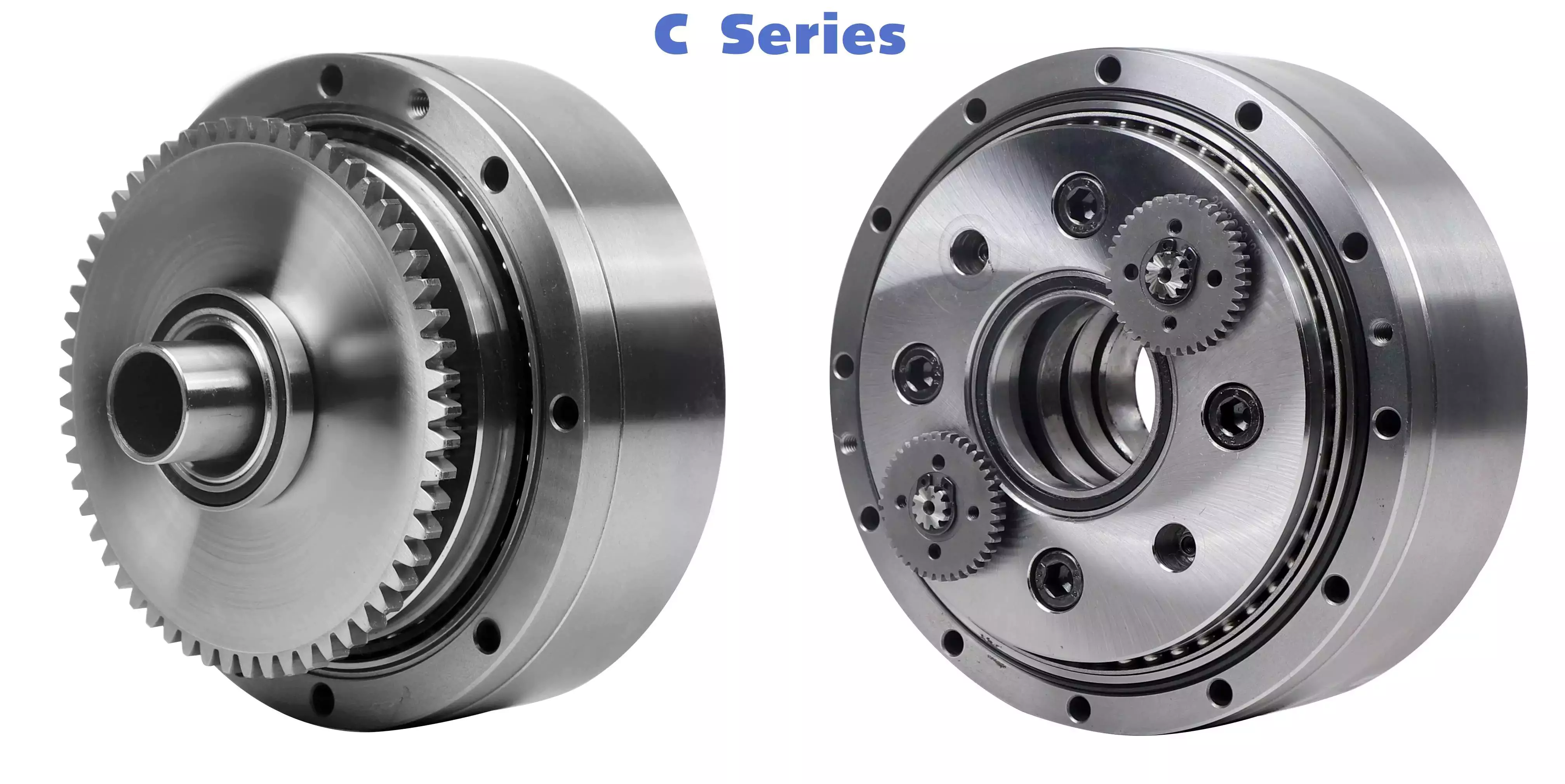
Product Classification
WF Series
High Precision Miniature Reducer
WF series is a high precision micro cycloidal reducer with flange, which has a wide range of applications. This series of reducers includes precise reduction mechanisms and radial – axial roller bearings. The unique design allows load to act directly on the output flange or housing without additional bearings. WF series reducer is characterized by module design, can be installed through the flange motor and reducer, belongs to the motor directly connected reducer.
WFH Series
High Precision Miniature Reducer
WFH series is a hollow form of high precision miniature cycloidal reducer, wire, compressed air pipeline, drive shaft can be through the hollow shaft, non-motor direct connection type reducer. The WFH series is fully sealed, full of grease and includes precise deceleration mechanism and radial – axial roller bearings. The unique design allows load to be acted directly on the output flange or housing without additional bearings.
WR Series
high-precision corner reducer
The WR series is a flange output corner reducer. Like the WF and WFH series, it is a high-precision reducer (backlash less than 1 arc.min), and the level 2 can also be within 1 arc.min, which is higher than other types. Corner type reducer. It can replace the harmonic drive reducer, and its life and rigidity are more than 3 times that of the harmonic.
Product Parameters
| Size | reduction ratio | Rated output moment | Allowable torque of start and stop | Instantaneous allowable moment | Rated input speed | Maximum input speed | Tilt stiffness | Torsional stiffness | No-load starting torque | Transmission accuracy | Error accuracy | Moment of inertia | Weight | |
| Axis rotation | Shell rotation | Nm | Nm | Nm | rpm | rpm | Nm/arcmin | Nm/arcmin | Nm | arcmin | arcmin | kg-m² | kg | |
| WR25 | 21 | 20 | 110 | 220 | 330 | 3000 | 5500 | 131 | 24 | 0.47 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | 6.12 | 2 |
| 31 | 30 | 0.41 | 5.67 | |||||||||||
| 41 | 40 | 0.38 | 4.9 | |||||||||||
| 51 | 50 | 0.35 | 4.56 | |||||||||||
| 81 | 80 | 0.31 | 4.25 | |||||||||||
| WR32 | 25 | 24 | 190 | 380 | 570 | 3000 | 4500 | 240 | 35 | 1.15 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | 11 | 4.2 |
| 31 | 30 | 1.1 | 10.8 | |||||||||||
| 51 | 50 | 0.77 | 9.35 | |||||||||||
| 81 | 80 | 0.74 | 8.32 | |||||||||||
| 101 | 100 | 0.6 | 7.7 | |||||||||||
| WR40 | 25 | 24 | 320 | 640 | 960 | 3000 | 4000 | 377 | 50 | 1.35 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | 13.2 | 6.6 |
| 31 | 30 | 1.32 | 12.96 | |||||||||||
| 51 | 50 | 0.92 | 11.22 | |||||||||||
| 81 | 80 | 0.81 | 9.84 | |||||||||||
| 121 | 120 | 0.72 | 8.4 | |||||||||||
Installation Instructions
Company Profile
Q: Speed reducer grease replacement time
A: When sealing appropriate amount of grease and running reducer, the standard replacement time is 20000 hours according to the aging condition of the grease. In addition, when the grease is stained or used in the surrounding temperature condition (above 40ºC), please check the aging and fouling of the grease, and specify the replacement time.
Q: Delivery time
A: Fubao has 2000+ production base, daily output of 1000+ units, standard models within 7 days of delivery.
Q: Reducer selection
A: Fubao provides professional product selection guidance, with higher product matching degree, higher cost performance and higher utilization rate.
Q: Application range of reducer
A: Fubao has a professional research and development team, complete category design, can match any stepping motor, servo motor, more accurate matching.
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
| Application: | Motor, Machinery, Agricultural Machinery, Humanoid Robot |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Vertical Type |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

The Basics of a Cyclone Gearbox
Besides being compact, cycloidal speed reducers also offer low backlash and high ratios. Because of the small size of the drive, they are ideal for applications where space is a problem.
Involute gear tooth profile
Almost all gears use an involute gear tooth profile. This profile has a single curve, which means that the gear teeth do not have to be aligned closely with each other. This profile is smooth and can be manufactured easily.
Cycloid gears have a combination of epicycloid and hypocycloid curves. This makes them stronger than involute gear teeth. However, they can be more expensive to manufacture. They also have larger reduction ratios. They transmit more power than involute gears. Cycloid gears can be found in clocks.
When designing a gear, you need to consider several factors. Some of these include the number of teeth, the tooth angle and the lubrication type. Having a gear tooth that is not perfectly aligned can result in transmission error, noise and vibration.
The tooth profile of an involute gear is usually considered the best. Because of this, it is used in a wide variety of gears. Some of the most common applications for this profile are power transmission gears. However, this profile is not the best for every application.
Cycloid gears require more complex manufacturing processes than involute gear teeth. This can cause a larger tooth cost. Cycloid gears are used for less noisy applications.
Cycloid gears also transmit more power than involute gears. This can cause problems if the radii change tangentially. However, the shape is more simple than involute gears. Involute gears can handle centre sifts better.
Cycloid gears are less susceptible to transmission error. Cycloid gears have a convex surface, which makes them stronger than involute teeth. Cycloid gears also have a larger reduction ratio than involute gears. Cycloid teeth do not interfere with the mating teeth. However, they have a smaller number of teeth than involute teeth.
Rotation on the inside of the reference pitch circle of the pins
Whether a cycloidal gearbox is designed for stationary or rotating applications, the fundamental law of gearing must be observed: The ratio of angular velocities must be constant. This requires the rotation on the inside of the reference pitch circle of the pins to be constant. This is achieved through a series of cycloidal teeth, which act like tiny levers to transmit motion.
A cycloidal disc has N lobes which are rotated by three lobes per rotation around N pins. The number of lobes on a cycloidal disc is a significant factor in determining the transmission ratio.
A cycloidal disc is driven by an eccentric input shaft which is mounted to an eccentric bearing within an output shaft. As the input shaft rotates, the cycloidal disc moves around the pins of the pin disc.
The drive pin rotates at a 40 deg angle while the cycloidal disc rotates on the inside of the reference pitch circle of pins. As the drive pin rotates, it will slow the output motion. This means that the output shaft will complete only three revolutions with the input shaft, as opposed to nine revolutions with the input shaft.
The number of teeth on a cycloidal disc must be small compared to the number of surrounding pins. The disc must also be constructed with an eccentric radius. This will determine the size of the hole which will be required for the pin to fit between the pins.
When the input shaft is turned, the cycloidal disc will rotate on the inside of the reference pitch circle of roller pins. This will then transmit motion to the output shaft. The output shaft is supported by two bearings in an output housing. This design has low wear and torsional stiffness.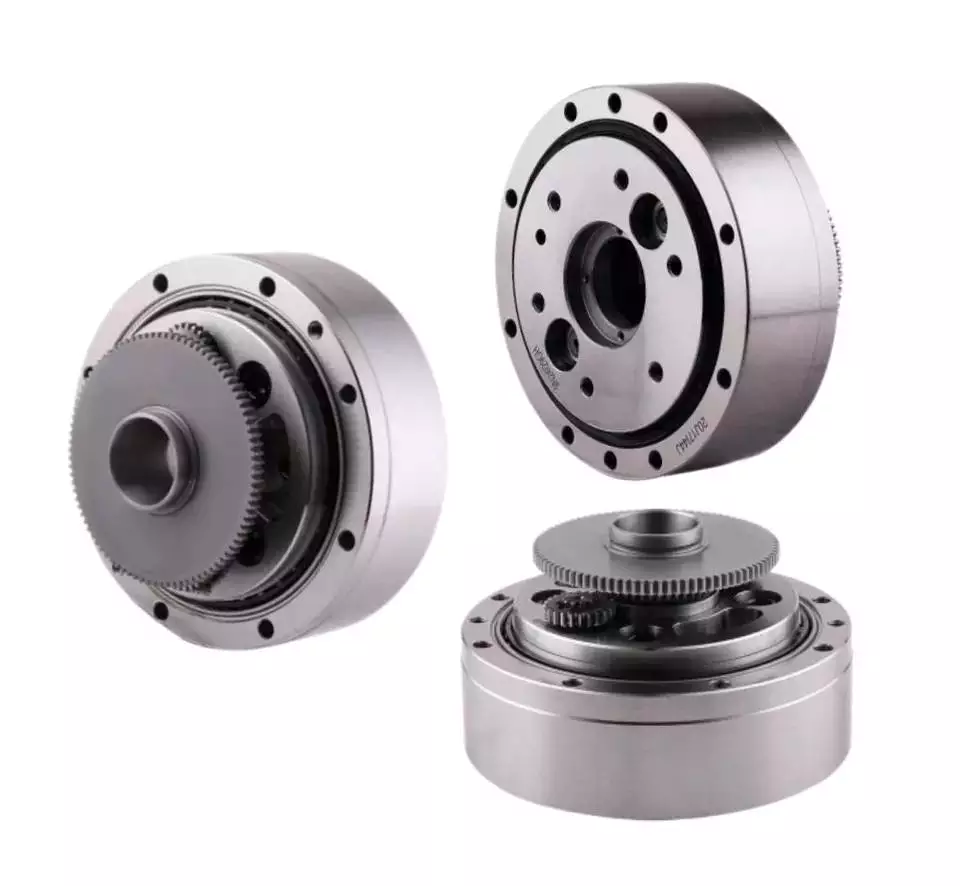
Transmission ratio
Choosing the right transmission ratio of cycloidal gearbox isn’t always easy. You might need to know the size of your gearbox before you can make an educated choice. You may also need to refer to the product catalog for guidance. For example, CZPT gearboxes have some unique ratios.
A cycloidal gear reducer is a compact and high-speed torque transmission device that reverses the direction of angular movement of the follower shaft. It consists of an eccentric cam positioned inside a cycloidal disc. Pin rollers on the follower shaft fit into matching holes in the cycloidal disc. In the process, the pins slide around the holes, in response to wobbling motion. The cycloidal disc is also capable of engaging the internal teeth of a ring-gear housing.
A cycloidal gear reducer can be used in a wide variety of applications, including industrial automation, robotics and power transmissions on boats and cranes. A cycloidal gear reducer is ideally suited for heavy duty applications with large payloads. They require specialized manufacturing processes, and are often used in equipment with precise output and high efficiency.
The cycloidal gear reducer is a relatively simple structure, but it does require some special tools. Cycloid gear reducers are also used to transmit torque, which is one of the reasons they are so popular in automation. Using a cycloidal gear reducer is a good choice for applications that require higher efficiency and lower backlash. It is also a good choice for applications where size is a concern. Cycloid gears are also a good choice for applications where high speed and high torque are required.
The transmission ratio of cycloidal gearbox is probably the most important function of a gearbox. You need to know the size of your gearbox and the type of gears it contains in order to make the right choice.
Vibration reduction
Considering the unique dynamics of a cycloidal gearbox, vibration reduction measures are required for a smooth operation. These measures can also help with the detection of faults.
A cycloidal gearbox is a gearbox with an eccentric bearing that rotates the center of the gears. It shares torque load with five outer rollers at any given time. It can be applied in many applications. It is a relatively inexpensive asset. However, if it fails, it can have significant economic impacts.
A typical input/output gearbox consists of a ring plate and two cranks mounted on the input shaft. The ring plate rotates when the input shaft rotates. There are two bearings on the output shaft.
The ring plate is a major noise source because it is not balanced. The cycloidal gear also produces noise when it meshes with the ring plate. This noise is generated by structural resonance. Several studies have been performed to solve this problem.
However, there is not much documented work on the condition monitoring of cycloidal gearboxes. In this article, we will introduce modern techniques for vibration diagnostics.
A cycloidal gearbox with a reduced reduction ratio has higher induced stresses in the cycloidal disc. In this case, the size of the output hole is larger and more material is removed from the cycloidal disc. This increase in the disc’s stresses leads to higher vibration amplitudes.
The load distribution along the width of the gear is an important design criterion. Using different gear profiles can help to optimize the transmission of torque. The contact stress of the cycloidal disc can also be investigated.
To determine the amplitude of the noise, the frequency of the gear mesh is multiplied by the shaft rate. If the RPM is relatively stable, the frequency can be used as a measure of magnitude. However, this is only accurate at close to failure.
Comparison with planetary gearboxes
Several differences exist between cycloidal gearboxes and planetary gearboxes. They are related to gear geometry and manufacturing processes. Among them, there are:
– The output shaft of a cycloidal gearbox has a larger torque than the input shaft. The rotational speed of the output shaft is lower than the input shaft.
– The cycloid gear disc rotates at variable velocity, while the planetary gear has a fixed speed. Consequently, the cycloid disc and output flange transmission accuracy is lower than that of the planetary gears.
– The cycloidal gearbox has a larger gripping area than the planetary gear. This is an advantage of the cycloidal gearbox in that it can handle larger loads.
– The cycloid profile has a significant impact on the quality of contact meshing between the tooth surfaces. The width of the contact ellipses increases by 90%. This is a result of the elimination of undercuts of the lobes. In this way, the contact force on the cycloid disc is decreased significantly.
– The cycloid drive has lower backlash and high torsional stiffness. This allows a cycloidal drive to be more stable against shock loads. The cycloid drive is also a compact design, which is ideally suited for applications with large transmission ratios.
– The output hub of the cycloid gearbox has movable pins and rollers. These components are attached to the ring gear in the outer gearbox. The output shaft is also turned by the planet carrier. The output hub of the cycloid system is composed of two parts: the ring gear and the output flange.
– The input shaft of a cycloidal gearbox is connected to a servomotor. The input shaft is a cylindrical element that is fixed to the planet carrier.

editor by CX 2023-05-30
China wholesaler The Reducer Factory Produces Gearboxes with Small Size and High Torque cycloidal drive gear ratio
Product Description
Product Description
The reducer factory produces gearboxes with small size and high torque
WF series gearboxes for 5 axis machining center developed and manufactured by WEITENSTAN together with German and ZheJiang technicians for many years.
High precision miniature cycloidal gearbox has the characteristics of smaller, ultra-thin, lightweight and high rigidity, anti-overload and high torque. With good deceleration performance, smooth operation and accurate positioning can be achieved. Integrated design, can be directly connected with the motor, to achieve high precision, high rigidity, high durability and other advantages. It is designed for high speed ratio, high geometric accuracy, low motion loss, large torque capacity and high stiffness applications. The compact design (minimum OD ≈40mm, currently the world’s smallest precision cycloidal pin-wheel reducer) allows it to be installed in limited Spaces.
Product Parameters
| Size | reduction ratio | Rated output moment | Allowable torque of start and stop | Instantaneous allowable moment | Rated input speed | Maximum input speed | Tilt stiffness | Torsional stiffness | No-load starting torque | Transmission accuracy | Error accuracy | Moment of inertia | Weight | |
| Axis rotation | Shell rotation | Nm | Nm | Nm | rpm | rpm | Nm/arcmin | Nm/arcmin | Nm | arcmin | arcmin | kg-m² | kg | |
| WF07 | 21 | 20 | 15 | 30 | 45 | 3000 | 6000 | 6 | 1.1 | 0.12 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | 0.52 | 0.42 |
| 41 | 40 | 0.11 | 0.47 | |||||||||||
| WF17 | 21 | 20 | 50 | 100 | 150 | 3000 | 6000 | 28 | 6 | 0.21 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | 0.88 | 0.85 |
| 41 | 40 | 0.18 | 0.72 | |||||||||||
| 61 | 60 | 0.14 | 0.69 | |||||||||||
| WF25 | 21 | 20 | 110 | 220 | 330 | 3000 | 5500 | 131 | 24 | 0.47 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | 6.12 | 2 |
| 31 | 30 | 0.41 | 5.67 | |||||||||||
| 41 | 40 | 0.38 | 4.9 | |||||||||||
| 51 | 50 | 0.35 | 4.56 | |||||||||||
| 81 | 80 | 0.31 | 4.25 | |||||||||||
| WF32 | 25 | 24 | 190 | 380 | 570 | 3000 | 4500 | 240 | 35 | 1.15 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | 11 | 4.2 |
| 31 | 30 | 1.1 | 10.8 | |||||||||||
| 51 | 50 | 0.77 | 9.35 | |||||||||||
| 81 | 80 | 0.74 | 8.32 | |||||||||||
| 101 | 100 | 0.6 | 7.7 | |||||||||||
| WF40 | 25 | 24 | 320 | 640 | 960 | 3000 | 4000 | 377 | 50 | 1.35 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | 13.2 | 6.6 |
| 31 | 30 | 1.32 | 12.96 | |||||||||||
| 51 | 50 | 0.92 | 11.22 | |||||||||||
| 81 | 80 | 0.81 | 9.84 | |||||||||||
| 121 | 120 | 0.72 | 8.4 | |||||||||||
product drawings
Detailed Photos
The reducer factory produces gearboxes with small size and high torque
advantages:
1, fine precision cycloidal structure
Ultra flat shape is achieved through differential reduction mechanism and thin cross roller bearing, contributing to the compact size of the equipment. The combination of small size and unmatched superior parameters achieves the best combination of performance, price and size (high cost performance).
2. Excellent accuracy (transmission loss ≤1 arcmin)
Through the complex meshing of precision cycloid gear and high precision roller pin, higher transmission accuracy is achieved while maintaining small size and high speed ratio.
3, high rigidity
Increase the mesh rate to disperse the load, so the rigidity is high.
4. High overload capacity
It maintains trouble-free operation under abnormally low noise and vibration conditions while ensuring excellent overturning and torsional stiffness parameters. Integrated axial radial cross roller bearings, high load capacity and overload capacity of the reducer, can ensure users to provide a variety of temperature range of applications.
5, the motor installation is simple
Electromechanical integration design, can be directly connected with the motor, any brand of motor can be installed directly, without adding any device.
6. Maintenance free
Seal grease to achieve maintenance free. No refueling, no mounting direction restrictions.
7, stable performance
The manufacturing process of high wear-resistant materials and high precision parts has been certified by ISO9000 quality system, which guarantees the reliable operation of the reducer.
Product Classification
WF Series
High Precision Miniature Reducer
WF series is a high precision micro cycloidal reducer with flange, which has a wide range of applications. This series of reducers includes precise reduction mechanisms and radial – axial roller bearings. The unique design allows load to act directly on the output flange or housing without additional bearings. WF series reducer is characterized by module design, can be installed through the flange motor and reducer, belongs to the motor directly connected reducer.
WFH Series
High Precision Miniature Reducer
WFH series is a hollow form of high precision miniature cycloidal reducer, wire, compressed air pipeline, drive shaft can be through the hollow shaft, non-motor direct connection type reducer. The WFH series is fully sealed, full of grease and includes precise deceleration mechanism and radial – axial roller bearings. The unique design allows load to be acted directly on the output flange or housing without additional bearings.
WR Series
high-precision corner reducer
The WR series is a flange output corner reducer. Like the WF and WFH series, it is a high-precision reducer (backlash less than 1 arc.min), and the level 2 can also be within 1 arc.min, which is higher than other types. Corner type reducer. It can replace the harmonic drive reducer, and its life and rigidity are more than 3 times that of the harmonic.
Installation Instructions
Company Profile
FAQ
Q:Are you a factory or a trading company ? where is your office ?
A:We are a company integrating industry and trade.The company is located at No. 101, Building F, HangZhou Industrial Park, No. 1 CZPT Street, Xiaobian Community, Chang’an Town, HangZhou City.
Q: What are your main products?
A: We currently have self-developed and manufactured planetary gearboxes, rv reducers, cycloidal gearboxes, hollow rotating platforms, steering gears, couplings and other products. You can view the specifications of the above products on our website, you can send us an email or leave a message, and our technical consultants will choose the product that suits you according to your needs.
Q: What’s your delivery time?
A: Generally speaking, it takes 15-30 days for our regular standard products, and it takes longer for customized products. But we are very flexible about the delivery time, it will depend on the specific order.
Q: Delivery time
A: Fubao has 2000+ production base, daily output of 1000+ units, standard models within 7 days of delivery.
Q: Reducer selection
A: Fubao provides professional product selection guidance, with higher product matching degree, higher cost performance and higher utilization rate.
Q: Application range of reducer
A: Fubao has a professional research and development team, complete category design, can match any stepping motor, servo motor, more accurate matching.
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
| Application: | Motor, Machinery, Agricultural Machinery, Humanoid Robot |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Any Direction |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Condition Monitoring of Cyclone Gearboxes
Whether you’re considering using a cycloidal gearbox in your home, office, or garage, you’ll want to make sure it’s made of quality material. You also want to make sure it’s designed properly, so it won’t be damaged by vibrations.
Planetary gearboxes
Compared to cycloidal gearboxes, planetary gearboxes are lighter and more compact, but they lack the precision and durability of the former. They are better suited for applications with high torque or speed requirements. For this reason, they are usually used in robotics applications. But, cycloidal gearboxes are still better for some applications, including those involving shock loads.
There are many factors that affect the performance of gearboxes during production. One of these is the number of teeth. In the case of planetary gearboxes, the number of teeth increases with the number of planets. The number of teeth is reduced in cycloidal gearboxes, which results in higher transmission ratios. These gearboxes also have lower breakaway torques, which means that they can be controlled more easily by the user.
A cycloid gearbox is comprised of three main parts: the ring gear, the sun gear, and the input shaft. The ring gear is fixed in the gearbox, while the sun gear transmits the rotation to the planet gears. The input shaft transfers motion to the sun gear, which in turn transmits it to the output shaft. The output shaft has a larger torque than the input shaft.
Cycloid gears have better torsional stiffness, lower wear, and lower Hertzian contact stress. However, they are also larger in size and require highly accurate manufacturing. Cycloid gears can be more difficult to manufacture than involute gears, which require large amounts of precision.
Cycloid gears can offer transmission ratios up to 300:1, and they can do this in a small package. They also have lower wear and friction, which makes them ideal for applications that require a high transmission ratio.
Cycloid gearboxes are usually equipped with a backlash of about one angular minute. This backlash provides the precision and control necessary for accurate movement. They also provide low wear and shock load capacity.
Planetary gearboxes are available in single and two-stage designs, which increase in length as stages are added. In addition to the two stages, they can be equipped with an optional output bearing, which takes up mounting space. In some applications, a third stage is also available.
Involute gears
Generally, involute gears are more complex to manufacture than cycloidal gears. For example, an involute gear tooth profile has a single curve while a cycloidal gear tooth profile has two curves. In addition, the involute curve is not within the base circle.
The involute curve is a very important component of a gear tooth and it can significantly influence the quality of contact meshing between teeth. Various works have been done on the subject, mainly focusing on the operating principles. In addition, the most important characteristic of the double-enveloping cycloid drive is its double contact lines between the meshing tooth pairs.
Cycloid gears are more powerful, less noisy, and last longer than involute gears. They also require less manufacturing operations during production. However, cycloid gears are more expensive than involute gears. Involute gears are more commonly used in linear motions while cycloid gears are used for rotary motions.
Although cycloid gears are more technically advanced, involute gears have the superior quality and are more aesthetically pleasing. Cycloid gears are used in various industrial applications such as pumps and compressors. They are also widely used in the watch industry. Nevertheless, involute gears have not yet replaced cycloid gears in the watch industry.
The cycloid disc has a number of pins around its outer edge, while an involute gear has only a single curve for the teeth. In addition, cycloid gears have a more robust and reliable design. Involute gears, on the other hand, have a cheaper rack cutter and less expensive involute teeth.
The cycloid disc’s transmission accuracy is about 98.5%, while the ring gear’s transmission accuracy is about 96%. The cycloid disc’s rotational velocity has a magnitude of 3 rad/s. A small change in the center distance does not affect the transmission accuracy. However, rotational velocity fluctuation can affect the transmission accuracy.
Cycloid gears also have the cycloid gear disc’s rotational velocity. The disc has N lobes. However, the cycloid gear disc’s transmission accuracy is still not perfect. This is because of the large rotational angles between the lobes. This also makes it difficult to manufacture.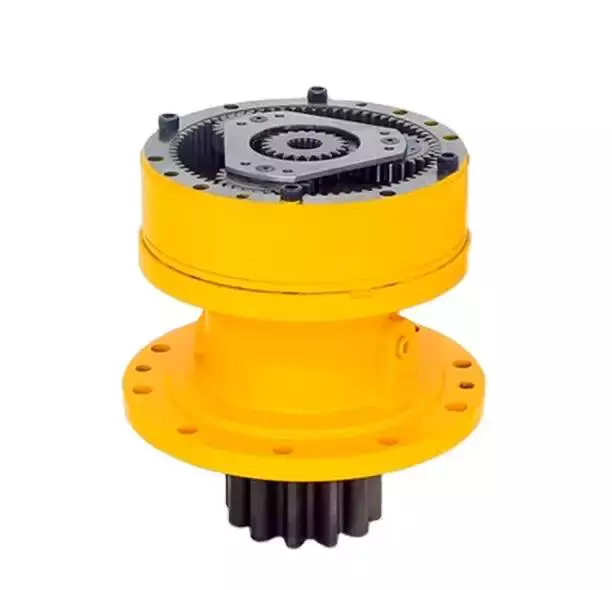
Vibrations
Using modern techniques for vibration diagnostics and data-driven methods, this article presents a new approach to condition monitoring of cycloidal gearboxes. This approach focuses on detecting the root cause of gearbox failure. The article aims to provide a unified approach to gear designers.
A cycloidal gearbox is a high-precision gearbox that is used in heavy-duty machines. It has a large reduction ratio, which makes it necessary to have a very large input speed. Cycloid gears have high accuracy, but they are susceptible to vibration issues. In this article, the authors describe how a cycloidal gearbox works and how vibrations are measured. They also show how this gearbox can be used to detect faults.
The gearbox is used in positioners, multi-axis robots, and heavy-duty machines. The main characteristics of this gearbox are the high accuracy, the overload capacity, and the large reduction ratio.
There is little documentation on vibrations and condition monitoring of cycloidal gearboxes. The authors describe their approach to the problem, using a cycloidal gearbox and a testing bench. Their approach involves measuring the frequency of the gearbox with different input speeds.
The results show a good separation between the healthy and damaged states. Fault frequencies show up in the lower orders of frequencies. Faults can be detected using binning, which eliminates the need for a tachometer. In addition, binning is combined with Principal Component Analysis to determine the state of the gearbox.
This method is compared to traditional techniques. In addition, the results show how binning can be used to calculate the defect frequencies of the bearings. It is also used to determine the frequencies of the components.
The signals from the test bench are acquired using four sensors. These sensors are medium sensitivity 100 mV/g accelerometers. The signals are then processed using different signal processing techniques. The results show that the vibration signals are correlated with the internal motion of the gearbox. This information is used to identify the internal frequency of the transmission.
The frequency analysis of vibration signals is performed in cyclostationary and noncyclostationary conditions. The signals are then analyzed to determine the magnitude of the gear meshing frequency.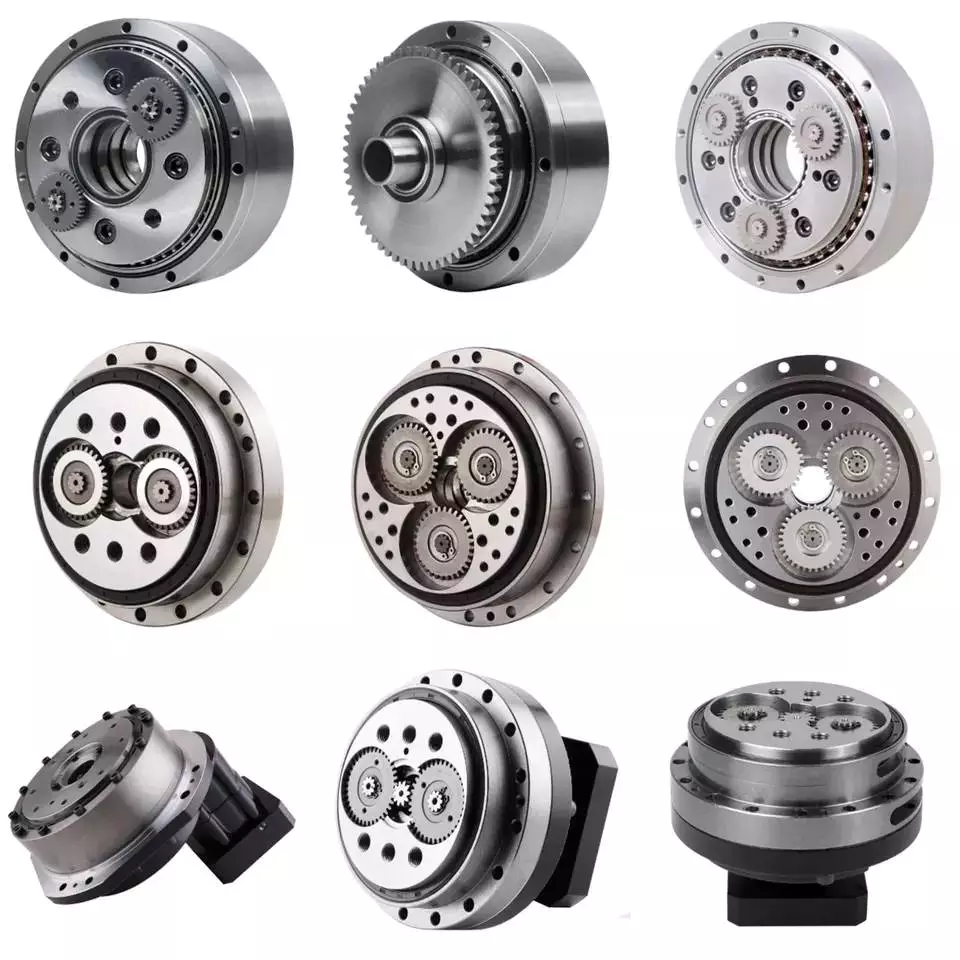
Design
Using precision gearboxes, servomotors can now control heavy loads at high speed. Unlike cam indexing devices, cycloidal gears provide extremely accurate positioning and high torque. They also provide excellent torsional stiffness and shock load capacity.
Cycloid gears are specially designed to minimize vibration at high RPM. Unlike involute gears, they are not stacked, which reduces friction and forces experienced by each tooth. In addition, cycloidal gears have lower Hertzian contact stress.
Cycloid gears are often used in multi-axis robots for positioners. They can provide transmission ratios as high as 300:1 in a compact package. They are also used in first joints in heavy machines. However, they require extremely accurate manufacturing. They are also more difficult to produce than involute gears.
A cycloidal gearbox is a type of planetary gearbox. Cycloid gears are specially designed for high gear ratios. They also have the ability to provide a large reduction ratio in a single stage. They are increasingly used in first joints in heavy machines. They are also becoming more common in robotics.
In order to achieve a large reduction ratio, the input speed of the gear must be very high. Generally, the input speed is between 500 rpm and 4500 rpm. However, in some cases, the input speed may be lower.
A cycloid is formed by rolling a rolling circle on a base circle. The ratio between the rolling circle diameter and the base circle diameter determines the shape of the cycloid. A hypocycloid is formed by rolling primarily on the inside of the base circle, while an epicycloid is formed by rolling primarily on the outside of the base circle.
Cycloid gears have a very small backlash, which minimizes the forces experienced by each tooth. These gears also have a good torsional stiffness, low friction, and shock load capacity. They also provide the best positioning accuracy.
The cycloidal gearbox was designed and built at Radom University. The design was based on three different cycloidal gears. The first pair had the external profile at the nominal dimension, while the second pair had the profile minus tolerance. The load plate had threaded screw holes arranged 15 mm away from the center.

editor by CX 2023-05-19
China Aluminum Gearbox Cast Iron Housing Transmission Drive Motor Shaft Nmrv Smr Series Reduction Helical Cycloidal Cyclo Planetary Worm Gearboxes Speed Gear Reducer cycloidal gearbox reducer
Product Description
Features
1.Wide transmission rate, strong output torque
two.Compact mechanical structure, light weight, small volume&Good heat-dissipating
3.Smooth operation with lower noise or vibration
4.Easy mounting, free linking, high efficiency
five. Best SUBSTITUDE FOR MOTOVARIO AND CZPT PRODUCTS
Programs
Wide range of application,including light industry of food &beverage, Cement,
package,construction material,chemicals and etc.
Complex knowledge:
| Product | RV a hundred thirty a hundred and fifty |
| Single unit variations | NMRV – equipped for motor flanged coupling, NRV – with enter shaft, NMRV-E motor flanged coupling with worm extension shaft, NRV-E with double extension worm shaft, |
| Power | .06—-15KW |
| Single device reduction ratio | 1:5 7.5 eighty a hundred |
| Output torque | 2.6—1195N.M |
| Worm shaft material | 20CrMnTi with carburizing and quenching.The hardness of surface area is fifty six-62HRC with carbonized layer .5-.8mm |
| Worm wheel material | worm mandrel is HT250,and worm ring equipment,ZQSn10-1,hardness is 60HRC |
Right after-sale support:
One particular yr warranty,subject matter to correct procedure and installationfree specialized support all the time.
|
/ Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated| Freight Cost Calculator |
|---|
###
| Application: | Motor |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened |
| Type: | Worm and Wormwheel |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 30/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
|---|
###
| Model | RV025 030 040 050 063 075 090 110 130 150 |
| Single unit versions | NMRV – fitted for motor flanged coupling, NRV – with input shaft, NMRV-E motor flanged coupling with worm extension shaft, NRV-E with double extension worm shaft, |
| Power | 0.06—-15KW |
| Single unit reduction ratio | 1:5 7.5 10 15 20 25 30 40 50 60 80 100 |
| Output torque | 2.6—1195N.M |
| Worm shaft material | 20CrMnTi with carburizing and quenching.The hardness of surface is 56-62HRC with carbonized layer 0.5-0.8mm |
| Worm wheel material | worm mandrel is HT250,and worm ring gear,ZQSn10-1,hardness is 60HRC |
|
/ Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated| Freight Cost Calculator |
|---|
###
| Application: | Motor |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened |
| Type: | Worm and Wormwheel |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 30/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
|---|
###
| Model | RV025 030 040 050 063 075 090 110 130 150 |
| Single unit versions | NMRV – fitted for motor flanged coupling, NRV – with input shaft, NMRV-E motor flanged coupling with worm extension shaft, NRV-E with double extension worm shaft, |
| Power | 0.06—-15KW |
| Single unit reduction ratio | 1:5 7.5 10 15 20 25 30 40 50 60 80 100 |
| Output torque | 2.6—1195N.M |
| Worm shaft material | 20CrMnTi with carburizing and quenching.The hardness of surface is 56-62HRC with carbonized layer 0.5-0.8mm |
| Worm wheel material | worm mandrel is HT250,and worm ring gear,ZQSn10-1,hardness is 60HRC |
Condition Monitoring of Cyclone Gearboxes
Whether you’re considering using a cycloidal gearbox in your home, office, or garage, you’ll want to make sure it’s made of quality material. You also want to make sure it’s designed properly, so it won’t be damaged by vibrations.
Planetary gearboxes
Compared to cycloidal gearboxes, planetary gearboxes are lighter and more compact, but they lack the precision and durability of the former. They are better suited for applications with high torque or speed requirements. For this reason, they are usually used in robotics applications. But, cycloidal gearboxes are still better for some applications, including those involving shock loads.
There are many factors that affect the performance of gearboxes during production. One of these is the number of teeth. In the case of planetary gearboxes, the number of teeth increases with the number of planets. The number of teeth is reduced in cycloidal gearboxes, which results in higher transmission ratios. These gearboxes also have lower breakaway torques, which means that they can be controlled more easily by the user.
A cycloid gearbox is comprised of three main parts: the ring gear, the sun gear, and the input shaft. The ring gear is fixed in the gearbox, while the sun gear transmits the rotation to the planet gears. The input shaft transfers motion to the sun gear, which in turn transmits it to the output shaft. The output shaft has a larger torque than the input shaft.
Cycloid gears have better torsional stiffness, lower wear, and lower Hertzian contact stress. However, they are also larger in size and require highly accurate manufacturing. Cycloid gears can be more difficult to manufacture than involute gears, which require large amounts of precision.
Cycloid gears can offer transmission ratios up to 300:1, and they can do this in a small package. They also have lower wear and friction, which makes them ideal for applications that require a high transmission ratio.
Cycloid gearboxes are usually equipped with a backlash of about one angular minute. This backlash provides the precision and control necessary for accurate movement. They also provide low wear and shock load capacity.
Planetary gearboxes are available in single and two-stage designs, which increase in length as stages are added. In addition to the two stages, they can be equipped with an optional output bearing, which takes up mounting space. In some applications, a third stage is also available.
Involute gears
Generally, involute gears are more complex to manufacture than cycloidal gears. For example, an involute gear tooth profile has a single curve while a cycloidal gear tooth profile has two curves. In addition, the involute curve is not within the base circle.
The involute curve is a very important component of a gear tooth and it can significantly influence the quality of contact meshing between teeth. Various works have been done on the subject, mainly focusing on the operating principles. In addition, the most important characteristic of the double-enveloping cycloid drive is its double contact lines between the meshing tooth pairs.
Cycloid gears are more powerful, less noisy, and last longer than involute gears. They also require less manufacturing operations during production. However, cycloid gears are more expensive than involute gears. Involute gears are more commonly used in linear motions while cycloid gears are used for rotary motions.
Although cycloid gears are more technically advanced, involute gears have the superior quality and are more aesthetically pleasing. Cycloid gears are used in various industrial applications such as pumps and compressors. They are also widely used in the watch industry. Nevertheless, involute gears have not yet replaced cycloid gears in the watch industry.
The cycloid disc has a number of pins around its outer edge, while an involute gear has only a single curve for the teeth. In addition, cycloid gears have a more robust and reliable design. Involute gears, on the other hand, have a cheaper rack cutter and less expensive involute teeth.
The cycloid disc’s transmission accuracy is about 98.5%, while the ring gear’s transmission accuracy is about 96%. The cycloid disc’s rotational velocity has a magnitude of 3 rad/s. A small change in the center distance does not affect the transmission accuracy. However, rotational velocity fluctuation can affect the transmission accuracy.
Cycloid gears also have the cycloid gear disc’s rotational velocity. The disc has N lobes. However, the cycloid gear disc’s transmission accuracy is still not perfect. This is because of the large rotational angles between the lobes. This also makes it difficult to manufacture.
Vibrations
Using modern techniques for vibration diagnostics and data-driven methods, this article presents a new approach to condition monitoring of cycloidal gearboxes. This approach focuses on detecting the root cause of gearbox failure. The article aims to provide a unified approach to gear designers.
A cycloidal gearbox is a high-precision gearbox that is used in heavy-duty machines. It has a large reduction ratio, which makes it necessary to have a very large input speed. Cycloid gears have high accuracy, but they are susceptible to vibration issues. In this article, the authors describe how a cycloidal gearbox works and how vibrations are measured. They also show how this gearbox can be used to detect faults.
The gearbox is used in positioners, multi-axis robots, and heavy-duty machines. The main characteristics of this gearbox are the high accuracy, the overload capacity, and the large reduction ratio.
There is little documentation on vibrations and condition monitoring of cycloidal gearboxes. The authors describe their approach to the problem, using a cycloidal gearbox and a testing bench. Their approach involves measuring the frequency of the gearbox with different input speeds.
The results show a good separation between the healthy and damaged states. Fault frequencies show up in the lower orders of frequencies. Faults can be detected using binning, which eliminates the need for a tachometer. In addition, binning is combined with Principal Component Analysis to determine the state of the gearbox.
This method is compared to traditional techniques. In addition, the results show how binning can be used to calculate the defect frequencies of the bearings. It is also used to determine the frequencies of the components.
The signals from the test bench are acquired using four sensors. These sensors are medium sensitivity 100 mV/g accelerometers. The signals are then processed using different signal processing techniques. The results show that the vibration signals are correlated with the internal motion of the gearbox. This information is used to identify the internal frequency of the transmission.
The frequency analysis of vibration signals is performed in cyclostationary and noncyclostationary conditions. The signals are then analyzed to determine the magnitude of the gear meshing frequency.
Design
Using precision gearboxes, servomotors can now control heavy loads at high speed. Unlike cam indexing devices, cycloidal gears provide extremely accurate positioning and high torque. They also provide excellent torsional stiffness and shock load capacity.
Cycloid gears are specially designed to minimize vibration at high RPM. Unlike involute gears, they are not stacked, which reduces friction and forces experienced by each tooth. In addition, cycloidal gears have lower Hertzian contact stress.
Cycloid gears are often used in multi-axis robots for positioners. They can provide transmission ratios as high as 300:1 in a compact package. They are also used in first joints in heavy machines. However, they require extremely accurate manufacturing. They are also more difficult to produce than involute gears.
A cycloidal gearbox is a type of planetary gearbox. Cycloid gears are specially designed for high gear ratios. They also have the ability to provide a large reduction ratio in a single stage. They are increasingly used in first joints in heavy machines. They are also becoming more common in robotics.
In order to achieve a large reduction ratio, the input speed of the gear must be very high. Generally, the input speed is between 500 rpm and 4500 rpm. However, in some cases, the input speed may be lower.
A cycloid is formed by rolling a rolling circle on a base circle. The ratio between the rolling circle diameter and the base circle diameter determines the shape of the cycloid. A hypocycloid is formed by rolling primarily on the inside of the base circle, while an epicycloid is formed by rolling primarily on the outside of the base circle.
Cycloid gears have a very small backlash, which minimizes the forces experienced by each tooth. These gears also have a good torsional stiffness, low friction, and shock load capacity. They also provide the best positioning accuracy.
The cycloidal gearbox was designed and built at Radom University. The design was based on three different cycloidal gears. The first pair had the external profile at the nominal dimension, while the second pair had the profile minus tolerance. The load plate had threaded screw holes arranged 15 mm away from the center.

editor by CX 2023-03-27
China China Hydraulic Gearbox Marine Pumps Gearboxes Boat Gearbox for Sale Worm Gear Box cycloidal pin gear reducer
Solution Description
China Hydraulic Gearbox Maritime Pumps Gearboxes
General Description
Dredger gearboxes are designed with respect to harsh situations and long lifestyle. Our dredger gearboxes are operated on little or mid-size dredgers appropriate for servicing dredging or huge-dimension dredging vessels best equipped for land reclamation and larger sand and gravel servicing operates as well as other kinds of vessels such as cutter suction dredgers. Our pump generator equipment models are produced in accordance to the customers’ specifications and provide tailor-created transmission ratios and multi-stage concepts. Our merchandise portfolio includes equipment units for jet pumps, dredge pumps, generators, cutters and winches. The gear units are made to the customer’s technical specs and RELONG’s in-residence security requirements.
Attribute
– Dependable
– Gearing that interlocks completely
– Reliable base and robust housing, designed for higher loads
– Slide bearings of the maximum high quality for upkeep-cost-free equipment models
Parameter
RELONG Story
Relong Surroundings Technology Co., Ltd. is positioned in HangZhou City, ZheJiang Province. It is a firm dedicated to intelligent robots, ship style, h2o transportation equipment, maritime drinking water good quality and ecological setting screening, salvage services industrial automatic control program devices, radar and supporting equipment, interaction products, which is a high-tech organization integrating sales and artificial intelligence application development, like consulting, design,manufacturing,installation,and operation administration.
FAQ
- Q: What are your manufacturing unit workshops?
A: Our manufacturing unit production method contains casting, mechanical process, lathe method, heat remedy, assembly, and test, etc. Warmly welcome to visit & test my manufacturing unit any time. - Q: How does your manufacturing unit do concerning high quality manage?
A: “Quality is a priority. We always attach excellent importance to top quality controlling from the commencing to the end. Our factory has fifteen~thirty QC. - Q: Is it easy for consumers to modify the components by on their own?
A: Of course, the structure is easy, customers can adjust it really effortlessly. We will also supply you with servicing instruments for cost-free.
|
US $1,000-4,000 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Motor, Marine, Dredger |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Clutch, Change Drive Torque, Change Drive Direction, Speed Changing, Speed Reduction, Speed Increase |
| Layout: | Cycloidal |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Vertical Type |
| Step: | Three-Step |
|
US $1,000-4,000 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Motor, Marine, Dredger |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Clutch, Change Drive Torque, Change Drive Direction, Speed Changing, Speed Reduction, Speed Increase |
| Layout: | Cycloidal |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Vertical Type |
| Step: | Three-Step |
The Basics of Designing a Cyclone Gearbox
Compared to conventional gearboxes, the cycloidal gearbox offers a number of advantages including a higher ratio of transmission, robustness against shock loads, and greater positioning accuracy. However, designing a cycloidal gearbox can be complicated. This article will discuss some of the basic design principles. In addition, it will cover topics such as size, position accuracy, and transmission ratios.
Basic design principles
Unlike a conventional ring gear, a cycloidal gearbox uses a cycloidal disc to provide torque multiplication. The output direction of the cycloidal gear disc is opposite to the rotation of the input shaft. This allows for more compact gear construction. It also allows for increased load capacity.
Cycloid drive kinematics can appear complex, but they are actually quite simple. Instead of rotating around the center of gravity like conventional gears, the cycloidal disc rotates around fixed pins. This provides a higher reduction ratio.
To reduce vibrations and noise, multiple cycloidal discs are used. This allows for uniform distribution of forces on the carrier pin devices. This also provides a better rotational balance. In addition, multiple cycloidal discs reduce the axial moment of the carrier pin devices.
The cycloidal gear disc is supported by a separate gear disc bearing. This design provides a low component count and reduces wear. This type of kinematics can also be used in an electric motor with a high power density.
The cycloidal gear disc provides a high reduction ratio, which allows for compact construction. Unlike a ring gear, the cycloidal disc has fewer teeth. It also provides a higher reduction ratio, which is advantageous for high rotational input speed applications.
Cycloid gear discs have cylindrical holes, which allow for carrier pin devices to protrude through them. This is useful because the carrier pin devices can roll along the inside wall of the cylindrical hole in the gear disc.
A load plate is also used to provide anchorage for external structures. This plate contains threaded screw holes arranged 15mm away from the center. It has a 9mm external diameter and a 3mm through hole.
Transmission ratios up to 300:1
cycloidal gearboxes are used in a wide range of applications, from machine tools to medical imaging devices. Compared to planetary gearboxes, they offer superior positioning accuracy, torsional stiffness, backlash, and fatigue performance.
Cycloid gearboxes are also capable of transmitting more torque than planetary gears. In addition, they have a lower Hertzian contact stress and higher overload protection. Cycloid gearboxes are able to provide transmission ratios up to 300:1 in a small package.
Cycloid gears also have lower backlash over extended periods, making them an ideal choice for applications with critical positioning accuracy. Cycloid gearboxes also have good wear resistance, as well as low friction. Cycloid gears are lightweight and have good torsional stiffness, making them ideal for applications with heavy loads.
Cycloid gearboxes have several different designs. They can provide transmission ratios up to 300:1 without the need for additional pre-stages. Cycloid gears also require more accurate manufacturing processes than involute gears. Cycloid gearboxes can also be used for applications that require high power consumption, and can withstand shock loads.
Cycloid gearboxes can be adapted to fit most common servomotors. They have a modular design, all-round corrosion protection, and easy installation. Cycloid gears have a radial clamping ring, which reduces inertia by up to 39%.
CZPT Precision Europe GmbH, a subsidiary of CZPT Group, has developed an innovative online configurator to simplify the configuration of gearboxes. CZPT cycloidal gearheads are precision-built, robust, and reliable. They have a two-stage reduction principle, which minimises vibration and provides even force distribution.
Cycloid gears are capable of providing transmission ratios from 30:1 to 300:1. Cycloid gearboxes can achieve high gear ratios because they require fewer moving parts, and they have a low backlash.
Robustness against shock loads
Unlike conventional gearboxes that are easily damaged by shock loads, the cycloidal gearbox is extremely robust. It is a versatile solution that is ideally suited for handling equipment, food manufacturing, and machine tools.
The mechanical construction of a cycloidal gearbox consists of several mechanical components. These include cycloidal wheels, bearings, transformation elements, and needles. In addition, it has high torsional stiffness and tilting moment. It is also accompanied by highly nonlinear friction characteristic.
In order to assess the robustness of the cycloidal gearbox against shock loads, a mathematical model was developed. The model was used to calculate the stress distribution on the cycloid disc. This model can be used as a basis for more complex mechanical models.
The model is based on new approach, which allows to model stiction in all quadrants of the cycloid gear. In addition, it can be applied to actuator control.
The mathematical model is presented together with the procedure for measuring the contact stress. The results are compared to the measurement performed in the real system. The model and the measurement are found to be very close to each other.
The model also allows for the analysis of different gear profiles for load distribution. In addition, it is possible to analyze contact stresses with different geometric parameters. The mesh refinement along the disc width helps to ensure an even distribution of contact forces.
The stiction breakaway speed is calculated to the motor side. The non-zero current is then derived to the input side of the gearbox. In addition, a small steady phase is modeled during the speed direction transition. The results of the simulation are compared to the measurement. The results show that the model is extremely accurate.
Positioning accuracy
Getting the correct positioning accuracy from a cycloidal gearbox is no small feat. This is because the gears are compact, and the clearances are relatively small. This means you can expect a lot of torque from your output shaft. However, this is only part of the picture. Other concerns, such as backlash, kinematic error, and loading are all important considerations.
Getting the best possible positioning accuracy from a cycloidal gearbox means choosing a reducer that is well-made and correctly configured. A properly-selected reducer will eliminate repeatable inaccuracies and provide absolute positioning accuracy at all times. In addition, this type of gearbox offers several advantages over conventional gearboxes. These include high efficiency, low backlash, and high overload protection.
Getting the correct positioning accuracy from a gearbox also involves choosing a supplier that knows what it is doing. The best vendors are those who have experience with the product, offer a wide variety, and provide support and service to ensure the product is installed and maintained correctly. Another consideration is the manufacturer’s warranty. A reputable manufacturer will offer warranties for the gearbox. The aforementioned factors will ensure that your investment in a cycloidal gearbox pays off for years to come.
Getting the correct positioning accuracy from your cycloidal gearbox involves choosing a manufacturer that specializes in this type of product. This is particularly true if you are involved in robotics, automated painting, or any other industrial process that requires the best possible accuracy. A good manufacturer will offer the latest technology, and have the expertise to help you find the best solution for your application. This will ensure your product is a success from start to finish.
Size
Choosing the right size of cycloidal gearbox is important for its efficient operation. However, it is not a simple task. The process involves complex machining and requires the creation of many parts. There are different sizes of cycloidal gearboxes, and a few basic rules of thumb can help you choose the right size.
The first rule of thumb for choosing the right size of cycloidal gearboxes is to use a gearbox with the same diameter of the input shaft. This means that the gearbox must be at least 5mm thick. The cycloid will also require a base and a bearing to hold the driveshaft in place. The base should be large enough to house the pins. The bearing must be the same size as the input shaft.
The next rule of thumb is to have a hole in the cycloid for the output shaft. In this way, the output will be back-drivable and has low backlash. There should be at least four to six output holes. The size of the holes should be such that the centerline of the cycloid is equal to the size of the center of the bearing.
Using a Desmos graph, you can then create the gear parameters. The number of pins should be equal to the number of teeth in the cycloidal gear, and the size of the pins should be twice the size of the gear. The radius of the pins should be equal to the value of C from Desmos, and the size of the pin circle should be equal to the R value.
The final rule of thumb is to ensure that the cycloid has no sharp edges or discontinuities. It should also have a smooth line.

editor by czh 2023-01-21
China Cycloidal Gearbox Cyclo Gear Best Price Manufacture Box Drive Motor Speed Reducer Gearboxes Planetary Sumitomo Power Industrial Transmissio Cycloidal Gearbox cycloidal drive components
Product Description
Cycloidal gearbox cyclo speed reducer gearboxes gear best price manufacture box drive motor planetary sumitomo electrical power industrial transmissio Cycloidal gearbox
X / B collection high good quality cycloidal gearbox tiny planetary reducer
Fast Specifics:
Variety: XB collection Cycloidal Pin Wheel Pace Reducer
Enter Speed: a thousand-1500rmp
Output Velocity: .3-280rpm
Certification: ISO9001 CE
Ex Electrical power:.09-132KW
Warranty: 1Years
| Product Title | X/B sequence Cycloidal Pin Wheel Velocity Reducer |
| The Gear Material | GCR15 |
| The circumstance Content | Forged Iron |
| Colour | Blue,Inexperienced, or Customized |
| HS Code | 84834090 |
| Design | X3 |
| Shipping and delivery time | seven-10days |
| Manufacturer | TIANGOU |
|
US $10-999 / Piece | |
100 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Clutch, Change Drive Torque, Change Drive Direction, Speed Changing, Speed Reduction, Speed Increase |
| Layout: | Coaxial |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Horizontal Type |
| Step: | Three-Step |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 9999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Product Name | X/B series Cycloidal Pin Wheel Speed Reducer |
| The Gear Material | GCR15 |
| The case Material | Cast Iron |
| Color | Blue,Green, or Customized |
| HS Code | 84834090 |
| Model | X3 |
| Delivery time | 7-10days |
| Brand | TIANGOU |
|
US $10-999 / Piece | |
100 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Clutch, Change Drive Torque, Change Drive Direction, Speed Changing, Speed Reduction, Speed Increase |
| Layout: | Coaxial |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Horizontal Type |
| Step: | Three-Step |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 9999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Product Name | X/B series Cycloidal Pin Wheel Speed Reducer |
| The Gear Material | GCR15 |
| The case Material | Cast Iron |
| Color | Blue,Green, or Customized |
| HS Code | 84834090 |
| Model | X3 |
| Delivery time | 7-10days |
| Brand | TIANGOU |
The Basics of a Cyclone Gearbox
Besides being compact, cycloidal speed reducers also offer low backlash and high ratios. Because of the small size of the drive, they are ideal for applications where space is a problem.
Involute gear tooth profile
Almost all gears use an involute gear tooth profile. This profile has a single curve, which means that the gear teeth do not have to be aligned closely with each other. This profile is smooth and can be manufactured easily.
Cycloid gears have a combination of epicycloid and hypocycloid curves. This makes them stronger than involute gear teeth. However, they can be more expensive to manufacture. They also have larger reduction ratios. They transmit more power than involute gears. Cycloid gears can be found in clocks.
When designing a gear, you need to consider several factors. Some of these include the number of teeth, the tooth angle and the lubrication type. Having a gear tooth that is not perfectly aligned can result in transmission error, noise and vibration.
The tooth profile of an involute gear is usually considered the best. Because of this, it is used in a wide variety of gears. Some of the most common applications for this profile are power transmission gears. However, this profile is not the best for every application.
Cycloid gears require more complex manufacturing processes than involute gear teeth. This can cause a larger tooth cost. Cycloid gears are used for less noisy applications.
Cycloid gears also transmit more power than involute gears. This can cause problems if the radii change tangentially. However, the shape is more simple than involute gears. Involute gears can handle centre sifts better.
Cycloid gears are less susceptible to transmission error. Cycloid gears have a convex surface, which makes them stronger than involute teeth. Cycloid gears also have a larger reduction ratio than involute gears. Cycloid teeth do not interfere with the mating teeth. However, they have a smaller number of teeth than involute teeth.
Rotation on the inside of the reference pitch circle of the pins
Whether a cycloidal gearbox is designed for stationary or rotating applications, the fundamental law of gearing must be observed: The ratio of angular velocities must be constant. This requires the rotation on the inside of the reference pitch circle of the pins to be constant. This is achieved through a series of cycloidal teeth, which act like tiny levers to transmit motion.
A cycloidal disc has N lobes which are rotated by three lobes per rotation around N pins. The number of lobes on a cycloidal disc is a significant factor in determining the transmission ratio.
A cycloidal disc is driven by an eccentric input shaft which is mounted to an eccentric bearing within an output shaft. As the input shaft rotates, the cycloidal disc moves around the pins of the pin disc.
The drive pin rotates at a 40 deg angle while the cycloidal disc rotates on the inside of the reference pitch circle of pins. As the drive pin rotates, it will slow the output motion. This means that the output shaft will complete only three revolutions with the input shaft, as opposed to nine revolutions with the input shaft.
The number of teeth on a cycloidal disc must be small compared to the number of surrounding pins. The disc must also be constructed with an eccentric radius. This will determine the size of the hole which will be required for the pin to fit between the pins.
When the input shaft is turned, the cycloidal disc will rotate on the inside of the reference pitch circle of roller pins. This will then transmit motion to the output shaft. The output shaft is supported by two bearings in an output housing. This design has low wear and torsional stiffness.
Transmission ratio
Choosing the right transmission ratio of cycloidal gearbox isn’t always easy. You might need to know the size of your gearbox before you can make an educated choice. You may also need to refer to the product catalog for guidance. For example, CZPT gearboxes have some unique ratios.
A cycloidal gear reducer is a compact and high-speed torque transmission device that reverses the direction of angular movement of the follower shaft. It consists of an eccentric cam positioned inside a cycloidal disc. Pin rollers on the follower shaft fit into matching holes in the cycloidal disc. In the process, the pins slide around the holes, in response to wobbling motion. The cycloidal disc is also capable of engaging the internal teeth of a ring-gear housing.
A cycloidal gear reducer can be used in a wide variety of applications, including industrial automation, robotics and power transmissions on boats and cranes. A cycloidal gear reducer is ideally suited for heavy duty applications with large payloads. They require specialized manufacturing processes, and are often used in equipment with precise output and high efficiency.
The cycloidal gear reducer is a relatively simple structure, but it does require some special tools. Cycloid gear reducers are also used to transmit torque, which is one of the reasons they are so popular in automation. Using a cycloidal gear reducer is a good choice for applications that require higher efficiency and lower backlash. It is also a good choice for applications where size is a concern. Cycloid gears are also a good choice for applications where high speed and high torque are required.
The transmission ratio of cycloidal gearbox is probably the most important function of a gearbox. You need to know the size of your gearbox and the type of gears it contains in order to make the right choice.
Vibration reduction
Considering the unique dynamics of a cycloidal gearbox, vibration reduction measures are required for a smooth operation. These measures can also help with the detection of faults.
A cycloidal gearbox is a gearbox with an eccentric bearing that rotates the center of the gears. It shares torque load with five outer rollers at any given time. It can be applied in many applications. It is a relatively inexpensive asset. However, if it fails, it can have significant economic impacts.
A typical input/output gearbox consists of a ring plate and two cranks mounted on the input shaft. The ring plate rotates when the input shaft rotates. There are two bearings on the output shaft.
The ring plate is a major noise source because it is not balanced. The cycloidal gear also produces noise when it meshes with the ring plate. This noise is generated by structural resonance. Several studies have been performed to solve this problem.
However, there is not much documented work on the condition monitoring of cycloidal gearboxes. In this article, we will introduce modern techniques for vibration diagnostics.
A cycloidal gearbox with a reduced reduction ratio has higher induced stresses in the cycloidal disc. In this case, the size of the output hole is larger and more material is removed from the cycloidal disc. This increase in the disc’s stresses leads to higher vibration amplitudes.
The load distribution along the width of the gear is an important design criterion. Using different gear profiles can help to optimize the transmission of torque. The contact stress of the cycloidal disc can also be investigated.
To determine the amplitude of the noise, the frequency of the gear mesh is multiplied by the shaft rate. If the RPM is relatively stable, the frequency can be used as a measure of magnitude. However, this is only accurate at close to failure.
Comparison with planetary gearboxes
Several differences exist between cycloidal gearboxes and planetary gearboxes. They are related to gear geometry and manufacturing processes. Among them, there are:
– The output shaft of a cycloidal gearbox has a larger torque than the input shaft. The rotational speed of the output shaft is lower than the input shaft.
– The cycloid gear disc rotates at variable velocity, while the planetary gear has a fixed speed. Consequently, the cycloid disc and output flange transmission accuracy is lower than that of the planetary gears.
– The cycloidal gearbox has a larger gripping area than the planetary gear. This is an advantage of the cycloidal gearbox in that it can handle larger loads.
– The cycloid profile has a significant impact on the quality of contact meshing between the tooth surfaces. The width of the contact ellipses increases by 90%. This is a result of the elimination of undercuts of the lobes. In this way, the contact force on the cycloid disc is decreased significantly.
– The cycloid drive has lower backlash and high torsional stiffness. This allows a cycloidal drive to be more stable against shock loads. The cycloid drive is also a compact design, which is ideally suited for applications with large transmission ratios.
– The output hub of the cycloid gearbox has movable pins and rollers. These components are attached to the ring gear in the outer gearbox. The output shaft is also turned by the planet carrier. The output hub of the cycloid system is composed of two parts: the ring gear and the output flange.
– The input shaft of a cycloidal gearbox is connected to a servomotor. The input shaft is a cylindrical element that is fixed to the planet carrier.

editor by czh 2022-12-30
China Gpb090 Planetary Gvb Gpg Gear Box Transmission Gearbox Gearhead with Good Price cycloidal gearboxes
Item Description
TaiBang Motor Industry Group Co., Ltd.
The main products is induction motor, reversible motor, DC brush equipment motor, DC brushless gear motor, CH/CV massive gear motors, Planetary equipment motor ,Worm gear motor etc, which utilized extensively in various fields of producing pipelining, transportation, meals, medication, printing, cloth, packing, office, equipment, leisure and many others, and is the chosen and matched product for automatic equipment.
Design Instruction
GB090-10-P2
| GB | 090 | 571 | P2 |
| Reducer Collection Code | Exterior Diameter | Reduction Ratio | Reducer Backlash |
| GB:Higher Precision Sq. Flange Output
GBR:Large Precision Proper Angle Sq. Flange Output GE:High Precision Round Flange Output GER:Substantial Precision Right Round Flange Output |
050:ø50mm 070:ø70mm 090:ø90mm one hundred twenty:ø120mm a hundred and fifty five:ø155mm 205:ø205mm 235:ø235mm 042:42x42mm 060:60x60mm 090:90x90mm 115:115x115mm 142:142x142mm a hundred and eighty:180x180mm 220:220x220mm |
571 indicates 1:ten | P0:Substantial Precision Backlash
P1:Precision Backlash P2:Standard Backlash |
Principal Technological Efficiency
| Product | Quantity of stage | Reduction Ratio | GB042 | GB060 | GB060A | GB090 | GB090A | GB115 | GB142 | GB180 | GB220 |
| Rotary Inertia | 1 | 3 | .03 | .16 | .sixty one | three.25 | nine.21 | 28.98 | 69.sixty one | ||
| 4 | .03 | .fourteen | .forty eight | 2.74 | 7.54 | 23.sixty seven | 54.37 | ||||
| 5 | .03 | .thirteen | .forty seven | two.71 | seven.42 | 23.29 | fifty three.27 | ||||
| six | .03 | .13 | .45 | two.65 | 7.twenty five | 22.75 | fifty one.seventy two | ||||
| 7 | .03 | .thirteen | .45 | 2.62 | 7.14 | 22.forty eight | 50.97 | ||||
| eight | .03 | .13 | .44 | two.58 | 7.07 | 22.59 | fifty.eighty four | ||||
| 9 | .03 | .thirteen | .44 | 2.fifty seven | 7.04 | 22.fifty three | 50.sixty three | ||||
| ten | .03 | .thirteen | .forty four | two.57 | 7.03 | 22.fifty one | fifty.fifty six | ||||
| 2 | 15 | .03 | .03 | .13 | .thirteen | .47 | .forty seven | two.71 | seven.forty two | 23.29 | |
| twenty | .03 | .03 | .13 | .thirteen | .forty seven | .47 | 2.71 | seven.42 | 23.29 | ||
| twenty five | .03 | .03 | .13 | .thirteen | .47 | .forty seven | 2.71 | 7.forty two | 23.29 | ||
| 30 | .03 | .03 | .thirteen | .thirteen | .47 | .forty seven | two.71 | seven.forty two | 23.29 | ||
| 35 | .03 | .03 | .thirteen | .thirteen | .forty seven | .forty seven | two.seventy one | 7.forty two | 23.29 | ||
| forty | .03 | .03 | .13 | .13 | .47 | .47 | two.seventy one | seven.forty two | 23.29 | ||
| forty five | .03 | .03 | .13 | .thirteen | .47 | .forty seven | 2.71 | seven.forty two | 23.29 | ||
| 50 | .03 | .03 | .13 | .thirteen | .forty four | .44 | two.57 | 7.03 | 22.fifty one | ||
| sixty | .03 | .03 | .13 | .thirteen | .forty four | .44 | two.57 | 7.03 | 22.fifty one | ||
| 70 | .03 | .03 | .thirteen | .13 | .forty four | .44 | 2.fifty seven | seven.03 | 22.51 | ||
| eighty | .03 | .03 | .thirteen | .thirteen | .44 | .forty four | two.57 | 7.03 | 22.fifty one | ||
| 90 | .03 | .03 | .thirteen | .thirteen | .44 | .44 | two.57 | 7.03 | 22.fifty one | ||
| a hundred | .03 | .03 | .thirteen | .thirteen | .44 | .forty four | 2.fifty seven | 7.03 | 22.fifty one |
| Item | Variety of phase | GB042 | GB060 | GB060A | GB90 | GB090A | GB115 | GB142 | GB180 | GB220 | |
| Backlash(arcmin) | High Precision P0 | one | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | |||
| 2 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | |||||||
| Precision P1 | 1 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | |
| 2 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ||
| Standard P2 | one | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | |
| two | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ||
| Torsional Rigidity(N.M/arcmin) | 1 | three | seven | seven | fourteen | fourteen | 25 | fifty | a hundred forty five | 225 | |
| two | three | seven | seven | 14 | 14 | 25 | 50 | 145 | 225 | ||
| Noise(dB) | one,2 | ≤56 | ≤58 | ≤58 | ≤60 | ≤60 | ≤63 | ≤65 | ≤67 | ≤70 | |
| Rated input velocity(rpm) | 1,two | 5000 | 5000 | 5000 | 4000 | 4000 | 4000 | 3000 | 3000 | 2000 | |
| Max enter pace(rpm) | 1,2 | ten thousand | ten thousand | ten thousand | 8000 | 8000 | 8000 | 6000 | 6000 | 4000 | |
Noise take a look at common:Distance 1m,no load.Measured with an input speed 3000rpm
|
US $50 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Machinery, Agricultural Machinery |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Change Drive Torque, Change Drive Direction, Speed Reduction |
| Layout: | Cycloidal |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Vertical Type |
| Step: | Double-Step |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| GB | 090 | 010 | P2 |
| Reducer Series Code | External Diameter | Reduction Ratio | Reducer Backlash |
| GB:High Precision Square Flange Output
GBR:High Precision Right Angle Square Flange Output GE:High Precision Round Flange Output GER:High Precision Right Round Flange Output |
050:ø50mm 070:ø70mm 090:ø90mm 120:ø120mm 155:ø155mm 205:ø205mm 235:ø235mm 042:42x42mm 060:60x60mm 090:90x90mm 115:115x115mm 142:142x142mm 180:180x180mm 220:220x220mm |
010 means 1:10 | P0:High Precision Backlash
P1:Precision Backlash P2:Standard Backlash |
###
| Item | Number of stage | Reduction Ratio | GB042 | GB060 | GB060A | GB090 | GB090A | GB115 | GB142 | GB180 | GB220 |
| Rotary Inertia | 1 | 3 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.61 | 3.25 | 9.21 | 28.98 | 69.61 | ||
| 4 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.48 | 2.74 | 7.54 | 23.67 | 54.37 | ||||
| 5 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | 53.27 | ||||
| 6 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 2.65 | 7.25 | 22.75 | 51.72 | ||||
| 7 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 2.62 | 7.14 | 22.48 | 50.97 | ||||
| 8 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 2.58 | 7.07 | 22.59 | 50.84 | ||||
| 9 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.04 | 22.53 | 50.63 | ||||
| 10 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | 50.56 | ||||
| 2 | 15 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | |
| 20 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 25 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 30 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 35 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 40 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 45 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 50 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 60 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 70 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 80 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 90 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 100 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 |
###
| Item | Number of stage | GB042 | GB060 | GB060A | GB90 | GB090A | GB115 | GB142 | GB180 | GB220 | |
| Backlash(arcmin) | High Precision P0 | 1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | |||
| 2 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | |||||||
| Precision P1 | 1 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | |
| 2 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ||
| Standard P2 | 1 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | |
| 2 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ||
| Torsional Rigidity(N.M/arcmin) | 1 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 14 | 14 | 25 | 50 | 145 | 225 | |
| 2 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 14 | 14 | 25 | 50 | 145 | 225 | ||
| Noise(dB) | 1,2 | ≤56 | ≤58 | ≤58 | ≤60 | ≤60 | ≤63 | ≤65 | ≤67 | ≤70 | |
| Rated input speed(rpm) | 1,2 | 5000 | 5000 | 5000 | 4000 | 4000 | 4000 | 3000 | 3000 | 2000 | |
| Max input speed(rpm) | 1,2 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 8000 | 8000 | 8000 | 6000 | 6000 | 4000 | |
|
US $50 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Machinery, Agricultural Machinery |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Change Drive Torque, Change Drive Direction, Speed Reduction |
| Layout: | Cycloidal |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Vertical Type |
| Step: | Double-Step |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| GB | 090 | 010 | P2 |
| Reducer Series Code | External Diameter | Reduction Ratio | Reducer Backlash |
| GB:High Precision Square Flange Output
GBR:High Precision Right Angle Square Flange Output GE:High Precision Round Flange Output GER:High Precision Right Round Flange Output |
050:ø50mm 070:ø70mm 090:ø90mm 120:ø120mm 155:ø155mm 205:ø205mm 235:ø235mm 042:42x42mm 060:60x60mm 090:90x90mm 115:115x115mm 142:142x142mm 180:180x180mm 220:220x220mm |
010 means 1:10 | P0:High Precision Backlash
P1:Precision Backlash P2:Standard Backlash |
###
| Item | Number of stage | Reduction Ratio | GB042 | GB060 | GB060A | GB090 | GB090A | GB115 | GB142 | GB180 | GB220 |
| Rotary Inertia | 1 | 3 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.61 | 3.25 | 9.21 | 28.98 | 69.61 | ||
| 4 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.48 | 2.74 | 7.54 | 23.67 | 54.37 | ||||
| 5 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | 53.27 | ||||
| 6 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 2.65 | 7.25 | 22.75 | 51.72 | ||||
| 7 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 2.62 | 7.14 | 22.48 | 50.97 | ||||
| 8 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 2.58 | 7.07 | 22.59 | 50.84 | ||||
| 9 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.04 | 22.53 | 50.63 | ||||
| 10 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | 50.56 | ||||
| 2 | 15 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | |
| 20 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 25 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 30 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 35 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 40 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 45 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 50 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 60 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 70 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 80 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 90 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 100 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 |
###
| Item | Number of stage | GB042 | GB060 | GB060A | GB90 | GB090A | GB115 | GB142 | GB180 | GB220 | |
| Backlash(arcmin) | High Precision P0 | 1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | |||
| 2 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | |||||||
| Precision P1 | 1 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | |
| 2 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ||
| Standard P2 | 1 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | |
| 2 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ||
| Torsional Rigidity(N.M/arcmin) | 1 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 14 | 14 | 25 | 50 | 145 | 225 | |
| 2 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 14 | 14 | 25 | 50 | 145 | 225 | ||
| Noise(dB) | 1,2 | ≤56 | ≤58 | ≤58 | ≤60 | ≤60 | ≤63 | ≤65 | ≤67 | ≤70 | |
| Rated input speed(rpm) | 1,2 | 5000 | 5000 | 5000 | 4000 | 4000 | 4000 | 3000 | 3000 | 2000 | |
| Max input speed(rpm) | 1,2 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 8000 | 8000 | 8000 | 6000 | 6000 | 4000 | |
Developing a Mathematical Model of a Cyclone Gearbox
Compared to planetary gearboxes, cycloidal gearboxes are often seen as the ideal choice for a wide range of applications. They feature compact designs that are often low friction and high reduction ratios.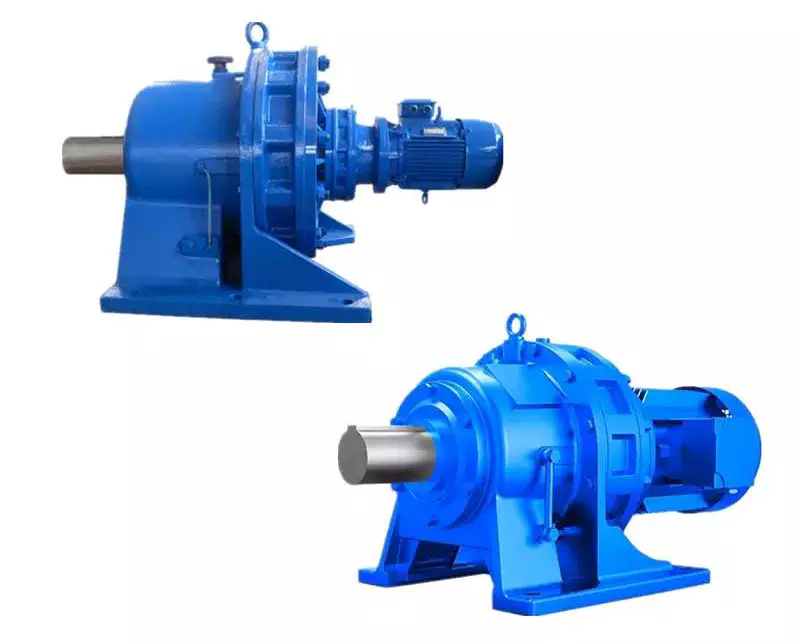
Low friction
Developing a mathematical model of a cycloidal gearbox was a challenge. The model was able to show the effects of a variety of geometric parameters on contact stresses. It was able to model stiction in all quadrants. It was able to show a clear correlation between the results from simulation and real-world measurements.
The model is based on a new approach that enables modeling stiction in all quadrants of a gearbox. It is also able to display non-zero current at standstill. Combined with a good simulation algorithm, the model can be used to improve the dynamic behaviour of a controlled system.
A cycloidal gearbox is a compact actuator used for industrial automation. This type of gearbox provides high gear ratios, low wear, and good torsional stiffness. In addition, it has good shock load capacity.
The model is based on cycloidal discs that engage with pins on a stationary ring gear. The resulting friction function occurs when the rotor begins to rotate. It also occurs when the rotor reverses its rotation. The model has two curves, one for motor and one for generator mode.
The trochoidal profile on the cycloidal disc’s periphery is required for proper mating of the rotating parts. In addition, the profile should be defined accurately. This will allow an even distribution of contact forces.
The model was used to compare the relative performance of a cycloidal gearbox with that of an involute gearbox. This comparison indicates that the cycloidal gearbox can withstand more load than an involute gearbox. It is also able to last longer. It is also able to produce high gear ratios in a small space.
The model used is able to capture the exact geometry of the parts. It can also allow a better analysis of stresses.
Compact
Unlike helical gearing, compact cycloidal gearboxes can provide higher reduction ratios. They are more compact and less weighty. In addition, they provide better positioning accuracy.
Cycloid drives provide high torque and load capacity. They are also very efficient and robust. They are ideal for applications with heavy loads or shock loads. They also feature low backlash and high torsional stiffness. Cycloid gearboxes are available in a variety of designs.
Cycloid discs are mounted on an eccentric input shaft, which drives them around a stationary ring gear. The ring gear consists of many pins, and the cycloidal disc moves one lobe for every rotation of the input shaft. The output shaft contains roller pins, which rotate around holes in the cycloidal disc.
Cycloid drives are ideally suited to heavy loads and shock loads. They have high torsional stiffness and high reduction ratios, making them very efficient. Cycloid gearboxes have low backlash and high torque and are very compact.
Cycloid gearboxes are used for a wide variety of applications, including marine propulsion systems, CNC machining centers, medical technology, and manipulation robots. They are especially useful in applications with critical positioning accuracy, such as surgical positioning systems. Cycloid gearboxes feature extremely low hysteresis loss and low backlash over extended periods of use.
Cycloid discs are usually designed with a reduced cycloid diameter to minimize unbalance forces at high speeds. Cycloid drives also feature minimal backlash, a high reduction ratio, and excellent positioning accuracy. Cycloid gearboxes also have a long service life, compared to other gear drives. Cycloid drives are highly robust, and offer higher reduction ratios than helical gear drives.
Cycloid gearboxes have a low cost and are easy to print. CZPT gearboxes are available in a wide range of sizes and can produce high torque on the output axis.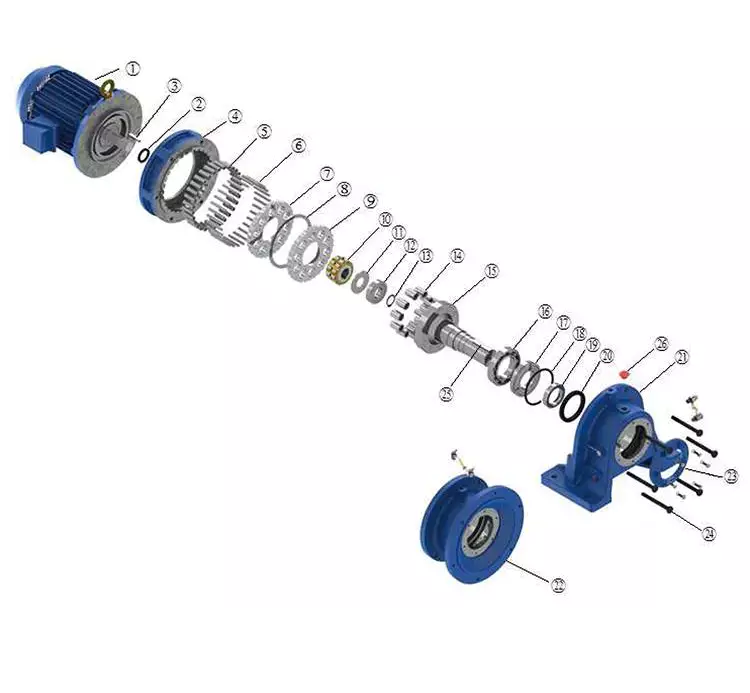
High reduction ratio
Among the types of gearboxes available, a high reduction ratio cycloidal gearbox is a popular choice in the automation field. This gearbox is used in applications requiring precise output and high efficiency.
Cycloid gears can provide high torque and transmit it well. They have low friction and a small backlash. They are widely used in robotic joints. However, they require special tools to manufacture. Some have even been 3D printed.
A cycloidal gearbox is typically a three-stage structure that includes an input hub, an output hub, and two cycloidal gears that rotate around each other. The input hub mounts movable pins and rollers, while the output hub mounts a stationary ring gear.
The input shaft is driven by an eccentric bearing. The disc is then pushed against the ring gear, which causes it to rotate around the bearing. As the disc rotates, the pins on the ring gear drive the pins on the output shaft.
The input shaft rotates a maximum of nine revolutions, while the output shaft rotates three revolutions. This means that the input shaft has to rotate over eleven million times before the output shaft is able to rotate. The output shaft also rotates in the opposite direction of the input shaft.
In a two-stage differential cycloidal speed reducer, the input shaft uses a crank shaft design. The crank shaft connects the first and second cycloidal gears and actuates them simultaneously.
The first stage is a cycloidal disc, which is a gear tooth profile. It has n=7 lobes on its circumference. Each lobe moves around a reference pitch circle of pins. The disc then advances in 360deg steps.
The second stage is a cycloidal disc, also known as a “grinder gear”. The teeth on the outer gear are fewer than the teeth on the inner gear. This allows the gear to be geardown based on the number of teeth.
Kinematics
Various scholars have studied the kinematics of cycloidal gearbox. They have developed various approaches to modify the tooth profile of cycloidal gears. Some of these approaches involve changing the shape of the cycloidal disc, and changing the grinding wheel center position.
This paper describes a new approach to cycloid gear profile modification. It is based on a mathematical model and incorporates several important parameters such as pressure angle, backlash, and root clearance. The study offers a new way for modification design of cycloid gears in precision reducers for robots.
The pressure angle of a tooth profile is an intersegment angle between the normal direction and the velocity direction at a meshing point. The pressure angle distribution is important for determining force transmission performance of gear teeth in meshing. The distribution trend can be obtained by calculating the equation (5).
The mathematical model for modification of the tooth profile can be obtained by establishing the relationship between the pressure angle distribution and the modification function. The dependent variable is the modification DL and the independent variable is the pressure angle a.
The position of the reference point A is a major consideration in the modification design. It ensures the force transmission performance of the meshing segment is optimal. It is determined by the smallest profile pressure angle. The position is also dependent on the type of gear that is being modified. It is also influenced by the tooth backlash.
The mathematical model governing the pressure angle distribution is developed with DL=f(a). It is a piecewise function that determines the pressure angle distribution of a tooth profile. It can also be expressed as DL=ph.
The pressure angle of a tooth is also an angle between the common normal direction at the meshing point and the rotation velocity direction of the cycloid gear.
Planetary gearboxes vs cycloidal gearboxes
Generally, there are two types of gearboxes that are used for motion control applications: cycloidal gearbox and planetary gearbox. Cycloid gearboxes are used for high-frequency motions, while planetary gearboxes are suitable for low-speed applications. Both are highly accurate and precise gearboxes that are capable of handling heavy loads at high cycle rates. But they have different advantages and disadvantages. So, engineers need to determine which type of gearbox is best suited for their application.
Cycloid gearboxes are commonly used in industrial automation. They provide excellent performance with ratios as low as 10:1. They offer a more compact design, higher torque density and greater overload protection. They also require less space and are less expensive than planetary gearboxes.
On the other hand, planetary gearboxes are lightweight and offer a higher torque density. They are also capable of handling higher ratios. They have a longer life span and are more precise and durable. They can be found in a variety of styles, including square-framed, round-framed and double-frame designs. They offer a wide range of torque and speed capabilities and are used for numerous applications.
Cycloid gearboxes can be manufactured with different types of cycloidal cams, including single or compound cycloidal cams. Cycloid cams are cylindrical elements that have cam followers that rotate in an eccentric fashion. The cam followers act like teeth on the internal gear. Cycloid cams are a simple concept, but they have numerous advantages. They have a low backlash over extended periods of time, allowing for more accurate positioning. They also have internal compressive stresses and an overlap factor between the rolling elements.
Planetary gearboxes are characterized by three basic force-transmitting elements: ring gear, sun gear, and planet gear. They are generally two-stage gearboxes. The sun gear is attached to the input shaft, which in turn is attached to the servomotor. The ring gear turns the sun gear and the planet gear turns the output shaft.

editor by czh 2022-12-14
China Cycloidal Gearbox Cyclo Speed Reducer Gearboxes Gear Best Price Manufacture Box Drive Motor Planetary Sumitomo Power Industrial Transmissio Cycloidal Gearbox best automatic gearbox
Product Description
Cycloidal gearbox cyclo gear box drive motor speed reducer gearboxes planetary sumitomo power industrial transmission best price manufacture Cycloidal gearbox
X / B series high quality cycloidal gearbox small planetary reducer
Quick Details:
Type: XB series Cycloidal Pin Wheel Speed Reducer
Input Speed: 1000-1500rmp
Output Speed: 0.3-280rpm
Certification: ISO9001 CE
Ex Power:0.09-132KW
Warranty: 1Years
| Product Name | X/B series Cycloidal Pin Wheel Speed Reducer |
| The Gear Material | GCR15 |
| The case Material | Cast Iron |
| Color | Blue,Green, or Customized |
| HS Code | 84834090 |
| Model | X3 |
| Delivery time | 7-10days |
| Brand | TIANGOU |
| Application: | Motor, Machinery, Agricultural Machinery |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Speed Reduction, Speed Increase |
| Output Torque: | 2.6-20000n.M |
| Output Speed: | 11-280rpm |
| Input Speed: | 750-3000rpm |
| Ratio: | 6-51133 |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 9999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Product Name | X/B series Cycloidal Pin Wheel Speed Reducer |
| The Gear Material | GCR15 |
| The case Material | Cast Iron |
| Color | Blue,Green, or Customized |
| HS Code | 84834090 |
| Model | X3 |
| Delivery time | 7-10days |
| Brand | TIANGOU |
| Application: | Motor, Machinery, Agricultural Machinery |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Speed Reduction, Speed Increase |
| Output Torque: | 2.6-20000n.M |
| Output Speed: | 11-280rpm |
| Input Speed: | 750-3000rpm |
| Ratio: | 6-51133 |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 9999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Product Name | X/B series Cycloidal Pin Wheel Speed Reducer |
| The Gear Material | GCR15 |
| The case Material | Cast Iron |
| Color | Blue,Green, or Customized |
| HS Code | 84834090 |
| Model | X3 |
| Delivery time | 7-10days |
| Brand | TIANGOU |
Choosing a Gearbox For Your Application
The gearbox is an essential part of bicycles. It is used for several purposes, including speed and force. A gearbox is used to achieve one or both of these goals, but there is always a trade-off. Increasing speed increases wheel speed and forces on the wheels. Similarly, increasing pedal force increases the force on the wheels. This makes it easier for cyclists to accelerate their bicycles. However, this compromise makes the gearbox less efficient than an ideal one.
Dimensions
Gearboxes come in different sizes, so the size of your unit depends on the number of stages. Using a chart to determine how many stages are required will help you determine the dimensions of your unit. The ratios of individual stages are normally greater at the top and get smaller as you get closer to the last reduction. This information is important when choosing the right gearbox for your application. However, the dimensions of your gearbox do not have to be exact. Some manufacturers have guides that outline the required dimensions.
The service factor of a gearbox is a combination of the required reliability, the actual service condition, and the load that the gearbox will endure. It can range from 1.0 to 1.4. If the service factor of a gearbox is 1.0, it means that the unit has just enough capacity to meet your needs, but any extra requirements could cause the unit to fail or overheat. However, service factors of 1.4 are generally sufficient for most industrial applications, since they indicate that a gearbox can withstand 1.4 times its application requirement.
Different sizes also have different shapes. Some types are concentric, while others are parallel or at a right angle. The fourth type of gearbox is called shaft mount and is used when mounting the gearbox by foot is impossible. We will discuss the different mounting positions later. In the meantime, keep these dimensions in mind when choosing a gearbox for your application. If you have space constraints, a concentric gearbox is usually your best option.
Construction
The design and construction of a gearbox entails the integration of various components into a single structure. The components of a gearbox must have sufficient rigidity and adequate vibration damping properties. The design guidelines note the approximate values for the components and recommend the production method. Empirical formulas were used to determine the dimensions of the various components. It was found that these methods can simplify the design process. These methods are also used to calculate the angular and axial displacements of the components of the gearbox.
In this project, we used a 3D modeling software called SOLIDWORKS to create a 3-D model of a gear reducer. We used this software to simulate the structure of the gearbox, and it has powerful design automation tools. Although the gear reducer and housing are separate parts, we model them as a single body. To save time, we also removed the auxiliary elements, such as oil inlets and oil level indicators, from the 3D model.
Our method is based on parameter-optimized deep neural networks (DBNs). This model has both supervised and unsupervised learning capabilities, allowing it to be self-adaptive. This method is superior to traditional methods, which have poor self-adaptive feature extraction and shallow network generalization. Our algorithm is able to recognize faults in different states of the gearbox using its vibration signal. We have tested our model on two gearboxes.
With the help of advanced material science technologies, we can now manufacture the housing for the gearbox using high-quality steel and aluminium alloys. In addition, advanced telematics systems have increased the response time of manufacturers. These technologies are expected to create tremendous opportunities in the coming years and fuel the growth of the gearbox housing market. There are many different ways to construct a gearbox, and these techniques are highly customizable. In this study, we will consider the design and construction of various gearbox types, as well as their components.
Working
A gearbox is a mechanical device that transmits power from one gear to another. The different types of gears are called planetary gears and are used in a variety of applications. Depending on the type of gearbox, it may be concentric, parallel, or at a right angle. The fourth type of gearbox is a shaft mount. The shaft mount type is used in applications that cannot be mounted by foot. The various mounting positions will be discussed later.
Many design guidelines recommend a service factor of 1.0, which needs to be adjusted based on actual service conditions. This factor is the combined measure of external load, required reliability, and overall gearbox life. In general, published service factors are the minimum requirements for a particular application, but a higher value is necessary for severe loading. This calculation is also recommended for high-speed gearboxes. However, the service factor should not be a sole determining factor in the selection process.
The second gear of a pair of gears has more teeth than the first gear. It also turns slower, but with greater torque. The second gear always turns in the opposite direction. The animation demonstrates this change in direction. A gearbox can also have more than one pair of gears, and a first gear may be used for the reverse. When a gear is shifted from one position to another, the second gear is engaged and the first gear is engaged again.
Another term used to describe a gearbox is “gear box.” This term is an interchangeable term for different mechanical units containing gears. Gearboxes are commonly used to alter speed and torque in various applications. Hence, understanding the gearbox and its parts is essential to maintaining your car’s performance. If you want to extend the life of your vehicle, be sure to check the gearbox’s efficiency. The better its functioning, the less likely it is to fail.
Advantages
Automatic transmission boxes are almost identical to mechanical transmission boxes, but they also have an electronic component that determines the comfort of the driver. Automatic transmission boxes use special blocks to manage shifts effectively and take into account information from other systems, as well as the driver’s input. This ensures accuracy and positioning. The following are a few gearbox advantages:
A gearbox creates a small amount of drag when pedaling, but this drag is offset by the increased effort to climb. The external derailleur system is more efficient when adjusted for friction, but it does not create as little drag in dry conditions. The internal gearbox allows engineers to tune the shifting system to minimize braking issues, pedal kickback, and chain growth. As a result, an internal gearbox is a great choice for bikes with high-performance components.
Helical gearboxes offer some advantages, including a low noise level and lower vibration. They are also highly durable and reliable. They can be extended in modular fashion, which makes them more expensive. Gearboxes are best for applications involving heavy loads. Alternatively, you can opt for a gearbox with multiple teeth. A helical gearbox is more durable and robust, but it is also more expensive. However, the benefits far outweigh the disadvantages.
A gearbox with a manual transmission is often more energy-efficient than one with an automatic transmission. Moreover, these cars typically have lower fuel consumption and higher emissions than their automatic counterparts. In addition, the driver does not have to worry about the brakes wearing out quickly. Another advantage of a manual transmission is its affordability. A manual transmission is often available at a lower cost than its automatic counterpart, and repairs and interventions are easier and less costly. And if you have a mechanical problem with the gearbox, you can control the fuel consumption of your vehicle with appropriate driving habits.
Application
While choosing a gearbox for a specific application, the customer should consider the load on the output shaft. High impact loads will wear out gear teeth and shaft bearings, requiring higher service factors. Other factors to consider are the size and style of the output shaft and the environment. Detailed information on these factors will help the customer choose the best gearbox. Several sizing programs are available to determine the most appropriate gearbox for a specific application.
The sizing of a gearbox depends on its input speed, torque, and the motor shaft diameter. The input speed must not exceed the required gearbox’s rating, as high speeds can cause premature seal wear. A low-backlash gearbox may be sufficient for a particular application. Using an output mechanism of the correct size may help increase the input speed. However, this is not recommended for all applications. To choose the right gearbox, check the manufacturer’s warranty and contact customer service representatives.
Different gearboxes have different strengths and weaknesses. A standard gearbox should be durable and flexible, but it must also be able to transfer torque efficiently. There are various types of gears, including open gearing, helical gears, and spur gears. Some of the types of gears can be used to power large industrial machines. For example, the most popular type of gearbox is the planetary drive gearbox. These are used in material handling equipment, conveyor systems, power plants, plastics, and mining. Gearboxes can be used for high-speed applications, such as conveyors, crushers, and moving monorail systems.
Service factors determine the life of a gearbox. Often, manufacturers recommend a service factor of 1.0. However, the actual value may be higher or lower than that. It is often useful to consider the service factor when choosing a gearbox for a particular application. A service factor of 1.4 means that the gearbox can handle 1.4 times the load required. For example, a 1,000-inch-pound gearbox would need a 1,400-inch-pound gearbox. Service factors can be adjusted to suit different applications and conditions.


editor by czh 2022-11-25