Product Description
Product Description
The Stepper motor rotary table hollow divider Can be connected to gear reducer has many advantages. First, we pay attention to the quality and stability of our products. We choose high precision materials and processing technology to ensure the accuracy and stability of products. Secondly, we provide perfect after-sales service. We have professional technical personnel responsible for pre-sales consultation and after-sales service for customers to solve various technical problems. Finally, we offer competitive prices. We have a variety of product models and specifications, can meet different customer needs, at the same time is very competitive in price.
Hollow rotary platform is widely used in various fields. Our products are widely used in CNC machining, automatic assembly, robotics, medical equipment and other fields. Our customers all over the world, we will continue to improve the quality of products and services, to meet the needs of customers.
As a hollow rotary platform manufacturer, Fubao Electromechanical Technology will, as always, be committed to the development and production of high quality products. We will continue to work with our customers to promote industrial automation and intelligent manufacturing.
A hollow rotating platform is a new rotating load device, which integrates the advantages of high transmission efficiency, high precision, high rigidity, and high-performance ratio. It integrates the advantages of servo motor, cam splitter, and direct-drive motor.
Detailed Photos
Product Details
Product Advantage
Product features:
1, the work can be directly locked
Rotating disk surface can directly lock the working object, improve the workpiece loading convenience.
2, convenient wiring
This rotary platform is hollow design, whether it is convenient for wiring or piping.
3. High precision
The positioning accuracy is less than 1arcmin.
The repetition accuracy can reach 5arcsec.
4, smooth operation
Disk rotation is smooth, smooth, and fast positioning.
Other products
Company Profile
Factory Display
FAQ
Q:Key points of selection of planetary reducer
A:1. Frame number determined by torque: the power source will have the effect of torque amplification after deceleration ratio. The output torque value of the reducer is proportional to the deceleration ratio, and the larger the ratio, the higher the torque value will be; But the gear group of the reducer has the limit, so the rated output torque of the planetary reducer is to say that the product can work stably under the data operation, so the box number must be selected according to the demand torque.
2, according to the accuracy to determine the model: in the process of automation will need positioning, when the positioning accuracy requirements are higher, you need to choose a higher level of products, and vice versa. The precision of the planetary reducer is called the “backgap”, which refers to the gap of the gear group. The definition is the Angle value that the output shaft of the planetary reducer can rotate when the input end is fixed. The smaller the return clearance is, the higher the accuracy is and the higher the cost is. The user can choose the right accuracy according to their actual situation.
3, according to the installation size selection: that is, the size of the front end of the servo motor. The input end of the planetary reducer must match the output end of the servo motor.
4, according to the appearance selection: according to customer demand output shaft and connecting surface has a standard series for users to choose, can also be customized according to user special needs.
5, according to the axial and radial force selection: the life of the planetary reducer is affected by the internal bearing, bearing life can be calculated through the load and speed, when the axial and radial force load of the reducer is higher, the bearing life will be shortened, at this time it is recommended to choose a large product.
| Application: | Motor, Machinery, Agricultural Machinery |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Vertical Type |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How to Use a Cyclone Gearbox
Often, a cycloidal gearbox is used in order to achieve a torque transfer from a motor or pump. This type of gearbox is often a common choice as it has a number of advantages over a regular gearbox. Its main advantage is that it is easy to make, which means that it can be incorporated into a variety of applications. However, if you want to use a cycloidal gearbox, there are a few things that you need to know. These include the operation principle, the structure and the dynamic and inertial effects that come with it.
Dynamic and inertial effects
Several studies have been carried out on the static and dynamic properties of cycloidal gears. The study of these effects is beneficial in assisting optimal design of cycloidal speed reducers.
In this paper, the dynamic and inertial effects of a two-stage cycloidal speed reducer have been investigated using the CZPT program package. Moreover, a new model for cycloidal reducers based on non-linear contact dynamics has been developed. The new model aims to predict several operational conditions.
The normal excitation contact force for the cycloid discs of the first and second stage is very similar. However, the total deformation at the contact point is different. This effect is mainly due to the system’s own oscillations. The cycloid discs of the second stage turn around the ring gear roller with a 180deg angle. This angle is a significant contributor to the torque loads. The total excitation force on the cycloid discs of first and second stage is 1848 N and 2068.7 N, respectively.
In order to analyze the contact stress, different gear profiles were investigated. The mesh density was considered as an important design criterion. It was found that a bigger hole reduces the material content of the cycloidal disc and results in more stresses.
Moreover, it is possible to reduce the contact forces in a more efficient manner by changing the geometric parameters. This can be done by mesh refinement along the disc width. The cycloidal disc has the greatest influence on the output results.
The efficiency of a cycloidal drive increases with the increase in load. The efficiency of a cycloidal reducer also depends on the eccentricity of the input shaft and the cycloidal plate. The efficiency curve for small loads is linear. However, for the larger loads, the efficiency curve becomes more non-linear. This is because the stiffness of the cycloid reducer increases as the load increases.
Structure
Despite the fact that it looks like a complicated engineering puzzle, the construction of a cycloidal gearbox is actually quite simple. The key elements are the base, the load plate and the thrust bearing. All these elements work together to create a stable, compact gearbox.
The base is a circular section with several cylindrical pins around its outer edge. The pins are fixed on a fixed ring that holds them in a circular path. The ring serves as a reference circle. The circle’s size is approximately 5mm in diameter.
The load plate is a series of threaded screw holes. These are arranged 15mm away from the center. These are used to anchor external structures. The load plate must be rotated around the X and Y axis.
The thrust bearing is placed on top of the load plate. The bearing is made of an internal diameter of 35mm and an external diameter of 52mm. It is used to allow rotation around the Z axis.
The cycloidal disc is the centerpiece of the cycloidal gearbox. The disc has holes for the pins that drive the output shaft. The holes are larger than those used in output roller pins. The disc also has a reduced eccentricity.
The pins are attached to the cycloidal disc by rolling pins. The pins are made of a material that provides mechanical support for the drive during high-torque situations. The pins have a 9mm external diameter. The disc has a number of lobes and is rotated by one lobe per shaft revolution.
The cycloidal gearbox also has a top cover that helps keep the components together. The cover has a pocket for tools. The top cover also has threads that screw into the casing.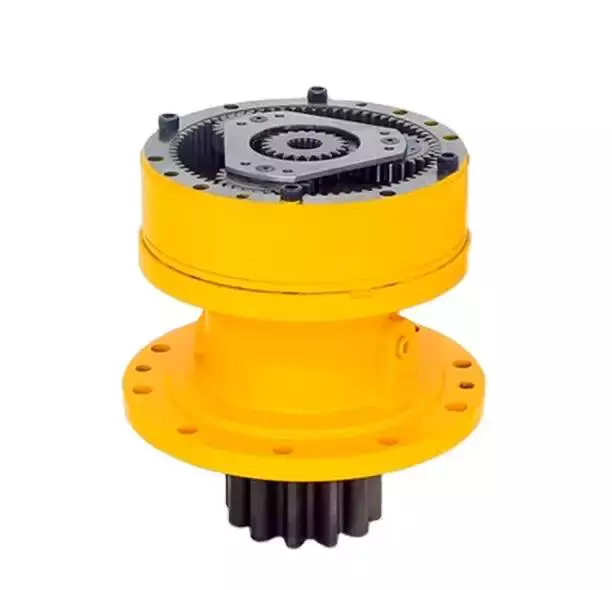
Operation principle
Among many types of gear transmissions, cycloidal gearboxes are used in heavy machinery and multi-axis robots. They are highly effective, compact and capable of high ratios. In addition, they have an overload capability.
Cycloid disks are driven by eccentric shafts that rotate around fixed ring pins. Roller pins of the pin disc engage with holes in the cycloidal disc. These roller pins drive the pin disc and the pin disc transfers the motion to the output shaft.
Unlike conventional gear drives, cycloidal drives have low backlash and high torsional stiffness. They are ideally suited to heavy loads and all drive technologies. The lower mass and compact design of the cycloidal disk also contributes to its high efficiency and positioning accuracy.
The cycloidal disc plays a central role in the gearbox kinematics. It rotates around a fixed ring in a circle. When the disc is pushed against the ring gear, the pins engage with the disc and the roller pins rotate around the pins. This rotating motion generates vibration, which travels through the driven shafts.
Cycloid discs are typically designed with a short cycloid, so that the eccentricity is minimized. This reduces unbalance forces at high speeds. Ideally, the number of lobes on the cycloid is smaller than the number of surrounding pins. This reduces the amount of Hertzian contact stress.
Unlike planetary gears, cycloidal gears have high accuracy and are capable of withstanding shock loads. They also experience low friction and less wear on tooth flanks. They also have higher efficiency and load capacity.
Cycloid gears are generally more difficult to manufacture than involute gears. Cycloid gears are not suitable for stacking gear stages. They require extreme accuracy for manufacturing. However, their smaller size and low backlash, high torsional stiffness, and low vibration make them ideal for use in heavy machines.
Involute gear tooth profile
Almost all gears are manufactured with an involute gear tooth profile. Cycloid gears are also produced with this profile. Compared with involute gears, cycloid gears are stronger and can transmit more power. However, they can also be more difficult to manufacture. This makes them costlier.
The involute gear tooth profile is a smooth curve. It is derived from the involute curve of a circle. A tangent to the base circle is the normal at any point of an involute.
This curve has properties that allow the involute gear teeth to transfer motion in perpendicular direction. It is also the path traced by the end of the string unwrapping from a cylinder.
An involute profile has the advantage of being easy to manufacture. It also allows for smooth meshing despite misalignment of the centre distance. This profile is also preferred over a cycloid tooth profile, but it is not the best in every regard.
Cycloid gear teeth are also made of two curves. Unlike involute teeth, cycloid gear teeth have a consistent radius. Cycloid gears are less likely to produce noise. But they are also more expensive to manufacture.
Involute teeth are easier to manufacture because they have only one curve. Cycloid gears can also be made with a rack type cutter. This makes them cheaper to manufacture. However, they require an expert design. They can also be manufactured with a gear shaper that includes a pinion cutter.
The tooth profiles that satisfy the law of gear-tooth action are sometimes called conjugate profiles. The involute profile is the most common of these. It allows for constant torque transmission.
Backlash
Typically, cycloidal drives provide a high ratio of transmission with no backlash. This is because the cycloid disc is driven by an eccentric shaft. During rotation, the cycloid disc rotates around a fixed ring. This ring also rotates independently of the center of gravity.
The cycloid disc is typically shortened to reduce the eccentricity. This helps to minimize the unbalance forces that may occur at high speeds. The cycloid also offers a larger gear ratio than traditional gears. This provides a better positional accuracy.
Cycloid drives also have a high torsional stiffness. This provides greater torsional resilience and shock load capabilities. This is important for a number of reasons, such as in heavy-duty applications.
Cycloid drives also have lower mass. These benefits make them ideally suited for all drive technologies. The design also allows for higher torsional stiffness and service life. These drives also have a much smaller profile.
Cycloid drives are also used to reduce speed. Because of the high torsional stiffness of the cycloid, they also have high positioning accuracy.
Cycloid drives are well-suited to a variety of applications, including electric motors, generators, and pump motors. They are also highly resistant to shock loads, which is important in a variety of applications. This design is ideal for applications that require a large transmission ratio in a compact design.
Cycloid drives also have the advantage of minimizing the clearance between the mating components. This helps to eliminate interference and ensure a positive fit. This is particularly important in gearboxes. It also allows for the use of a load cell and potentiometer to determine the backlash of the gearbox.

editor by CX 2023-11-22
China factory Hollow-Shaft Torque-Arm Cone Worm Gearbox/Speed Reducer cycloidal gearbox reducer
Product Description
Product Description
Characteristic of Hollow-Shaft Torque-Arm Cone Worm Gearbox/Speed Reducer:
In a Worm Gearbox, Worm Reduction Gear Box, Worm Speed Reducer and Gear Motor Manufacturer, three to 11 gear teeth are typically in contact with the worm, depending CZPT the ratio. The increased number of driven gear teeth that are in contact with the worm significantly increases torque capacity also raises shock load resistance. In addition to increasing the number of driven gear teeth in contact with the worm, Worm Gearbox, Worm Reduction Gear Box, Worm Speed Reducer and Gear Motor Manufacturer also increases the contact area on each gear tooth. The actual areas of instantaneous contact between the worm threads and the driven gear tooth are lines. These lines of contact move across the face of the gear tooth as it progresses through its total time of mesh with the worm. The lines of contact in double-enveloping worm gearing are configured to increase the power transmission capability and reduce the stress on each gear tooth.
Working conditions
Two shafts for 90 ° Intersect, input speed must not be more than 1500 rpm.The working environment temperature should range from 0 ~ 40 ° C, when the environment temperature below 0 ° C or above 40 ° C.Before starting the lubricating oil to corresponding heating and cooling, The worm shafts, reverse operation can be positive.
Advantage:
The advantage of Worm Gearbox, Worm Reduction Gear Box, Worm Speed Reducer and Gear Motor Manufacturer design are dramatic. First, the total load is divided among more individual gear teeth, and the load is further divided where teeth support 2 lines of contact. This superior load distribution greatly increases load carrying capacity. Second, the improved torque throughput allows a smaller reducer to produce the same amount of torque, resulting in size and weight savings.
Double-enveloping worm gearing can carry loads that would require much larger and heavier cylindrical worm gearing.
Double-enveloping worm gearbox figure :
(Click on picture for more information)
Packaging & Shipping
Package :
SGR gearbox use standard wood case per gear motor | gear unit.
Shipping :
According to Customer requirement, we delivery products by different transport, Sea shipping, Air Transportation / Express or Truck transportation etc.
Our Services
With all our activities DNV-ISO 9001, SGS -certified, we stand for top-quality service. Entrusting your gearboxes to the care of our Services.
Help protect your gearbox from wear and grinding , SGR gearbox converts torque reliably and efficiently.
We customize our CZPT planetary gear units , double enveloping worm gearbox , helical gear motor , modular design helical gear unit , worm gearbox , cycloidal gearbox etc to fit your application and meet your needs.
These features enable a reliable and safe service life of over 200 000 operational hours.
Our customers have been placing their trust in CZPT gear units since 1997. More than 500 000 gear units of our gearbox are in use reliably around the world, in many cases under very harsh conditions.
Our Honour and Patent :
Company Information
ABOUT US:
ZheJiang CZPT Heavy Industry Machinery Co., Ltd.(formerly known as ZheJiang CZPT Reducer Co., Ltd. ) (sgrgear ) has accumulated rich original designing & manufacturing experience after being founded in 1996. CZPT brand planetary gear reducer has won honor of “Science and Technology Advancement Prize” awarded by the National Speed Reducer & Variator Industry Association.
We produce planetary gear units, planar double-enveloping worm gear speed reducers (cone worm gear reducer), helical-bevel gear motors, worm gear reducers, helical worm gear motors, helical gear motors and many other types of gear units. CZPT gear motors and gear units have given satisfactory performance in different industrial applications, including metallurgy, mineral, architecture, shipbuilding, petroleum combination, aviation space-flight, lift routeing, textile mechanic, cement, pharmaceuticals, pumps, general mechanic and other domain.
With the advantage of high quality & competitive price, CZPT gear motor and gear units are widely welcomed in the domestic market and exported to Southeast Asia, Middle Asia, North America and European countries etc.
With the excellent testing program, CZPT company is always keeping up with the most advanced technology in the world. We have already acquired DNV-ISO9001: 2008 certificate,SGS, CE etc and a patent on CZPT branded gearbox.
We have adopted advanced CAD and CIMS in design & manufacture, which help our engineers develop 3 – 5 series of new efficient products each year. All staff in sales & service department are well trained termly, thus you will be always warmly welcomed and understood by our company.
More Products (Click Products pictures for details ) :
FAQ
- Q: What is your business type?
- A: CZPT is gearbox manufacturer and Solutions Provider, we are experts of the planetary gear reducer, cone worm gearbox, modular design helical gear motor, worm gearbox etc. A suitable model will offer to you according to your requirement, besides, CZPT also has professional technical team special in the custom gearbox and gearbox repair.
- Q: How long can you provide products guarantee Period?
- A: Based on different gearbox types, 12-18 months.
- Q: What’s Certification your product acquiry ?
- A: DNV-ISO9001:2008 ,SGS ,CE etc. and new products patent.
- Q: How many technical employees in your company?
- A: We have 10 engineers in our R&D Dep., included 2 engineers who enjoy government ‘s allowance.
- Q: Where is your company & how to contact you?
- A: Our factory located in No.879 , JinLiu Rd, JinShan District , ZheJiang City , China .
Feel free contact me by Below Information:
| Application: | Motor, Machinery, Marine, Industry |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Change Drive Torque, Change Drive Direction, Speed Changing, Speed Reduction, Speed Increase |
| Layout: | Angle |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Horizontal Type |
| Step: | Single-Step |
| Samples: |
US$ 600/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

A Mathematical Model of a Cycloid Gearbox
Having a gearbox with a cycloidal rotor is an ideal design for a car or any other vehicle, as the cycloidal design can reduce the amplitude of vibration, which is a key component in car performance. Using a cycloidal gearbox is also a great way to reduce the amount of friction between the gears in the gearbox, which can help to reduce noise and wear and tear. A cycloidal gearbox is also a very efficient design for a vehicle that needs to perform under high loads, as the gearbox can be very robust against shock loads.
Basic design principles
cycloidal gearboxes are used for precision gearing applications. Cycloidal drives are compact and robust and offer lower backlash, torsional stiffness and a longer service life. They are also suitable for applications involving heavy loads.
Cycloidal drives are compact in size and provide very high reduction ratios. They are also very robust and can handle shock loads. Cycloidal drives are ideally suited to a wide range of drive technologies. Cycloidal gears have excellent torsional stiffness and can provide a transmission ratio of 300:1. They can also be used in applications where stacking multiple gear stages is not desired.
In order to achieve a high reduction ratio, cycloidal gears must be manufactured extremely accurately. Cycloidal gears have a curved tooth profile that removes shear forces at any point of contact. This provides a positive fit for the gear disc. This profile can be provided on a separate outer bushing or as an internal gear profile insert.
Cycloidal drives are used in marine propulsion systems, where the load plate rotates around the X and Y axis. The plate is anchored by a threaded screw hole arranged 15mm away from the center.
A secondary carrier body is used in a cycloidal gearbox to support the load plate. The secondary carrier body is composed of a mounting carrier body and a secondary carrier disc.
Low friction
Several studies have been conducted to understand the static problems of gears. In this paper, we discuss a mathematical model of a low friction cycloidal gearbox. This model is designed to calculate various parameters that affect the performance of the gearbox during production.
The model is based on a new approach that includes the stiction effect and the nonlinear friction characteristic. These parameters are not covered by the conventional rule of thumb.
The stiction effect is present when the speed direction is changed. During this time, the input torque is required to prevail over the stiction effect to generate movement. The model also enables us to calculate the magnitude of the stiction effect and its breakaway speed.
The most important thing is that the model can be used to improve the dynamic behavior of a controlled system. In this regard, the model has a high degree of accuracy. The model is tested in several quadrants of the gearbox to find the optimum stiction breakaway speed. The simulation results of the model show that this model is effective in predicting the efficiency of a low friction cycloidal gearbox.
In addition to the stiction model, we also studied the efficiency of a low friction cycloidal reducer. The reduction ratio of this gearbox was estimated from the formula. It is found that the ratio approaches negative infinity when the motor torque is close to zero Nm.
Compact
Unlike standard planetary gears, cycloidal gearboxes are compact, low friction and feature virtually zero backlash. They also offer high reduction ratios, high load capacity and high efficiency. These features make them a viable option for a variety of applications.
Cycloid disks are driven by an eccentric input shaft. They are then driven by a stationary ring gear. The ring gear rotates the cycloidal disk at a higher rate. The input shaft rotates nine times to complete a full rotation. The ring gear is designed to correct the dynamic imbalance.
CZPT cycloidal gearheads are designed for precision and stable operation. These reducers are robust and can handle large translocations. They also offer high overload protection. They are suitable for shock wave therapy. CZPT gearheads are also well suited for applications with critical positioning accuracy. They also require low assembly and design costs. They are designed for long service life and low hysteresis loss.
CZPT cycloidal reducers are used in a variety of industrial applications, including CNC machining centers, robot positioners and manipulators. They offer a unique design that can handle high forces on the output axis, and are especially suitable for large translocations. These gearheads are highly efficient, reducing costs, and are available in a variety of sizes. They are ideal for applications that require millimetre accuracy.
High reduction ratios
Compared to other gearboxes, cycloidal gearboxes offer high reduction ratios and small backlash. They are also less expensive. Cycloid gearboxes can be used in a variety of industries. They are suitable for robotic applications. They also have high efficiency and load capacity.
A cycloidal gearbox works by rotating a cycloidal disc. This disc contains holes that are bigger than the pins on the output shaft. When the disc is rotated, the output pins move in the holes to generate a steady output shaft rotation. This type of gearbox does not require stacking stages.
Cycloid gearboxes are usually shorter than planetary gearboxes. Moreover, they are more robust and can transmit higher torques.
Cycloid gearboxes have an eccentric cam that drives the cycloidal disc. The cycloidal disc advances in 360deg/pivot/roller steps. It also rotates in an eccentric pattern. It meshes with the ring-gear housing. It also engages the internal teeth of the ring-gear housing.
The number of lobes on the cycloidal disc is not sufficient to generate a good transmission ratio. In fact, the number of lobes must be less than the number of pins surrounding the cycloidal disc.
The cycloidal disc is rotated by an eccentric cam that extends from the base shaft. The cam also spins inside the cycloidal disc. The eccentric motion of the cam helps the cycloidal disc rotate around the pins of the ring-gear housing.
Reducing amplitude of the vibration
Various approaches to reducing amplitude of the vibration in a cycloidal gearbox have been studied. These approaches are based on the kinematic analysis of gearbox.
A cycloidal gearbox is a gearbox that consists of bearings, gears, and an eccentric bearing that drives a cycloidal disc. This gearbox has a high reduction ratio, which is achieved by a series of output shaft pins that drive the output shaft as the disc rotates.
The test bench used in the studies has four sensors. Each sensor acquires signals with different signal processing techniques. In addition, there is a tachometer that acquires variations in rotational velocity at the input side.
The kinematic study of the robotic gearbox was performed to understand the frequency of vibrations and to determine whether the gearbox is faulty. It was found that the gearbox is in healthy operation when the amplitude of the x and y is low. However, when the amplitude is high, it is indicative of a malfunctioning element.
The frequency analysis of vibration signals is performed for both cyclostationary and noncyclostationary conditions. The frequencies that are selected are those that appear in both types of conditions.
Robust against shock loads
Compared to traditional gearboxes, cycloidal gearboxes have significant benefits when it comes to shock loads. These include high shock-load capacity, high efficiency, reduced cost, lower weight, lower friction, and better positioning accuracy.
Cycloid gears can be used to replace traditional planetary gears in applications where inertia is important, such as the transportation of heavy loads. They have a lighter design and can be manufactured to a more compact size, which helps reduce cost and installation expense. Cycloid gears are also able to provide transmission ratios of up to 300:1 in a small package.
Cycloid gears are also suitable for applications where a long service life is essential. Their radial clamping ring reduces inertia by up to 39%. Cycloid gears have a torsional stiffness that is five times higher than that of conventional planetary gears.
Cycloid gearboxes can provide significant improvements in concrete mixers. They are a highly efficient design, which allows for important innovations. They are also ideal for servo applications, machine tools, and medical technology. They feature user-friendly screw connections, effective corrosion protection, and effective handling.
Cycloid gears are especially useful for applications with critical positioning accuracy. For example, in the control of large parabolic antennas, high shock load capacity is required to maintain accuracy. Cycloid gears can withstand shock loads up to 500% of their rated torque.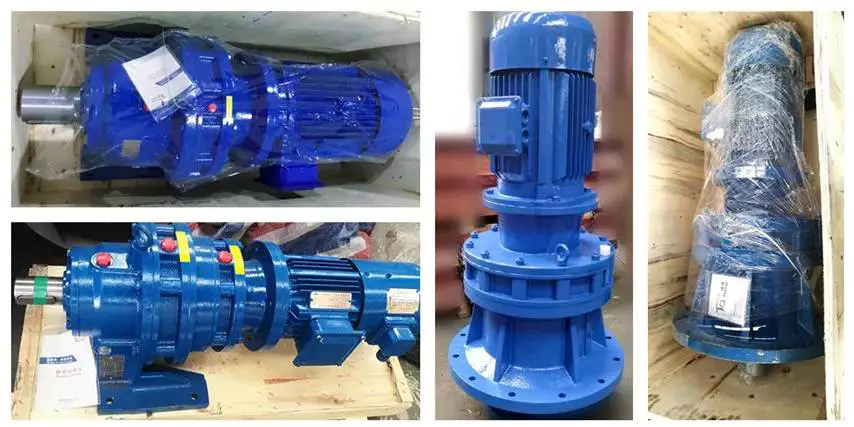
Inertial effects
Various studies have been conducted to investigate the static problems of gears. However, there is still a need for a proper model to investigate the dynamic behaviour of a controlled system. For this, a mathematical model of a cycloidal gearbox has been developed. The presented model is a simple model that can be used as the basis for a more complex mechanical model.
The mathematical model is based on the cycloidal gearbox’s mechanical construction and has a nonlinear friction characteristic. The model is able to reproduce the current peaks and breaks at standstill. It also considers the stiction effect. However, it does not cover backlash or torsional stiffness.
This model is used to calculate the torque generating current and the inertia of the motor. These values are then compared with the real system measurement. The results show that the simulation results are very close to the real system measurement.
Several parameters are considered in the model to improve its dynamic behaviour. These parameters are calculated from the harmonic drive system analysis. These are torque-generating current, inertia, and the contact forces of the rotating parts.
The model has a high level of accuracy and can be used for motor control. It is also able to reproduce the dynamic behaviour of a controlled system.

editor by CX 2023-10-26
China Custom 2-Stage Cycloidal Motor Speed Reducer with Direct Connection Motor supplier
Product Description
Product Description
2-stage cycloidal motor speed reducer with direct connection motor
Components:
1. Housing: Cast Iron
2. Gearset: Cycloid Wheel & Pin Wheel
3. Input Configurations:
Equipped with Electric Motors (AC Motor, Brake Motor, Explosion-proof Motor, Regulated Speed Motor, Hydraulic Motor)
IEC-normalized Motor Flange
Keyed CZPT Shaft Input
4. Output Configurations:
Keyed CZPT Shaft Output
Detailed Photos
Features:
1. Large reduction ratio, 1-stage ratio 9~87, 2-stage ratio 121~1849, larger reduction ratio is available by 3-stage or multistage combinations
2. High efficiency, the average efficiency is over 90%
3. Compact structure, light weight
4. Stable and reliable operation, low noise5. Long service life
Product Parameters
Parameters:
| Models | Power | Ratio | Max. Torque | Output Shaft Dia. | Input Shaft Dia. |
| 1 Stage | |||||
| X2(B0/B12) | 0.37~1.5 | 9~87 | 150 | Φ25(Φ30) | Φ15 |
| X3(B1/B15) | 0.55~2.2 | 9~87 | 250 | Φ35 | Φ18 |
| X4(B2/B18) | 0.75~4.0 | 9~87 | 500 | Φ45 | Φ22 |
| X5(B3/B22) | 1.5~7.5 | 9~87 | 1,000 | Φ55 | Φ30 |
| X6(B4/B27) | 2.2~11 | 9~87 | 2,000 | Φ65(Φ70) | Φ35 |
| X7 | 3.0~11 | 9~87 | 2,700 | Φ80 | Φ40 |
| X8(B5/B33) | 5.5~18.5 | 9~87 | 4,500 | Φ90 | Φ45 |
| X9(B6/B39) | 7.5~30 | 9~87 | 7,100 | Φ100 | Φ50 |
| X10(B7/B45) | 15~45 | 9~87 | 12,000 | Φ110 | Φ55 |
| X11(B8/B55) | 18.5~55 | 9~87 | 20,000 | Φ130 | Φ70 |
| 2 Stage | |||||
| X32(B10) | 0.25~0.55 | 121~1849 | – | Φ35 | Φ15 |
| X42(B20/B1812) | 0.37~0.75 | 121~1849 | – | Φ45 | Φ15 |
| X53(B31/B2215) | 0.55~1.5 | 121~1849 | – | Φ55 | Φ18 |
| X63(B41/B2715) | 0.75~2.2 | 121~1849 | – | Φ65(Φ70) | Φ18 |
| X64(B42/B2718) | 0.75~2.2 | 121~1849 | – | Φ65(Φ70) | Φ22 |
| X74 | 1.1~3.0 | 121~1849 | – | Φ80 | Φ22 |
| X84(B52/B3318) | 1.5~4.0 | 121~1849 | – | Φ90 | Φ22 |
| X85(B53/B3322) | 2.2~5.5 | 121~1849 | – | Φ90 | Φ30 |
| X95(B63/B3922) | 3.0~7.5 | 121~1849 | – | Φ100 | Φ30 |
| X106(B74/B4527) | 4.0~11 | 121~1849 | – | Φ110 | Φ35 |
| X117(B84/B5527) | 4.0~15 | 121~1849 | – | Φ130 | Φ40(Φ35) |
1 Stage Ratio: 9, 11, 17, 23, 29, 35, 43, 59, 71, 87
2 Stage Ratio: 121, 187, 289, 385, 473, 595, 731, 989, 1225, 1849
Installation:
Foot Mounted
Flange Mounted
Lubrication:
| – | Foot-mounted | Flange-mounted | ||
| 1 Stage | X2~X4 | X5~X11 | X2~X4 | X5~X11 |
| Grease Lubrication | Oil-bath & Splash Lubrication | Grease Lubrication | Oil Pump Circulation Lubrication | |
| 2 Stage | X32~X42 | X53~X117 | X32~X42 | X53~X117 |
| Grease Lubrication | Oil-bath & Splash Lubrication | Grease Lubrication | Oil Pump Circulation Lubrication | |
Cooling:
Natural Cooling
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
Our Advantages
FAQ
1.Q:What kinds of gearbox can you produce for us?
A:Main products of our company: UDL series speed variator,RV series worm gear reducer, ATA series shaft mounted gearbox, X,B series gear reducer,
P series planetary gearbox and R, S, K, and F series helical-tooth reducer, more
than 1 hundred models and thousands of specifications
2.Q:Can you make as per custom drawing?
A: Yes, we offer customized service for customers.
3.Q:What is your terms of payment ?
A: 30% Advance payment by T/T after signing the contract.70% before delivery
4.Q:What is your MOQ?
A: 1 Set
Welcome to contact us for more detail information and inquiry.
If you have specific parameters and requirement for our gearbox, customization is available.
| Application: | Motor, Machinery, Agricultural Machinery, Industry |
|---|---|
| Function: | Change Drive Torque, Change Drive Direction, Speed Changing, Speed Reduction, Speed Increase |
| Layout: | Cycloidal |
| Hardness: | Hardened |
| Installation: | Vertical Type |
| Step: | Double-Step |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How to Use a Cyclone Gearbox
Often, a cycloidal gearbox is used in order to achieve a torque transfer from a motor or pump. This type of gearbox is often a common choice as it has a number of advantages over a regular gearbox. Its main advantage is that it is easy to make, which means that it can be incorporated into a variety of applications. However, if you want to use a cycloidal gearbox, there are a few things that you need to know. These include the operation principle, the structure and the dynamic and inertial effects that come with it.
Dynamic and inertial effects
Several studies have been carried out on the static and dynamic properties of cycloidal gears. The study of these effects is beneficial in assisting optimal design of cycloidal speed reducers.
In this paper, the dynamic and inertial effects of a two-stage cycloidal speed reducer have been investigated using the CZPT program package. Moreover, a new model for cycloidal reducers based on non-linear contact dynamics has been developed. The new model aims to predict several operational conditions.
The normal excitation contact force for the cycloid discs of the first and second stage is very similar. However, the total deformation at the contact point is different. This effect is mainly due to the system’s own oscillations. The cycloid discs of the second stage turn around the ring gear roller with a 180deg angle. This angle is a significant contributor to the torque loads. The total excitation force on the cycloid discs of first and second stage is 1848 N and 2068.7 N, respectively.
In order to analyze the contact stress, different gear profiles were investigated. The mesh density was considered as an important design criterion. It was found that a bigger hole reduces the material content of the cycloidal disc and results in more stresses.
Moreover, it is possible to reduce the contact forces in a more efficient manner by changing the geometric parameters. This can be done by mesh refinement along the disc width. The cycloidal disc has the greatest influence on the output results.
The efficiency of a cycloidal drive increases with the increase in load. The efficiency of a cycloidal reducer also depends on the eccentricity of the input shaft and the cycloidal plate. The efficiency curve for small loads is linear. However, for the larger loads, the efficiency curve becomes more non-linear. This is because the stiffness of the cycloid reducer increases as the load increases.
Structure
Despite the fact that it looks like a complicated engineering puzzle, the construction of a cycloidal gearbox is actually quite simple. The key elements are the base, the load plate and the thrust bearing. All these elements work together to create a stable, compact gearbox.
The base is a circular section with several cylindrical pins around its outer edge. The pins are fixed on a fixed ring that holds them in a circular path. The ring serves as a reference circle. The circle’s size is approximately 5mm in diameter.
The load plate is a series of threaded screw holes. These are arranged 15mm away from the center. These are used to anchor external structures. The load plate must be rotated around the X and Y axis.
The thrust bearing is placed on top of the load plate. The bearing is made of an internal diameter of 35mm and an external diameter of 52mm. It is used to allow rotation around the Z axis.
The cycloidal disc is the centerpiece of the cycloidal gearbox. The disc has holes for the pins that drive the output shaft. The holes are larger than those used in output roller pins. The disc also has a reduced eccentricity.
The pins are attached to the cycloidal disc by rolling pins. The pins are made of a material that provides mechanical support for the drive during high-torque situations. The pins have a 9mm external diameter. The disc has a number of lobes and is rotated by one lobe per shaft revolution.
The cycloidal gearbox also has a top cover that helps keep the components together. The cover has a pocket for tools. The top cover also has threads that screw into the casing.
Operation principle
Among many types of gear transmissions, cycloidal gearboxes are used in heavy machinery and multi-axis robots. They are highly effective, compact and capable of high ratios. In addition, they have an overload capability.
Cycloid disks are driven by eccentric shafts that rotate around fixed ring pins. Roller pins of the pin disc engage with holes in the cycloidal disc. These roller pins drive the pin disc and the pin disc transfers the motion to the output shaft.
Unlike conventional gear drives, cycloidal drives have low backlash and high torsional stiffness. They are ideally suited to heavy loads and all drive technologies. The lower mass and compact design of the cycloidal disk also contributes to its high efficiency and positioning accuracy.
The cycloidal disc plays a central role in the gearbox kinematics. It rotates around a fixed ring in a circle. When the disc is pushed against the ring gear, the pins engage with the disc and the roller pins rotate around the pins. This rotating motion generates vibration, which travels through the driven shafts.
Cycloid discs are typically designed with a short cycloid, so that the eccentricity is minimized. This reduces unbalance forces at high speeds. Ideally, the number of lobes on the cycloid is smaller than the number of surrounding pins. This reduces the amount of Hertzian contact stress.
Unlike planetary gears, cycloidal gears have high accuracy and are capable of withstanding shock loads. They also experience low friction and less wear on tooth flanks. They also have higher efficiency and load capacity.
Cycloid gears are generally more difficult to manufacture than involute gears. Cycloid gears are not suitable for stacking gear stages. They require extreme accuracy for manufacturing. However, their smaller size and low backlash, high torsional stiffness, and low vibration make them ideal for use in heavy machines.
Involute gear tooth profile
Almost all gears are manufactured with an involute gear tooth profile. Cycloid gears are also produced with this profile. Compared with involute gears, cycloid gears are stronger and can transmit more power. However, they can also be more difficult to manufacture. This makes them costlier.
The involute gear tooth profile is a smooth curve. It is derived from the involute curve of a circle. A tangent to the base circle is the normal at any point of an involute.
This curve has properties that allow the involute gear teeth to transfer motion in perpendicular direction. It is also the path traced by the end of the string unwrapping from a cylinder.
An involute profile has the advantage of being easy to manufacture. It also allows for smooth meshing despite misalignment of the centre distance. This profile is also preferred over a cycloid tooth profile, but it is not the best in every regard.
Cycloid gear teeth are also made of two curves. Unlike involute teeth, cycloid gear teeth have a consistent radius. Cycloid gears are less likely to produce noise. But they are also more expensive to manufacture.
Involute teeth are easier to manufacture because they have only one curve. Cycloid gears can also be made with a rack type cutter. This makes them cheaper to manufacture. However, they require an expert design. They can also be manufactured with a gear shaper that includes a pinion cutter.
The tooth profiles that satisfy the law of gear-tooth action are sometimes called conjugate profiles. The involute profile is the most common of these. It allows for constant torque transmission.
Backlash
Typically, cycloidal drives provide a high ratio of transmission with no backlash. This is because the cycloid disc is driven by an eccentric shaft. During rotation, the cycloid disc rotates around a fixed ring. This ring also rotates independently of the center of gravity.
The cycloid disc is typically shortened to reduce the eccentricity. This helps to minimize the unbalance forces that may occur at high speeds. The cycloid also offers a larger gear ratio than traditional gears. This provides a better positional accuracy.
Cycloid drives also have a high torsional stiffness. This provides greater torsional resilience and shock load capabilities. This is important for a number of reasons, such as in heavy-duty applications.
Cycloid drives also have lower mass. These benefits make them ideally suited for all drive technologies. The design also allows for higher torsional stiffness and service life. These drives also have a much smaller profile.
Cycloid drives are also used to reduce speed. Because of the high torsional stiffness of the cycloid, they also have high positioning accuracy.
Cycloid drives are well-suited to a variety of applications, including electric motors, generators, and pump motors. They are also highly resistant to shock loads, which is important in a variety of applications. This design is ideal for applications that require a large transmission ratio in a compact design.
Cycloid drives also have the advantage of minimizing the clearance between the mating components. This helps to eliminate interference and ensure a positive fit. This is particularly important in gearboxes. It also allows for the use of a load cell and potentiometer to determine the backlash of the gearbox.

editor by CX 2023-10-23
China supplier Precise Machined Smrv 030-150 Motor Reductor Worm Gear Reducer cycloidal gearboxes
Product Description
Technical Features
The high degree of modularity is a design feature of SRC helical gearboxes range. It can be connected respectively with motors such as normal motor, brake motor, explosion-proof motor, frequency conversion motor, servo motor, IEC motor and so on. This kind of product is widely used in drive fields such as textile, foodstuff, ceramics packing, logistics, plastics and so on. It is possible to set up the version required using flanges or feet.
Products characteristics
SRC series helical gear units has more than 4 types. Power 0.12-4kw; Ratio 3.66-54; Torque max 120-500Nm. It can be connected (foot or flange) discretionary and use multi-mounting positions according to customers requirements.
Ground-hardened helical gears;
Modularity,can be combined in many forms;
Aluminium casing, light weight;
Gears in carbonize hard, durable;
Universal mounting;
Refined design,space effective and low noise
Structure feature
Model illuminate
|
1 |
Code for gear units series |
|
2 |
No F code means foot mounted.With F code B5 flange mounted.With Z code B14 flange mounted |
|
3 |
Specification code of gear units 01 |
|
4 |
I,II,III,B5 Output flange specification,default I not to write out is ok |
|
5 |
IEC: Input flange HS: shaft input |
|
6 |
Transmission ratio of gear units |
|
7 |
M1:Mounting position, default mounting position M1 not to write out is ok |
|
8 |
Position diagram for motor terminal box,default position o°(R) not to write out is ok |
|
9 |
No mark means without motor Model motor(poles of power) |
|
10 |
Voltage – frequency |
|
11 |
Coil in position for motor, default position S not to write out is ok |
4.2 Rotation speed n
n1 Gear units input speed
n2 Gear units output speed
If driven by the external gearing,1400r/min or lower rotation speed is suggested so as to optimize the working conditions and prolong the service life.Higher input rotation speed is permitted, but in this situation,the rated torque M2 will be reduced
4.5 Service factor fs
The effect of the driven machine on the gear unit is taken into account to a sufficient level of accuracy using the service factor fs. The service factor is determined according to the daily operation time and the starting frequency Z. Three load classifications are considered depending on the mass acceleration factor. You can read off the service factor applicable to your application in following figure. The service factor selected using this diagram must be less than or equal to the service factor as given in the performance parameter table.
* starting frequency Z: The cycles include all starting and braking procedures as well as change overs from low to high speed
SRC02..(HS) Performance parameter
|
kw |
Output speed |
Torque |
Speed ratio |
fs |
Model |
IEC |
|
0.37 |
16.7rpm |
204N.M |
54 |
1.0 |
SRC02 |
80B5/B14
|
Helical gearbox outline dimension heet
| Foot Code | U | V | V1 | V2 | V3 | W | X | X1 | Y | Z |
| B02 | 18 | 107.5 | 60 | – | 130 | 11 | 136 | 155 | 100 | 17 |
| M02 | 25 | 85 | – | 110 | 120 | 9 | 112 | 145 | 80 | 15 |
| M01 | 18 | 80 | – | 110 | 120 | 9 | 118 | 145 | 80 | 15 |
| B01 | 18 | 87 | 50 | 110 | – | 9 | 118 | 130 | 90 | 15 |
SRC helical gearbox with motor mounting position and terminal box orientation
Package
1 pc / carton,several cartons / wooden pallet
| Application: | Motor |
|---|---|
| Layout: | Cycloidal |
| Hardness: | Soft Tooth Surface |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How to Calculate Transmission Ratio for a Cycloidal Gearbox
Using a cycloidal gearbox can be very useful in a wide variety of situations. However, it’s important to understand how to use it properly before implementing it. This article discusses the benefits of using a cycloidal gearbox, how to calculate the transmission ratio, and how to determine the effects of dynamic and inertial forces on the gearbox.
Dynamic and inertial effects
Various studies have been done to study the dynamic and inertial effects of cycloidal gearboxes. These studies have been performed using numerical, analytical and experimental methods. Depending on the nature of the load and its distribution along the gear, a variety of models have been developed. These models use finite element method to determine accurate contact stresses. Some of these models have been developed to address the nonlinear elasticity of contacts.
Inertial imbalance in a cycloidal gearbox causes vibration and can affect the efficiency of the device. This can increase mechanical losses and increase wear and tear. The efficiency of the device also depends on the torque applied to the cycloidal disk. The effectiveness of the device increases as the load increases. Similarly, the nonlinear contact dynamics are also associated with an increase in efficiency.
A new model of a cycloidal reducer has been developed to predict the effects of several operational conditions. The model is based on rigid body dynamics and uses a non-linear stiffness coefficient. The model has been validated through numerical and analytical methods. The model offers drastic reduction in computational costs. The model allows for a quick analysis of several operational conditions.
The main contribution of the paper is the investigation of the load distribution on the cycloidal disc. The study of this aspect is important because it allows for an analysis of the rotating parts and stresses. It also provides an indication of which gear profiles are best suited for optimizing torque transmission. The study has been conducted with a variety of cycloidal gearboxes and is useful in determining the performance of different types of cycloidal gearboxes.
To study the load distribution on the cycloidal disc, the authors investigated the relationship between contact force, cycloidal gearboxes and different gear profiles. They found that the non-linear contact dynamics have a large impact on the efficiency of a cycloidal gearbox. The cycloidal gearbox is an ideal solution for applications that involve highly dynamic servos. It can also be used in machine tool applications and food processing industries.
The study found that there are three common design principles of cycloidal reducers. These are the contact force distribution, the speed reduction and the trochoidal profile of the cycloidal disc. The trochoidal profile has to be defined carefully to ensure correct mating of the rotating parts. The trochoidal profile provides an indication of which gear profiles are best for optimizing torque transmission. The contact force distribution can be improved by refining the mesh along the disc’s width.
As the input speed increases, the efficiency of the reducer increases. This is because contact forces are constantly changing in magnitude and orientation. A cycloidal reducer with a one tooth difference can reduce input speed by up to 87:1 in a single stage. It also has the ability to handle high-cycle moves without backlash.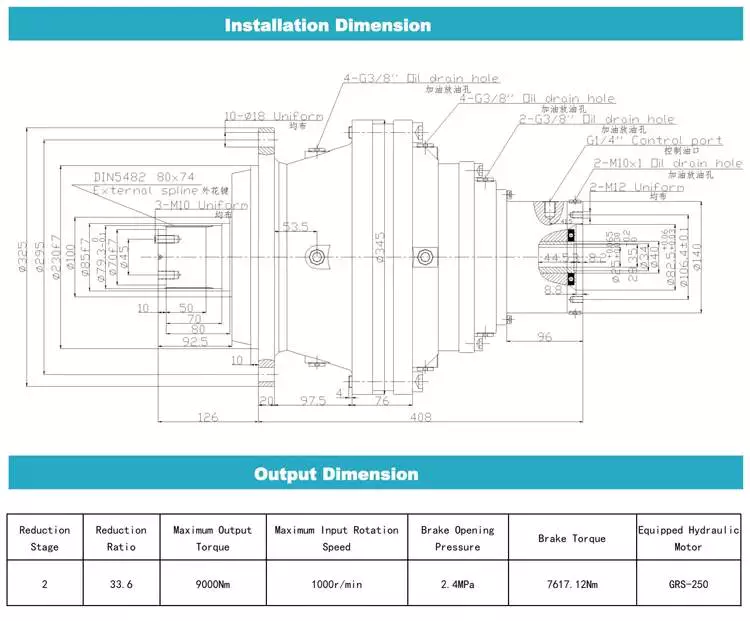
Transmission ratio calculation
Getting the correct transmission ratio calculation for a cycloidal gearbox requires a good understanding of what a gearbox is, as well as the product that it is being used for. The correct ratio is calculated by dividing the output speed of the output gear by the input speed of the input gear. This is usually accomplished by using a stopwatch. In some cases, a catalog or product specification may be required. The correct ratio is determined by a combination of factors, such as the amount of torque applied to the mechanism, as well as the size of the gears involved.
A cycloidal gear is a type of gear tooth profile that can be represented using a spline. It is also possible to model a gear with a cycloidal profile by using a spline to connect points against the beginning of a coordinate system. This is important in the design and functionality of a gear.
There are many different gears used in machines and devices. These include the herringbone gear, the helical gear and the spiral bevel gear. The best transmission ratios are typically obtained with a cycloidal gearbox. In addition to ensuring the accuracy of positioning, a cycloidal gearbox provides excellent backlash. Cycloid gears have a high degree of mechanical efficiency, low friction, and minimal moment of inertia.
A cycloidal gearbox is often referred to as a planetary gearbox, though it is technically a single-stage gearbox. In addition to having a ring gear, the gearbox has an eccentric bearing that drives the cycloidal disc in an eccentric rotation. This makes the cycloidal gearbox a good choice for high gear ratios in compact designs.
The cycloid disc is the key element of a cycloidal gearbox. The cycloid disc has n=9 lobes, and each lobe of the disc moves by a lobe for every revolution of the drive shaft. The cycloid disc is then geared to a stationary ring gear. The cycloidal disc’s lobes act like teeth on the stationary ring gear.
There are many different gears that are classified by the profile of the gear teeth. The most common gears are the involute and helical gears. Most motion control gears include spur designs. However, there are many other types of gears that are used in various applications. The cycloidal gear is one of the more complicated gears to design. The cycloid disc’s outline can be represented using markers or smooth lines, though a scatter chart will also do.
The cycloid disc’s lobes rotate on a reference pitch circle of pins. These pins rotate 40 deg during the eccentric rotation of the drive shaft. The pins rotate around the disc to achieve a steady rotation of the output shaft.
The cycloid disc’s other obvious, and possibly more important, feature is the’magic’ number of pins. This is the number of pins that protrude through the face of the disc. The disc has holes that are larger than the pins. This allows the pins to protrude through the disc and attach to the output shaft.
Application
Whether you’re building a robot drive or you’re simply looking for a gearbox to reduce the speed of your vehicle, a cycloidal gearbox is a great way to achieve a high reduction ratio. Cycloidal gearboxes are a low-friction, lightweight design that has an extremely stable transmission. They are suitable for industrial robots and can be used in many applications, including positioning robots.
Cycloidal gearboxes reduce speed by using eccentric motion. The eccentric motion enables the entire internal gear to rotate in wobbly cycloidal motion, which is then translated back into circular rotation. This eliminates the need for stacking gear stages. Cycloidal gearboxes also have less friction, higher strength, and greater durability than conventional gearboxes.
The cycloidal gearbox is also used in a number of applications, including marine propulsion systems, and robot drives. Cycloidal gearboxes reduce vibration by using offset gearing to cancel out vibrations.
Cycloidal gears have lower friction, higher strength, and better torsional stiffness than involute gears. They also have a reduced Hertzian contact stress, making them better than involute gears for use with shock loads. They also have a smaller size and weight than conventional gearboxes, and they have a higher reduction ratio than involute gears.
Cycloidal gears are typically used to reduce the speed of motors, but they also offer a number of other advantages. Cycloidal gearboxes have a smaller footprint than other gearboxes, allowing them to fit into confined spaces. They also have low backlash, allowing for precise movement. Cycloidal gears have a higher efficiency, resulting in lower power requirements and lower wear.
The cycloidal disc is one of the most important components of the gearbox. Cycloidal discs are normally designed with a short cycloid, which minimizes the eccentricity of the disc. They are also designed with a shortened flank, resulting in better strength and less stress concentration. Cycloidal discs are typically geared to a stationary ring gear. The cycloid is designed to roll around the stationary ring pins, which push against the circular holes in the disc. Cycloidal gearboxes typically employ two degrees of shift.
Cycloidal drives are ideal for heavy load applications. They also have high torsional stiffness, which makes them highly resistant to shock loads. Cycloidal drives also offer a high reduction ratio, which can be achieved without the need for a large input shaft. They are also compact and have a high service life.
The output shaft of a cycloidal gearbox always has two degrees of shifting, which ensures that the input and output shafts always rotate at a different speed. The output shaft would be a pin casing around the drive disks, which would also allow for easy maintenance.
Cycloidal gearboxes are also very compact and lightweight, so they are ideal for use in industrial robots. The cycloidal gearbox reducer is the most stable, low-vibration reducer in industrial robots, and it has a wide transmission ratio range.

editor by CX 2023-10-20
China supplier High Torque Right Angle Km Helical Hypoid Speed Reducer Gearbox Gear Reducer Gearbox Price wholesaler
Product Description
Km Series Aluminium Alloy 7.5~300 Ratio 90 Degree Hypoid Gear Motor Vertical Hypoid Reduction Gearbox with Electric Motor
Product Parameters
|
Applicable Industries |
Garment Shops, Manufacturing Plant, Machinery Repair Shops, Food & Beverage Factory |
|
Gearing Arrangement |
Hypoid |
|
Output Torque |
100~500NM |
|
Input Speed |
1400rpm |
|
Output Speed |
5~187 |
|
Place of Origin |
China |
|
Brand Name |
HUAKE |
|
Product name |
Hypoid gear reducer |
|
Color |
Blue |
|
Ratio |
5-400 |
|
Certificate |
ISO9001 CCC CE |
Detailed Photos
Product Description
KPM-KPB series helical-hypoid gearboxes are the new-generation product with a compromise of advanced technology both at home and abroad.This product is widely used in textile, foodstuff, beverage,tobacco, logistics industrial fields,etc.
Main Features:
(1) Driven by hypoid gears, which has big ratios.
(2) Large output torque, high efficiency(up to 92%), energy saving and environmental protection.
(3) High quality aluminum alloy housing, light in weight and non-rusting.
(4) Smooth in running and low in noise, and can work long time in dreadful conditions.
(5) Good-looking appearance, durable service life and small volume.
(6) Suitable for all round installation, wide application and easy use.
(7) KPM series can replace NMRV worm gearbox; KPB series can replace CZPT W series worm gearbox;
(8) Modular and multi-structure can meet the demands of various conditions.
Main Material:
(1) Housing: aluminum alloy
(2) Gear wheel: 20CrMnTiH1,carbonize & quencher heat treatment make the hardness of gears surface up to 56-62 HRC, retain carburization layers thickness between 0.3 and 0.5mm after precise grinding.
Gearbox Application
Company Profile
Certifications
Packaging & Shipping
FAQ
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car, Transmission Parts |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Clutch, Change Drive Torque, Change Drive Direction, Speed Changing, Speed Reduction, Speed Increase |
| Layout: | Cycloidal |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Torque Arm Type |
| Step: | Single-Step |
| Samples: |
US$ 80/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

The Advantages of Using a Cyclone Gearbox
Using a cycloidal gearbox to drive an input shaft is a very effective way to reduce the speed of a machine. It does this by reducing the speed of the input shaft by a predetermined ratio. It is capable of very high ratios in relatively small sizes.
Transmission ratio
Whether you’re building a marine propulsion system or a pump for the oil and gas industry, there are certain advantages to using cycloidal gearboxes. Compared to other gearbox types, they’re shorter and have better torque density. These gearboxes also offer the best weight and positioning accuracy.
The basic design of a cycloidal gearbox is similar to that of a planetary gearbox. The main difference is in the profile of the gear teeth.
Cycloid gears have less tooth flank wear and lower Hertzian contact stress. They also have lower friction and torsional stiffness. These advantages make them ideal for applications that involve heavy loads or high-speed drives. They’re also good for high gear ratios.
In a cycloidal gearbox, the input shaft drives an eccentric bearing, while the output shaft drives the cycloidal disc. The cycloidal disc rotates around a fixed ring, and the pins of the ring gear engage the holes in the disc. The pins then drive the output shaft as the disc rotates.
Cycloid gears are ideal for applications that require high gear ratios and low friction. They’re also good for applications that require high torsional stiffness and shock load resistance. They’re also suitable for applications that require a compact design and low backlash.
The transmission ratio of a cycloidal gearbox is determined by the number of lobes on the cycloidal disc. The n=n design of the cycloidal disc moves one lobe per revolution of the input shaft.
Cycloid gears can be manufactured to reduce the gear ratio from 30:1 to 300:1. These gears are suitable for high-end applications, especially in the automation industry. They also offer the best positioning accuracy and backlash. However, they require special manufacturing processes and require non-standard characteristics.
Compressive force
Compared with conventional gearboxes, the cycloidal gearbox has a unique set of kinematics. It has an eccentric bearing in a rotating frame, which drives the cycloidal disc. It is characterized by low backlash and torsional stiffness, which enables geared motion.
In this study, the effects of design parameters were investigated to develop the optimal design of a cycloidal reducer. Three main rolling nodes were studied: a cycloidal disc, an outer race and the input shaft. These were used to analyze the motion related dynamic forces, which can be used to calculate stresses and strains. The gear mesh frequency was calculated using a formula, which incorporated a correction factor for the rotating frame of the outer race.
A three-dimensional finite element analysis (FEA) study was conducted to evaluate the cycloidal disc. The effects of the size of the holes on the disc’s induced stresses were investigated. The study also looked at the torque ripple of a cycloidal drive.
The authors of this study also explored backlash distribution in the output mechanism, which took into account the machining deviations and structure and geometry of the output mechanism. The study also looked at the relative efficiency of a cycloidal reducer, which was based on a single disc cycloidal reducer with a one-tooth difference.
The authors of this study were able to deduce the contact stress of the cycloidal disc, which is calculated using the material-based contact stiffness. This can be used to determine accurate contact stresses in a cycloidal gearbox.
It is important to know the ratios needed for calculation of the bearing rate. This can be calculated using the formula f = k (S x R) where S is the volume of the element, R is the mass, k is the contact stiffness and f is the force vector.
Rotational direction
Unlike the conventional ring gear which has a single axis of rotation, cycloidal gearbox has three rotational axes which are parallel and are located in a single plane. A cycloidal gearbox has excellent torsional stiffness and shock load capacity. It also ensures constant angular velocity, and is used in high-speed gearbox applications.
A cycloidal gearbox consists of an input shaft, a drive member and a cycloidal disc. The disc rotates in one direction, while the input shaft rotates in the opposite direction. The input shaft eccentrically mounts to the drive member. The cycloidal disc meshes with the ring-gear housing, and the rotational motion of the cycloidal disc is transferred to the output shaft.
To calculate the rotational direction of a cycloidal gearbox, the cycloid must have the correct angular orientation and the centerline of the cycloid should be aligned with the center of the output hole. The cycloid’s shortest length should be equal to the radius of the pin circle. The cycloid’s largest radius should be the size of the bearing’s exterior diameter.
A single-stage gear will not have much space to work with, so you’ll need a multistage gear to maximize space. This is also the reason that cycloid gears are usually designed with a shortened cycloid.
To calculate the most efficient tooth profile for a cycloidal gear, a new method was devised. This method uses a mathematical model that uses the cycloid’s rotational direction and a few other geometric parameters. Using a piecewise function related to the distribution of pressure angle, the cycloid’s most efficient profile is determined. It is then superimposed on the theoretical profile. The new method is much more flexible than the conventional method, and can adapt to changing trends of the cycloidal profile.
Design
Several designs of cycloidal gearboxes have been developed. These gearboxes have a large reduction ratio in one stage. They are mainly used for heavy machines. They provide good torsional stiffness and shock load capacity. However, they also have vibrations at high RPM. Several studies have been conducted to find a solution to this problem.
A cycloidal gearbox is designed by calculating the reduction ratio of a mechanism. This ratio is obtained by the size of the input speed. This is then multiplied by the reduction ratio of the gear profile.
The most important factor in the design of a cycloidal gearbox is the load distribution along the width of the gear. Using this as a design criterion, the amplitude of vibration can be reduced. This will ensure that the gearbox is working properly. In order to generate proper mating conditions, the trochoidal profile on the cycloidal disc periphery must be defined accurately.
One of the most common forms of cycloidal gears is circular arc toothing. This is the most common type of toothing used today.
Another form of gear is the hypocycloid. This form requires the rolling circle diameter to be equal to half the base circle diameter. Another special case is the point tooth form. This form is also called clock toothing.
In order to make this gear profile work, the initial point of contact must remain fixed to the edge of the rolling disk. This will generate the hypocycloid curve. The curve is traced from this initial point.
To investigate this gear profile, the authors used a 3D finite element analysis. They used the mathematical model of gear manufacturing that included kinematics parameters, output moment calculations, and machining steps. The resulting design eliminated backlash.
Sizing and selection
Choosing a gearbox can be a complex task. There are many factors that need to be taken into account. You need to determine the type of application, the required speed, the load, and the ratio of the gearbox. By gaining this information, you can find a solution that works best for you.
The first thing you need to do is find the proper size. There are several sizing programs available to help you determine the best gearbox for your application. You can start by drawing a cycloidal gear to help you create the part.
During sizing, it is important to consider the environment. Shock loads, environmental conditions, and ambient temperatures can increase wear on the gear teeth. The temperature also has a significant impact on lubrication viscosities and seal materials.
You also need to consider the input and output speed. This is because the input speed will change your gearbox ratio calculations. If you exceed the input speed, you can damage the seals and cause premature wear on the shaft bearings.
Another important aspect of sizing is the service factor. This factor determines the amount of torque the gearbox can handle. The service factor can be as low as 1.4, which is sufficient for most industrial applications. However, high shock loads and impact loads will require higher service factors. Failure to account for these factors can lead to broken shafts and damaged bearings.
The output style is also important. You need to determine if you want a keyless or keyed hollow bore, as well as if you need an output flange. If you choose a keyless hollow bore, you will need to select a seal material that can withstand the higher temperatures.

editor by CX 2023-06-13
China OEM China Manufacturer Wholesale High Precision Worm Gear Speed Reducer and Robot Gearbox cycloidal drive gear ratio
Product Description
Product Description
China Manufacturer Wholesale high precision Worm Gear Speed Reducer and robot gearbox
HangZhou Fubao Electromechanical Technology Co., Ltd.WF series Speed Reducer and robot gearbox for 5 axis machining center developed and manufactured by WEITENSTAN together with German and ZheJiang technicians for many years.
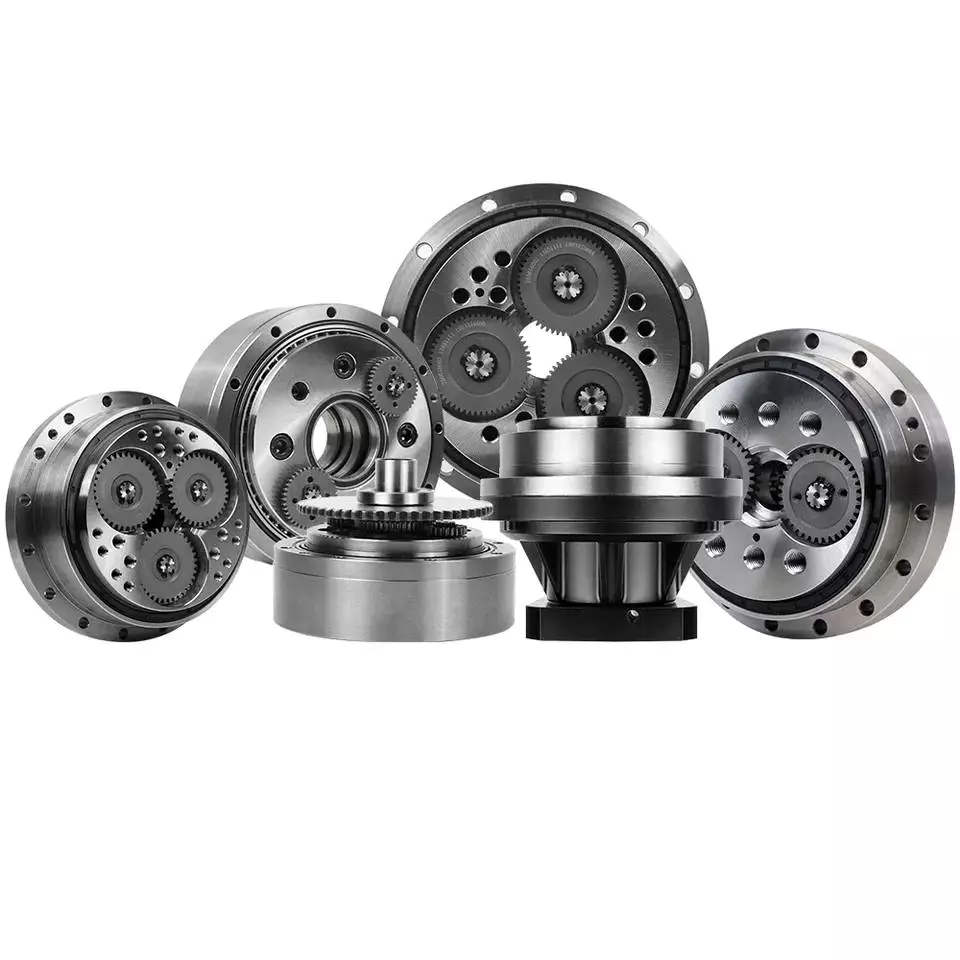
High precision miniature cycloidal gearbox has the characteristics of smaller, ultra-thin, lightweight and high rigidity, anti-overload and high torque. With good deceleration performance, smooth operation and accurate positioning can be achieved. Integrated design, can be directly connected with the motor, to achieve high precision, high rigidity, high durability and other advantages. It is designed for high speed ratio, high geometric accuracy, low motion loss, large torque capacity and high stiffness applications. The compact design (minimum OD ≈40mm, currently the world’s smallest precision cycloidal pin-wheel reducer) allows it to be installed in limited Spaces.
The design of WEITENSTAN high-precision reducers is based on a new reduction principle and newly developed radial and axial output bearings. The result is a new generation of power transmission systems. The new drive concept allows WEITENSTAN gear units to be used directly in the gears of robot joints, rotary tables and various transport systems.
WEITENSTAN high-precision reducers are designed for applications requiring large speed ratios, high precision, low-loss motion, high torque capacity, and high rigidity. At the same time, they are compact in design, can be installed in limited spaces, and have small inertia.
Reducer drawings
Detailed Photos
Product Advantage
China Manufacturer Wholesale high precision Worm Gear Speed Reducer and robot gearbox
advantages:
1, fine precision cycloidal structure
Ultra flat shape is achieved through differential reduction mechanism and thin cross roller bearing, contributing to the compact size of the equipment. The combination of small size and unmatched superior parameters achieves the best combination of performance, price and size (high cost performance).
2. Excellent accuracy (transmission loss ≤1 arcmin)
Through the complex meshing of precision cycloid gear and high precision roller pin, higher transmission accuracy is achieved while maintaining small size and high speed ratio.
3, high rigidity
Increase the mesh rate to disperse the load, so the rigidity is high.
4. High overload capacity
It maintains trouble-free operation under abnormally low noise and vibration conditions while ensuring excellent overturning and torsional stiffness parameters. Integrated axial radial cross roller bearings, high load capacity and overload capacity of the reducer, can ensure users to provide a variety of temperature range of applications.
5, the motor installation is simple
Electromechanical integration design, can be directly connected with the motor, any brand of motor can be installed directly, without adding any device.
6. Maintenance free
Seal grease to achieve maintenance free. No refueling, no mounting direction restrictions.
7, stable performance
The manufacturing process of high wear-resistant materials and high precision parts has been certified by ISO9000 quality system, which guarantees the reliable operation of the reducer.
Product Classification
WF Series
High Precision Miniature Reducer
WF series is a high precision micro cycloidal reducer with flange, which has a wide range of applications. This series of reducers includes precise reduction mechanisms and radial – axial roller bearings. The unique design allows load to act directly on the output flange or housing without additional bearings. WF series reducer is characterized by module design, can be installed through the flange motor and reducer, belongs to the motor directly connected reducer.
WFH Series
High Precision Miniature Reducer
WFH series is a hollow form of high precision miniature cycloidal reducer, wire, compressed air pipeline, drive shaft can be through the hollow shaft, non-motor direct connection type reducer. The WFH series is fully sealed, full of grease and includes precise deceleration mechanism and radial – axial roller bearings. The unique design allows load to be acted directly on the output flange or housing without additional bearings.
WR Series
high-precision corner reducer
The WR series is a flange output corner reducer. Like the WF and WFH series, it is a high-precision reducer (backlash less than 1 arc.min), and the level 2 can also be within 1 arc.min, which is higher than other types. Corner type reducer. It can replace the harmonic drive reducer, and its life and rigidity are more than 3 times that of the harmonic.
Product Parameters
| Size | reduction ratio | Rated output moment | Allowable torque of start and stop | Instantaneous allowable moment | Rated input speed | Maximum input speed | Tilt stiffness | Torsional stiffness | No-load starting torque | Transmission accuracy | Error accuracy | Moment of inertia | Weight | |
| Axis rotation | Shell rotation | Nm | Nm | Nm | rpm | rpm | Nm/arcmin | Nm/arcmin | Nm | arcmin | arcmin | kg-m² | kg | |
| WF07 | 21 | 20 | 15 | 30 | 45 | 3000 | 6000 | 6 | 1.1 | 0.12 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | 0.52 | 0.42 |
| 41 | 40 | 0.11 | 0.47 | |||||||||||
| WF17 | 21 | 20 | 50 | 100 | 150 | 3000 | 6000 | 28 | 6 | 0.21 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | 0.88 | 0.85 |
| 41 | 40 | 0.18 | 0.72 | |||||||||||
| 61 | 60 | 0.14 | 0.69 | |||||||||||
| WF25 | 21 | 20 | 110 | 220 | 330 | 3000 | 5500 | 131 | 24 | 0.47 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | 6.12 | 2 |
| 31 | 30 | 0.41 | 5.67 | |||||||||||
| 41 | 40 | 0.38 | 4.9 | |||||||||||
| 51 | 50 | 0.35 | 4.56 | |||||||||||
| 81 | 80 | 0.31 | 4.25 | |||||||||||
| WF32 | 25 | 24 | 190 | 380 | 570 | 3000 | 4500 | 240 | 35 | 1.15 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | 11 | 4.2 |
| 31 | 30 | 1.1 | 10.8 | |||||||||||
| 51 | 50 | 0.77 | 9.35 | |||||||||||
| 81 | 80 | 0.74 | 8.32 | |||||||||||
| 101 | 100 | 0.6 | 7.7 | |||||||||||
| WF40 | 25 | 24 | 320 | 640 | 960 | 3000 | 4000 | 377 | 50 | 1.35 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | 13.2 | 6.6 |
| 31 | 30 | 1.32 | 12.96 | |||||||||||
| 51 | 50 | 0.92 | 11.22 | |||||||||||
| 81 | 80 | 0.81 | 9.84 | |||||||||||
| 121 | 120 | 0.72 | 8.4 | |||||||||||
Installation Instructions
Company Profile
Q: Speed reducer grease replacement time
A: When sealing appropriate amount of grease and running reducer, the standard replacement time is 20000 hours according to the aging condition of the grease. In addition, when the grease is stained or used in the surrounding temperature condition (above 40ºC), please check the aging and fouling of the grease, and specify the replacement time.
Q: Delivery time
A: Fubao has 2000+ production base, daily output of 1000+ units, standard models within 7 days of delivery.
Q: Reducer selection
A: Fubao provides professional product selection guidance, with higher product matching degree, higher cost performance and higher utilization rate.
Q: Application range of reducer
A: Fubao has a professional research and development team, complete category design, can match any stepping motor, servo motor, more accurate matching.
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
| Application: | Motor, Machinery, Agricultural Machinery |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Horizontal Type |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
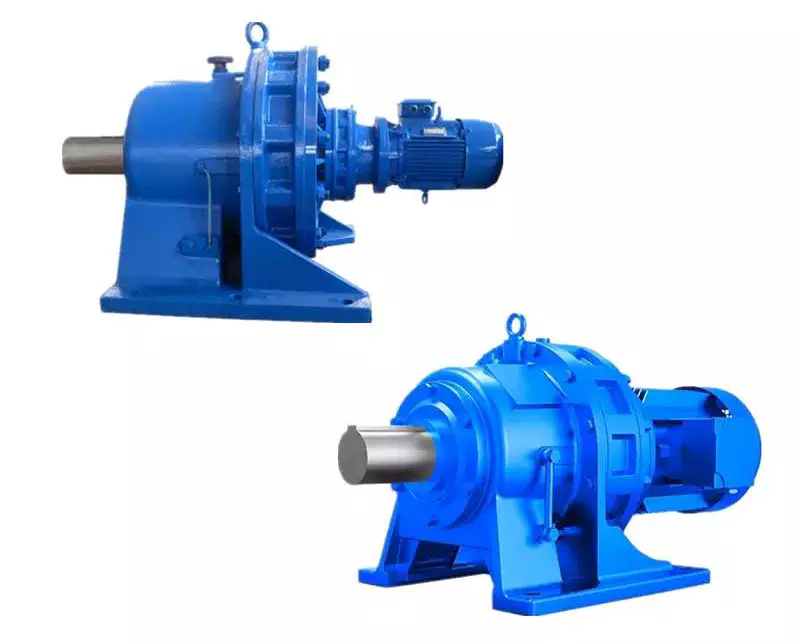

Developing a Mathematical Model of a Cyclone Gearbox
Compared to planetary gearboxes, cycloidal gearboxes are often seen as the ideal choice for a wide range of applications. They feature compact designs that are often low friction and high reduction ratios.
Low friction
Developing a mathematical model of a cycloidal gearbox was a challenge. The model was able to show the effects of a variety of geometric parameters on contact stresses. It was able to model stiction in all quadrants. It was able to show a clear correlation between the results from simulation and real-world measurements.
The model is based on a new approach that enables modeling stiction in all quadrants of a gearbox. It is also able to display non-zero current at standstill. Combined with a good simulation algorithm, the model can be used to improve the dynamic behaviour of a controlled system.
A cycloidal gearbox is a compact actuator used for industrial automation. This type of gearbox provides high gear ratios, low wear, and good torsional stiffness. In addition, it has good shock load capacity.
The model is based on cycloidal discs that engage with pins on a stationary ring gear. The resulting friction function occurs when the rotor begins to rotate. It also occurs when the rotor reverses its rotation. The model has two curves, one for motor and one for generator mode.
The trochoidal profile on the cycloidal disc’s periphery is required for proper mating of the rotating parts. In addition, the profile should be defined accurately. This will allow an even distribution of contact forces.
The model was used to compare the relative performance of a cycloidal gearbox with that of an involute gearbox. This comparison indicates that the cycloidal gearbox can withstand more load than an involute gearbox. It is also able to last longer. It is also able to produce high gear ratios in a small space.
The model used is able to capture the exact geometry of the parts. It can also allow a better analysis of stresses.
Compact
Unlike helical gearing, compact cycloidal gearboxes can provide higher reduction ratios. They are more compact and less weighty. In addition, they provide better positioning accuracy.
Cycloid drives provide high torque and load capacity. They are also very efficient and robust. They are ideal for applications with heavy loads or shock loads. They also feature low backlash and high torsional stiffness. Cycloid gearboxes are available in a variety of designs.
Cycloid discs are mounted on an eccentric input shaft, which drives them around a stationary ring gear. The ring gear consists of many pins, and the cycloidal disc moves one lobe for every rotation of the input shaft. The output shaft contains roller pins, which rotate around holes in the cycloidal disc.
Cycloid drives are ideally suited to heavy loads and shock loads. They have high torsional stiffness and high reduction ratios, making them very efficient. Cycloid gearboxes have low backlash and high torque and are very compact.
Cycloid gearboxes are used for a wide variety of applications, including marine propulsion systems, CNC machining centers, medical technology, and manipulation robots. They are especially useful in applications with critical positioning accuracy, such as surgical positioning systems. Cycloid gearboxes feature extremely low hysteresis loss and low backlash over extended periods of use.
Cycloid discs are usually designed with a reduced cycloid diameter to minimize unbalance forces at high speeds. Cycloid drives also feature minimal backlash, a high reduction ratio, and excellent positioning accuracy. Cycloid gearboxes also have a long service life, compared to other gear drives. Cycloid drives are highly robust, and offer higher reduction ratios than helical gear drives.
Cycloid gearboxes have a low cost and are easy to print. CZPT gearboxes are available in a wide range of sizes and can produce high torque on the output axis.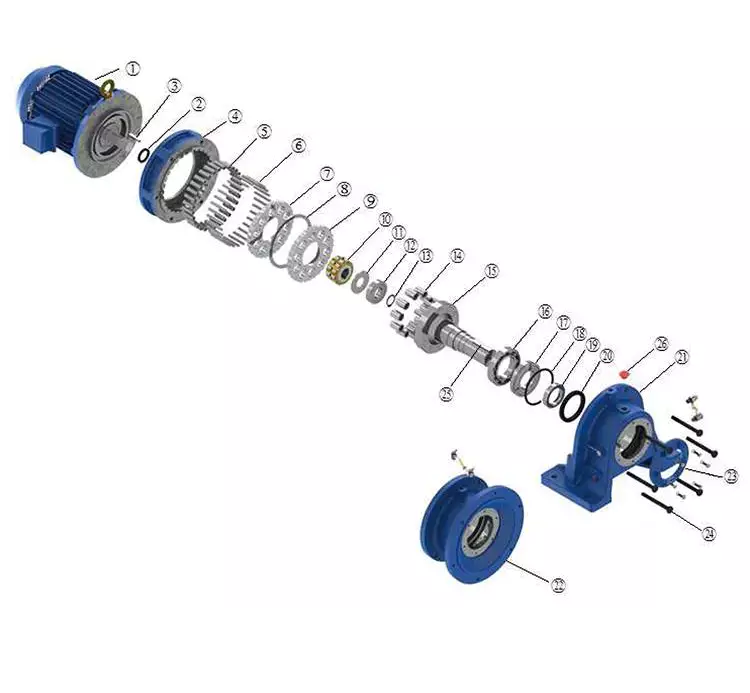
High reduction ratio
Among the types of gearboxes available, a high reduction ratio cycloidal gearbox is a popular choice in the automation field. This gearbox is used in applications requiring precise output and high efficiency.
Cycloid gears can provide high torque and transmit it well. They have low friction and a small backlash. They are widely used in robotic joints. However, they require special tools to manufacture. Some have even been 3D printed.
A cycloidal gearbox is typically a three-stage structure that includes an input hub, an output hub, and two cycloidal gears that rotate around each other. The input hub mounts movable pins and rollers, while the output hub mounts a stationary ring gear.
The input shaft is driven by an eccentric bearing. The disc is then pushed against the ring gear, which causes it to rotate around the bearing. As the disc rotates, the pins on the ring gear drive the pins on the output shaft.
The input shaft rotates a maximum of nine revolutions, while the output shaft rotates three revolutions. This means that the input shaft has to rotate over eleven million times before the output shaft is able to rotate. The output shaft also rotates in the opposite direction of the input shaft.
In a two-stage differential cycloidal speed reducer, the input shaft uses a crank shaft design. The crank shaft connects the first and second cycloidal gears and actuates them simultaneously.
The first stage is a cycloidal disc, which is a gear tooth profile. It has n=7 lobes on its circumference. Each lobe moves around a reference pitch circle of pins. The disc then advances in 360deg steps.
The second stage is a cycloidal disc, also known as a “grinder gear”. The teeth on the outer gear are fewer than the teeth on the inner gear. This allows the gear to be geardown based on the number of teeth.
Kinematics
Various scholars have studied the kinematics of cycloidal gearbox. They have developed various approaches to modify the tooth profile of cycloidal gears. Some of these approaches involve changing the shape of the cycloidal disc, and changing the grinding wheel center position.
This paper describes a new approach to cycloid gear profile modification. It is based on a mathematical model and incorporates several important parameters such as pressure angle, backlash, and root clearance. The study offers a new way for modification design of cycloid gears in precision reducers for robots.
The pressure angle of a tooth profile is an intersegment angle between the normal direction and the velocity direction at a meshing point. The pressure angle distribution is important for determining force transmission performance of gear teeth in meshing. The distribution trend can be obtained by calculating the equation (5).
The mathematical model for modification of the tooth profile can be obtained by establishing the relationship between the pressure angle distribution and the modification function. The dependent variable is the modification DL and the independent variable is the pressure angle a.
The position of the reference point A is a major consideration in the modification design. It ensures the force transmission performance of the meshing segment is optimal. It is determined by the smallest profile pressure angle. The position is also dependent on the type of gear that is being modified. It is also influenced by the tooth backlash.
The mathematical model governing the pressure angle distribution is developed with DL=f(a). It is a piecewise function that determines the pressure angle distribution of a tooth profile. It can also be expressed as DL=ph.
The pressure angle of a tooth is also an angle between the common normal direction at the meshing point and the rotation velocity direction of the cycloid gear.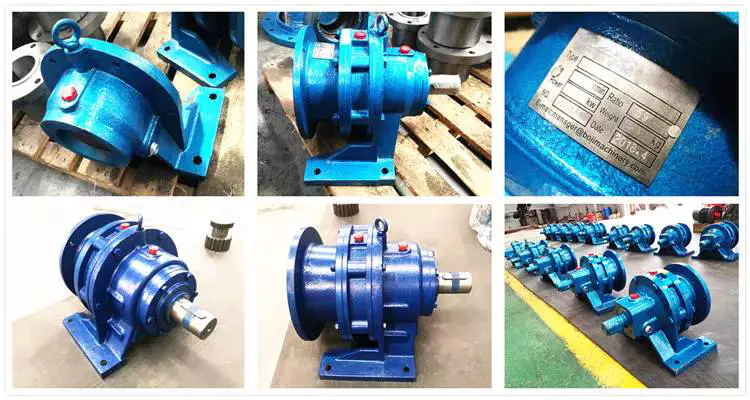
Planetary gearboxes vs cycloidal gearboxes
Generally, there are two types of gearboxes that are used for motion control applications: cycloidal gearbox and planetary gearbox. Cycloid gearboxes are used for high-frequency motions, while planetary gearboxes are suitable for low-speed applications. Both are highly accurate and precise gearboxes that are capable of handling heavy loads at high cycle rates. But they have different advantages and disadvantages. So, engineers need to determine which type of gearbox is best suited for their application.
Cycloid gearboxes are commonly used in industrial automation. They provide excellent performance with ratios as low as 10:1. They offer a more compact design, higher torque density and greater overload protection. They also require less space and are less expensive than planetary gearboxes.
On the other hand, planetary gearboxes are lightweight and offer a higher torque density. They are also capable of handling higher ratios. They have a longer life span and are more precise and durable. They can be found in a variety of styles, including square-framed, round-framed and double-frame designs. They offer a wide range of torque and speed capabilities and are used for numerous applications.
Cycloid gearboxes can be manufactured with different types of cycloidal cams, including single or compound cycloidal cams. Cycloid cams are cylindrical elements that have cam followers that rotate in an eccentric fashion. The cam followers act like teeth on the internal gear. Cycloid cams are a simple concept, but they have numerous advantages. They have a low backlash over extended periods of time, allowing for more accurate positioning. They also have internal compressive stresses and an overlap factor between the rolling elements.
Planetary gearboxes are characterized by three basic force-transmitting elements: ring gear, sun gear, and planet gear. They are generally two-stage gearboxes. The sun gear is attached to the input shaft, which in turn is attached to the servomotor. The ring gear turns the sun gear and the planet gear turns the output shaft.

editor by CX 2023-06-05
China Hot selling Transmission Loss ≤ 1arc. Min RV Series Gear Reducer Gearbox Price supplier
Product Description
Product Description
Transmission loss ≤1arc.min RV series gear reducer gearbox price
gear reducer gearbox Installed with radial thrust ball bearings, so it can support external load, torque rigidity, large allowable torque, can reduce the number of components required, easy installation. The revolution speed of WRV gears is slower and vibration is reduced, which can reduce the motor structure (input gear) and inertia.
gear reducer gearbox High precision, high rigidity, high torque, high load and other characteristics realize hollow design at the same time. After being hollowed out, the ease of use of the product is improved due to the variety of piping and cable layout options.
The gear reducer gearbox is developed on the basis of the traditional needle wheel reducer. It not only overcomes the shortcomings of the general needle pendulum transmission, but also has more advantages, such as long life, stable precision, high efficiency, smooth transmission, small size, Light weight, large reduction ratio range, etc. This RV reducer from FUBAO adopts a double support support mechanism and a pinwheel mechanism, even if a torque up to 6 times the rated torque is applied, the product will not be damaged, and the torsional rigidity is very large. Small backlash, small volume, large torque. In order to directly support large loads, main bearings (large angular contact ball bearings) are installed inside.
gear reducer gearbox mainly has the following characteristics:
A. Main bearing built-in mechanism
1. Improved reliability;
2. Total cost reduction;
3. Radial thrust ball bearings are installed, so they can support external loads, and the moment rigidity and allowable moment are large, which can reduce the number of required components;
4. The use of couplings and motor flanges makes the installation of the motor very simple.
B. 2-stage deceleration mechanism
1. Small vibration;
2. The revolution speed of the gear is slowed down, the vibration is reduced, and the direct connection part of the motor (input gear) can be reduced, and the inertia can be reduced.
C. Double column support mechanism
1. High torsional rigidity;
2. Strong impact resistance;
3. The crank shaft is supported by double columns in the reducer.
D. Rolling contact mechanism
1. Excellent starting power;
2. Small abrasion and long service life;
3. Small backlash (1arc.min).
Product Parameters
| WRV-E series | Specifications | WRV6E | WRV20E | WRV40E | WRV80E | WRV110E | WRV160E | WRV320E | WR450E |
| Rated output torque | 196 | 882 | 1666 | 2156 | 2940 | 3920 | 7056 | 17640 | |
| Reduction ratio | 31~103 | 57~161 | 57~153 | 57~153 | 81~175 | 81~171 | 81~185 | 81~192 | |
| Backlash | <=1 | ||||||||
Detailed Photos
Application Case
Company Profile
HangZhou Fubao Electromechanical Technology Co., Ltd. was established in 2008, the company has a complete precision reducer design, production capacity. Set R & D, manufacturing, assembly and sales, more in the field of gear manufacturing has more than 10 years of background, in the manufacturing equipment is equipped with Switzerland Riesenhahl gear grinding machine, domestic Qinchuan gear grinding machine, hamai gear hobbing machine and domestic Xihu (West Lake) Dis. gear hobbing machine, Japan Yasaki TLGmazak CNC lathe, CNC milling machine and other fully CNC equipment, In addition, it is equipped with other advanced measuring equipment such as Japanese TTI gear detector, 3 coordinate measurement, reducer backlash measurement instrument and so on. In a strong manufacturing capacity at the same time, can be stable, continuous manufacturing of high-quality precision reducer products.
The precision reducer produced by our company has the characteristics of high structural rigidity, small back backlash, precise transmission and so on. It is widely used in various industries. Companies adhering to the concept of let customers participate in manufacturing, and strive to provide customers with more personalized services. In the field of precision transmission has a unique achievements. It is our CZPT pursuit to make far-reaching contributions.
Factory Display
FAQ
Q: Speed reducer grease replacement time
A: When sealing appropriate amount of grease and running reducer, the standard replacement time is 20000 hours according to the aging condition of the grease. In addition, when the grease is stained or used in the surrounding temperature condition (above 40ºC), please check the aging and fouling of the grease, and specify the replacement time.
Q: Delivery time
A: Fubao has 2000+ production base, daily output of 1000+ units, standard models within 7 days of delivery.
Q: Reducer selection
A: Fubao provides professional product selection guidance, with higher product matching degree, higher cost performance and higher utilization rate.
Q: Application range of reducer
A: Fubao has a professional research and development team, complete category design, can match any stepping motor, servo motor, more accurate matching.
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
| Application: | Motor, Machinery, Agricultural Machinery, Robot Arm |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Change Drive Torque, Speed Changing, Speed Reduction, Speed Increase, Lower Rpm and Increase Torque |
| Layout: | Cycloidal |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How to Use a Cyclone Gearbox
Often, a cycloidal gearbox is used in order to achieve a torque transfer from a motor or pump. This type of gearbox is often a common choice as it has a number of advantages over a regular gearbox. Its main advantage is that it is easy to make, which means that it can be incorporated into a variety of applications. However, if you want to use a cycloidal gearbox, there are a few things that you need to know. These include the operation principle, the structure and the dynamic and inertial effects that come with it.
Dynamic and inertial effects
Several studies have been carried out on the static and dynamic properties of cycloidal gears. The study of these effects is beneficial in assisting optimal design of cycloidal speed reducers.
In this paper, the dynamic and inertial effects of a two-stage cycloidal speed reducer have been investigated using the CZPT program package. Moreover, a new model for cycloidal reducers based on non-linear contact dynamics has been developed. The new model aims to predict several operational conditions.
The normal excitation contact force for the cycloid discs of the first and second stage is very similar. However, the total deformation at the contact point is different. This effect is mainly due to the system’s own oscillations. The cycloid discs of the second stage turn around the ring gear roller with a 180deg angle. This angle is a significant contributor to the torque loads. The total excitation force on the cycloid discs of first and second stage is 1848 N and 2068.7 N, respectively.
In order to analyze the contact stress, different gear profiles were investigated. The mesh density was considered as an important design criterion. It was found that a bigger hole reduces the material content of the cycloidal disc and results in more stresses.
Moreover, it is possible to reduce the contact forces in a more efficient manner by changing the geometric parameters. This can be done by mesh refinement along the disc width. The cycloidal disc has the greatest influence on the output results.
The efficiency of a cycloidal drive increases with the increase in load. The efficiency of a cycloidal reducer also depends on the eccentricity of the input shaft and the cycloidal plate. The efficiency curve for small loads is linear. However, for the larger loads, the efficiency curve becomes more non-linear. This is because the stiffness of the cycloid reducer increases as the load increases.
Structure
Despite the fact that it looks like a complicated engineering puzzle, the construction of a cycloidal gearbox is actually quite simple. The key elements are the base, the load plate and the thrust bearing. All these elements work together to create a stable, compact gearbox.
The base is a circular section with several cylindrical pins around its outer edge. The pins are fixed on a fixed ring that holds them in a circular path. The ring serves as a reference circle. The circle’s size is approximately 5mm in diameter.
The load plate is a series of threaded screw holes. These are arranged 15mm away from the center. These are used to anchor external structures. The load plate must be rotated around the X and Y axis.
The thrust bearing is placed on top of the load plate. The bearing is made of an internal diameter of 35mm and an external diameter of 52mm. It is used to allow rotation around the Z axis.
The cycloidal disc is the centerpiece of the cycloidal gearbox. The disc has holes for the pins that drive the output shaft. The holes are larger than those used in output roller pins. The disc also has a reduced eccentricity.
The pins are attached to the cycloidal disc by rolling pins. The pins are made of a material that provides mechanical support for the drive during high-torque situations. The pins have a 9mm external diameter. The disc has a number of lobes and is rotated by one lobe per shaft revolution.
The cycloidal gearbox also has a top cover that helps keep the components together. The cover has a pocket for tools. The top cover also has threads that screw into the casing.
Operation principle
Among many types of gear transmissions, cycloidal gearboxes are used in heavy machinery and multi-axis robots. They are highly effective, compact and capable of high ratios. In addition, they have an overload capability.
Cycloid disks are driven by eccentric shafts that rotate around fixed ring pins. Roller pins of the pin disc engage with holes in the cycloidal disc. These roller pins drive the pin disc and the pin disc transfers the motion to the output shaft.
Unlike conventional gear drives, cycloidal drives have low backlash and high torsional stiffness. They are ideally suited to heavy loads and all drive technologies. The lower mass and compact design of the cycloidal disk also contributes to its high efficiency and positioning accuracy.
The cycloidal disc plays a central role in the gearbox kinematics. It rotates around a fixed ring in a circle. When the disc is pushed against the ring gear, the pins engage with the disc and the roller pins rotate around the pins. This rotating motion generates vibration, which travels through the driven shafts.
Cycloid discs are typically designed with a short cycloid, so that the eccentricity is minimized. This reduces unbalance forces at high speeds. Ideally, the number of lobes on the cycloid is smaller than the number of surrounding pins. This reduces the amount of Hertzian contact stress.
Unlike planetary gears, cycloidal gears have high accuracy and are capable of withstanding shock loads. They also experience low friction and less wear on tooth flanks. They also have higher efficiency and load capacity.
Cycloid gears are generally more difficult to manufacture than involute gears. Cycloid gears are not suitable for stacking gear stages. They require extreme accuracy for manufacturing. However, their smaller size and low backlash, high torsional stiffness, and low vibration make them ideal for use in heavy machines.
Involute gear tooth profile
Almost all gears are manufactured with an involute gear tooth profile. Cycloid gears are also produced with this profile. Compared with involute gears, cycloid gears are stronger and can transmit more power. However, they can also be more difficult to manufacture. This makes them costlier.
The involute gear tooth profile is a smooth curve. It is derived from the involute curve of a circle. A tangent to the base circle is the normal at any point of an involute.
This curve has properties that allow the involute gear teeth to transfer motion in perpendicular direction. It is also the path traced by the end of the string unwrapping from a cylinder.
An involute profile has the advantage of being easy to manufacture. It also allows for smooth meshing despite misalignment of the centre distance. This profile is also preferred over a cycloid tooth profile, but it is not the best in every regard.
Cycloid gear teeth are also made of two curves. Unlike involute teeth, cycloid gear teeth have a consistent radius. Cycloid gears are less likely to produce noise. But they are also more expensive to manufacture.
Involute teeth are easier to manufacture because they have only one curve. Cycloid gears can also be made with a rack type cutter. This makes them cheaper to manufacture. However, they require an expert design. They can also be manufactured with a gear shaper that includes a pinion cutter.
The tooth profiles that satisfy the law of gear-tooth action are sometimes called conjugate profiles. The involute profile is the most common of these. It allows for constant torque transmission.
Backlash
Typically, cycloidal drives provide a high ratio of transmission with no backlash. This is because the cycloid disc is driven by an eccentric shaft. During rotation, the cycloid disc rotates around a fixed ring. This ring also rotates independently of the center of gravity.
The cycloid disc is typically shortened to reduce the eccentricity. This helps to minimize the unbalance forces that may occur at high speeds. The cycloid also offers a larger gear ratio than traditional gears. This provides a better positional accuracy.
Cycloid drives also have a high torsional stiffness. This provides greater torsional resilience and shock load capabilities. This is important for a number of reasons, such as in heavy-duty applications.
Cycloid drives also have lower mass. These benefits make them ideally suited for all drive technologies. The design also allows for higher torsional stiffness and service life. These drives also have a much smaller profile.
Cycloid drives are also used to reduce speed. Because of the high torsional stiffness of the cycloid, they also have high positioning accuracy.
Cycloid drives are well-suited to a variety of applications, including electric motors, generators, and pump motors. They are also highly resistant to shock loads, which is important in a variety of applications. This design is ideal for applications that require a large transmission ratio in a compact design.
Cycloid drives also have the advantage of minimizing the clearance between the mating components. This helps to eliminate interference and ensure a positive fit. This is particularly important in gearboxes. It also allows for the use of a load cell and potentiometer to determine the backlash of the gearbox.

editor by CX 2023-06-01
China Professional 142mm Backlash 3arc. Min Planetary Gearhead Gear Speed Reducer Bevel Gearbox manufacturer
Product Description
Product Description
142mm Backlash 3arc.min planetary gearhead Gear Speed Reducer bevel gearbox
HangZhou Fubao Electromechanical Technology Co., Ltd. planetary gearhead Gear Speed Reducer bevel gearbox is a new generation of practical products independently developed by our company:
Low noise: less than 65db.
Low back clearance: up to 3 arc minutes in a CZPT and 5 arc minutes in a double stage.
High torque: higher than the standard planetary reducer torque.
High stability: high strength alloy steel, the whole gear after hardening treatment, not only the surface hard substitution.
High deceleration ratio: Modular design, planetary gearbox can be interlinked.
planetary gearhead Gear Speed Reducer bevel gearbox characteristic:
1.Planetary reducer manufacturer-Fubao Electromechanical Technology adopts an integrated planetary carrier and output shaft, which can provide better torsional rigidity. After precision machining, the gear set is not easy to eccentric, which can reduce interference, reduce wear and noise, and at the same time use a large The bearings are arranged with a wide span to distribute the load of the bearings, and once again strengthen the torque rigidity and radial load capacity of the planetary gearhead Gear Speed Reducer bevel gearbox. The output cover is made of aluminum alloy, which provides better heat dissipation capability for the product, so that the reducer produced by Fubao Electromechanical Technology can play an excellent role in the field of mechanical tools.
2.The planetary gear set is specially made of alloy steel. First, it undergoes quenching and tempering heat treatment to make the material hardness reach HRC30 degrees, and then undergoes nitriding surface treatment to HV860, so that the product has the characteristics of high surface hardness and high toughness in the center, and achieves the best product strength and service life. optimization.
3.The input shaft and the motor output shaft are connected by a bolted structure, with a round shaft seal design, and through dynamic balance analysis, it can ensure that there is no eccentric load at high speeds. After reducing unnecessary radial force, it can effectively Reduce the load on the motor side.
4.The material of the input cover/motor connection seat is made of aluminum alloy, which can provide better heat dissipation effect, and then provide good concentricity and verticality through professional lathe processing, so that the product can be stably combined with various motors, reducing the damage caused by insufficient precision. Unnecessary axial radial force makes the product have a longer life cycle.
Product Parameters
| WVB/WVBL series parameters | Model number | WVB042/WVBL50 | WVB60/WVBL70 | WVB/WVBL90 | WVB/WVBL120 | WVB142/WVBL155 | WVB180/WVBL205 | WVB220/WVBL235 |
| Rated output torque | 13-17Nm | 32-48Nm | 80-125Nm | 165-265Nm | 280-530Nm | 480-960Nm | 900-1360Nm | |
| Reduction ratio | L1: 3, 4, 5, 7, 10 | L2: 12, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 50, 70, 100 | ||||||
| Planetary gear backlash | L1: P1≤3 P2≤5 L2: P1≤5 P2≤7 | |||||||
Detailed Photos
Product Details
Other products
Product Advantage
Compared with other reduction machines, planetary gear reduction machines have high rigidity, high precision (single stage can be achieved within 1 point), high transmission efficiency (single stage in 97-98%), high torque/volume ratio, lifetime maintenance free and other characteristics.
Because of these characteristics, planetary gear reducer is mostly installed on the stepper motor and servo motor, used to reduce speed, increase torque, matching inertia.
Company Profile
HangZhou Fubao Electromechanical Technology Co., Ltd. was established in 2008, the company has a complete precision reducer design, production capacity. Set R & D, manufacturing, assembly and sales, more in the field of gear manufacturing has more than 10 years of background, in the manufacturing equipment is equipped with Switzerland Riesenhahl gear grinding machine, domestic Qinchuan gear grinding machine, hamai gear hobbing machine and domestic Xihu (West Lake) Dis. gear hobbing machine, Japan Yasaki TLGmazak CNC lathe, CNC milling machine and other fully CNC equipment, In addition, it is equipped with other advanced measuring equipment such as Japanese TTI gear detector, 3 coordinate measurement, reducer backlash measurement instrument and so on. In a strong manufacturing capacity at the same time, can be stable, continuous manufacturing of high-quality precision reducer products.
The precision reducer produced by our company has the characteristics of high structural rigidity, small back backlash, precise transmission and so on. It is widely used in various industries. Companies adhering to the concept of let customers participate in manufacturing, and strive to provide customers with more personalized services. In the field of precision transmission has a unique achievements. It is our CZPT pursuit to make far-reaching contributions.
Factory Display
Q: Speed reducer grease replacement time
A: When sealing appropriate amount of grease and running reducer, the standard replacement time is 20000 hours according to the aging condition of the grease. In addition, when the grease is stained or used in the surrounding temperature condition (above 40ºC), please check the aging and fouling of the grease, and specify the replacement time.
Q: Delivery time
A: Fubao has 2000+ production base, daily output of 1000+ units, standard models within 7 days of delivery.
Q: Reducer selection
A: Fubao provides professional product selection guidance, with higher product matching degree, higher cost performance and higher utilization rate.
Q: Application range of reducer
A: Fubao has a professional research and development team, complete category design, can match any stepping motor, servo motor, more accurate matching.
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
| Application: | Motor, Machinery, Agricultural Machinery, Pipe Bender |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Horizontal Type |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

The Advantages of Using a Cyclone Gearbox
Using a cycloidal gearbox to drive an input shaft is a very effective way to reduce the speed of a machine. It does this by reducing the speed of the input shaft by a predetermined ratio. It is capable of very high ratios in relatively small sizes.
Transmission ratio
Whether you’re building a marine propulsion system or a pump for the oil and gas industry, there are certain advantages to using cycloidal gearboxes. Compared to other gearbox types, they’re shorter and have better torque density. These gearboxes also offer the best weight and positioning accuracy.
The basic design of a cycloidal gearbox is similar to that of a planetary gearbox. The main difference is in the profile of the gear teeth.
Cycloid gears have less tooth flank wear and lower Hertzian contact stress. They also have lower friction and torsional stiffness. These advantages make them ideal for applications that involve heavy loads or high-speed drives. They’re also good for high gear ratios.
In a cycloidal gearbox, the input shaft drives an eccentric bearing, while the output shaft drives the cycloidal disc. The cycloidal disc rotates around a fixed ring, and the pins of the ring gear engage the holes in the disc. The pins then drive the output shaft as the disc rotates.
Cycloid gears are ideal for applications that require high gear ratios and low friction. They’re also good for applications that require high torsional stiffness and shock load resistance. They’re also suitable for applications that require a compact design and low backlash.
The transmission ratio of a cycloidal gearbox is determined by the number of lobes on the cycloidal disc. The n=n design of the cycloidal disc moves one lobe per revolution of the input shaft.
Cycloid gears can be manufactured to reduce the gear ratio from 30:1 to 300:1. These gears are suitable for high-end applications, especially in the automation industry. They also offer the best positioning accuracy and backlash. However, they require special manufacturing processes and require non-standard characteristics.
Compressive force
Compared with conventional gearboxes, the cycloidal gearbox has a unique set of kinematics. It has an eccentric bearing in a rotating frame, which drives the cycloidal disc. It is characterized by low backlash and torsional stiffness, which enables geared motion.
In this study, the effects of design parameters were investigated to develop the optimal design of a cycloidal reducer. Three main rolling nodes were studied: a cycloidal disc, an outer race and the input shaft. These were used to analyze the motion related dynamic forces, which can be used to calculate stresses and strains. The gear mesh frequency was calculated using a formula, which incorporated a correction factor for the rotating frame of the outer race.
A three-dimensional finite element analysis (FEA) study was conducted to evaluate the cycloidal disc. The effects of the size of the holes on the disc’s induced stresses were investigated. The study also looked at the torque ripple of a cycloidal drive.
The authors of this study also explored backlash distribution in the output mechanism, which took into account the machining deviations and structure and geometry of the output mechanism. The study also looked at the relative efficiency of a cycloidal reducer, which was based on a single disc cycloidal reducer with a one-tooth difference.
The authors of this study were able to deduce the contact stress of the cycloidal disc, which is calculated using the material-based contact stiffness. This can be used to determine accurate contact stresses in a cycloidal gearbox.
It is important to know the ratios needed for calculation of the bearing rate. This can be calculated using the formula f = k (S x R) where S is the volume of the element, R is the mass, k is the contact stiffness and f is the force vector.
Rotational direction
Unlike the conventional ring gear which has a single axis of rotation, cycloidal gearbox has three rotational axes which are parallel and are located in a single plane. A cycloidal gearbox has excellent torsional stiffness and shock load capacity. It also ensures constant angular velocity, and is used in high-speed gearbox applications.
A cycloidal gearbox consists of an input shaft, a drive member and a cycloidal disc. The disc rotates in one direction, while the input shaft rotates in the opposite direction. The input shaft eccentrically mounts to the drive member. The cycloidal disc meshes with the ring-gear housing, and the rotational motion of the cycloidal disc is transferred to the output shaft.
To calculate the rotational direction of a cycloidal gearbox, the cycloid must have the correct angular orientation and the centerline of the cycloid should be aligned with the center of the output hole. The cycloid’s shortest length should be equal to the radius of the pin circle. The cycloid’s largest radius should be the size of the bearing’s exterior diameter.
A single-stage gear will not have much space to work with, so you’ll need a multistage gear to maximize space. This is also the reason that cycloid gears are usually designed with a shortened cycloid.
To calculate the most efficient tooth profile for a cycloidal gear, a new method was devised. This method uses a mathematical model that uses the cycloid’s rotational direction and a few other geometric parameters. Using a piecewise function related to the distribution of pressure angle, the cycloid’s most efficient profile is determined. It is then superimposed on the theoretical profile. The new method is much more flexible than the conventional method, and can adapt to changing trends of the cycloidal profile.
Design
Several designs of cycloidal gearboxes have been developed. These gearboxes have a large reduction ratio in one stage. They are mainly used for heavy machines. They provide good torsional stiffness and shock load capacity. However, they also have vibrations at high RPM. Several studies have been conducted to find a solution to this problem.
A cycloidal gearbox is designed by calculating the reduction ratio of a mechanism. This ratio is obtained by the size of the input speed. This is then multiplied by the reduction ratio of the gear profile.
The most important factor in the design of a cycloidal gearbox is the load distribution along the width of the gear. Using this as a design criterion, the amplitude of vibration can be reduced. This will ensure that the gearbox is working properly. In order to generate proper mating conditions, the trochoidal profile on the cycloidal disc periphery must be defined accurately.
One of the most common forms of cycloidal gears is circular arc toothing. This is the most common type of toothing used today.
Another form of gear is the hypocycloid. This form requires the rolling circle diameter to be equal to half the base circle diameter. Another special case is the point tooth form. This form is also called clock toothing.
In order to make this gear profile work, the initial point of contact must remain fixed to the edge of the rolling disk. This will generate the hypocycloid curve. The curve is traced from this initial point.
To investigate this gear profile, the authors used a 3D finite element analysis. They used the mathematical model of gear manufacturing that included kinematics parameters, output moment calculations, and machining steps. The resulting design eliminated backlash.
Sizing and selection
Choosing a gearbox can be a complex task. There are many factors that need to be taken into account. You need to determine the type of application, the required speed, the load, and the ratio of the gearbox. By gaining this information, you can find a solution that works best for you.
The first thing you need to do is find the proper size. There are several sizing programs available to help you determine the best gearbox for your application. You can start by drawing a cycloidal gear to help you create the part.
During sizing, it is important to consider the environment. Shock loads, environmental conditions, and ambient temperatures can increase wear on the gear teeth. The temperature also has a significant impact on lubrication viscosities and seal materials.
You also need to consider the input and output speed. This is because the input speed will change your gearbox ratio calculations. If you exceed the input speed, you can damage the seals and cause premature wear on the shaft bearings.
Another important aspect of sizing is the service factor. This factor determines the amount of torque the gearbox can handle. The service factor can be as low as 1.4, which is sufficient for most industrial applications. However, high shock loads and impact loads will require higher service factors. Failure to account for these factors can lead to broken shafts and damaged bearings.
The output style is also important. You need to determine if you want a keyless or keyed hollow bore, as well as if you need an output flange. If you choose a keyless hollow bore, you will need to select a seal material that can withstand the higher temperatures.

editor by CX 2023-05-31
China Standard Backlash Less Than 1arc. Min Gear Decelerator & Agricultural Gearbox for 1000W Servomotor cycloidal pin gear reducer
Product Description
Product Description
Backlash less than 1arc.min Gear Decelerator & agricultural gearbox for 1000W servomotor
high-precision corner reducer for 5 axis machining center developed and manufactured by WEITENSTAN together with German and ZheJiang technicians for many years.
This high-precision corner reducer has high precision (backlash less than 1arcmin), low noise (68dB), and can replace the harmonic drive reducer. The life and rigidity are 3 times longer than the harmonic.
high-precision corner reducer has the characteristics of smaller, ultra-thin, lightweight and high rigidity, anti-overload and high torque. With good deceleration performance, smooth operation and accurate positioning can be achieved. Integrated design, can be directly connected with the motor, to achieve high precision, high rigidity, high durability and other advantages. It is designed for high speed ratio, high geometric accuracy, low motion loss, large torque capacity and high stiffness applications. The compact design (minimum OD ≈40mm, currently the world’s smallest precision cycloidal pin-wheel reducer) allows it to be installed in limited Spaces.
Reducer drawings
Detailed Photos
Product Advantage
Backlash less than 1arc.min Gear Decelerator & agricultural gearbox for 1000W servomotor
advantages:
1, fine precision cycloidal structure
Ultra flat shape is achieved through differential reduction mechanism and thin cross roller bearing, contributing to the compact size of the equipment. The combination of small size and unmatched superior parameters achieves the best combination of performance, price and size (high cost performance).
2. Excellent accuracy (transmission loss ≤1 arcmin)
Through the complex meshing of precision cycloid gear and high precision roller pin, higher transmission accuracy is achieved while maintaining small size and high speed ratio.
3, high rigidity
Increase the mesh rate to disperse the load, so the rigidity is high.
4. High overload capacity
It maintains trouble-free operation under abnormally low noise and vibration conditions while ensuring excellent overturning and torsional stiffness parameters. Integrated axial radial cross roller bearings, high load capacity and overload capacity of the reducer, can ensure users to provide a variety of temperature range of applications.
5, the motor installation is simple
Electromechanical integration design, can be directly connected with the motor, any brand of motor can be installed directly, without adding any device.
6. Maintenance free
Seal grease to achieve maintenance free. No refueling, no mounting direction restrictions.
7, stable performance
The manufacturing process of high wear-resistant materials and high precision parts has been certified by ISO9000 quality system, which guarantees the reliable operation of the reducer.
Product Classification
WF Series
High Precision Miniature Reducer
WF series is a high precision micro cycloidal reducer with flange, which has a wide range of applications. This series of reducers includes precise reduction mechanisms and radial – axial roller bearings. The unique design allows load to act directly on the output flange or housing without additional bearings. WF series reducer is characterized by module design, can be installed through the flange motor and reducer, belongs to the motor directly connected reducer.
WFH Series
High Precision Miniature Reducer
WFH series is a hollow form of high precision miniature cycloidal reducer, wire, compressed air pipeline, drive shaft can be through the hollow shaft, non-motor direct connection type reducer. The WFH series is fully sealed, full of grease and includes precise deceleration mechanism and radial – axial roller bearings. The unique design allows load to be acted directly on the output flange or housing without additional bearings.
WR Series
high-precision corner reducer
The WR series is a flange output corner reducer. Like the WF and WFH series, it is a high-precision reducer (backlash less than 1 arc.min), and the level 2 can also be within 1 arc.min, which is higher than other types. Corner type reducer. It can replace the harmonic drive reducer, and its life and rigidity are more than 3 times that of the harmonic.
Product Parameters
| Size | reduction ratio | Rated output moment | Allowable torque of start and stop | Instantaneous allowable moment | Rated input speed | Maximum input speed | Tilt stiffness | Torsional stiffness | No-load starting torque | Transmission accuracy | Error accuracy | Moment of inertia | Weight | |
| Axis rotation | Shell rotation | Nm | Nm | Nm | rpm | rpm | Nm/arcmin | Nm/arcmin | Nm | arcmin | arcmin | kg-m² | kg | |
| WR25 | 21 | 20 | 110 | 220 | 330 | 3000 | 5500 | 131 | 24 | 0.47 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | 6.12 | 2 |
| 31 | 30 | 0.41 | 5.67 | |||||||||||
| 41 | 40 | 0.38 | 4.9 | |||||||||||
| 51 | 50 | 0.35 | 4.56 | |||||||||||
| 81 | 80 | 0.31 | 4.25 | |||||||||||
| WR32 | 25 | 24 | 190 | 380 | 570 | 3000 | 4500 | 240 | 35 | 1.15 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | 11 | 4.2 |
| 31 | 30 | 1.1 | 10.8 | |||||||||||
| 51 | 50 | 0.77 | 9.35 | |||||||||||
| 81 | 80 | 0.74 | 8.32 | |||||||||||
| 101 | 100 | 0.6 | 7.7 | |||||||||||
| WR40 | 25 | 24 | 320 | 640 | 960 | 3000 | 4000 | 377 | 50 | 1.35 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | 13.2 | 6.6 |
| 31 | 30 | 1.32 | 12.96 | |||||||||||
| 51 | 50 | 0.92 | 11.22 | |||||||||||
| 81 | 80 | 0.81 | 9.84 | |||||||||||
| 121 | 120 | 0.72 | 8.4 | |||||||||||
Installation Instructions
Company Profile
Q: Speed reducer grease replacement time
A: When sealing appropriate amount of grease and running reducer, the standard replacement time is 20000 hours according to the aging condition of the grease. In addition, when the grease is stained or used in the surrounding temperature condition (above 40ºC), please check the aging and fouling of the grease, and specify the replacement time.
Q: Delivery time
A: Fubao has 2000+ production base, daily output of 1000+ units, standard models within 7 days of delivery.
Q: Reducer selection
A: Fubao provides professional product selection guidance, with higher product matching degree, higher cost performance and higher utilization rate.
Q: Application range of reducer
A: Fubao has a professional research and development team, complete category design, can match any stepping motor, servo motor, more accurate matching.
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
| Application: | Motor, Machinery, Agricultural Machinery, Humanoid Robot |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Vertical Type |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Condition Monitoring of Cyclone Gearboxes
Whether you’re considering using a cycloidal gearbox in your home, office, or garage, you’ll want to make sure it’s made of quality material. You also want to make sure it’s designed properly, so it won’t be damaged by vibrations.
Planetary gearboxes
Compared to cycloidal gearboxes, planetary gearboxes are lighter and more compact, but they lack the precision and durability of the former. They are better suited for applications with high torque or speed requirements. For this reason, they are usually used in robotics applications. But, cycloidal gearboxes are still better for some applications, including those involving shock loads.
There are many factors that affect the performance of gearboxes during production. One of these is the number of teeth. In the case of planetary gearboxes, the number of teeth increases with the number of planets. The number of teeth is reduced in cycloidal gearboxes, which results in higher transmission ratios. These gearboxes also have lower breakaway torques, which means that they can be controlled more easily by the user.
A cycloid gearbox is comprised of three main parts: the ring gear, the sun gear, and the input shaft. The ring gear is fixed in the gearbox, while the sun gear transmits the rotation to the planet gears. The input shaft transfers motion to the sun gear, which in turn transmits it to the output shaft. The output shaft has a larger torque than the input shaft.
Cycloid gears have better torsional stiffness, lower wear, and lower Hertzian contact stress. However, they are also larger in size and require highly accurate manufacturing. Cycloid gears can be more difficult to manufacture than involute gears, which require large amounts of precision.
Cycloid gears can offer transmission ratios up to 300:1, and they can do this in a small package. They also have lower wear and friction, which makes them ideal for applications that require a high transmission ratio.
Cycloid gearboxes are usually equipped with a backlash of about one angular minute. This backlash provides the precision and control necessary for accurate movement. They also provide low wear and shock load capacity.
Planetary gearboxes are available in single and two-stage designs, which increase in length as stages are added. In addition to the two stages, they can be equipped with an optional output bearing, which takes up mounting space. In some applications, a third stage is also available.
Involute gears
Generally, involute gears are more complex to manufacture than cycloidal gears. For example, an involute gear tooth profile has a single curve while a cycloidal gear tooth profile has two curves. In addition, the involute curve is not within the base circle.
The involute curve is a very important component of a gear tooth and it can significantly influence the quality of contact meshing between teeth. Various works have been done on the subject, mainly focusing on the operating principles. In addition, the most important characteristic of the double-enveloping cycloid drive is its double contact lines between the meshing tooth pairs.
Cycloid gears are more powerful, less noisy, and last longer than involute gears. They also require less manufacturing operations during production. However, cycloid gears are more expensive than involute gears. Involute gears are more commonly used in linear motions while cycloid gears are used for rotary motions.
Although cycloid gears are more technically advanced, involute gears have the superior quality and are more aesthetically pleasing. Cycloid gears are used in various industrial applications such as pumps and compressors. They are also widely used in the watch industry. Nevertheless, involute gears have not yet replaced cycloid gears in the watch industry.
The cycloid disc has a number of pins around its outer edge, while an involute gear has only a single curve for the teeth. In addition, cycloid gears have a more robust and reliable design. Involute gears, on the other hand, have a cheaper rack cutter and less expensive involute teeth.
The cycloid disc’s transmission accuracy is about 98.5%, while the ring gear’s transmission accuracy is about 96%. The cycloid disc’s rotational velocity has a magnitude of 3 rad/s. A small change in the center distance does not affect the transmission accuracy. However, rotational velocity fluctuation can affect the transmission accuracy.
Cycloid gears also have the cycloid gear disc’s rotational velocity. The disc has N lobes. However, the cycloid gear disc’s transmission accuracy is still not perfect. This is because of the large rotational angles between the lobes. This also makes it difficult to manufacture.
Vibrations
Using modern techniques for vibration diagnostics and data-driven methods, this article presents a new approach to condition monitoring of cycloidal gearboxes. This approach focuses on detecting the root cause of gearbox failure. The article aims to provide a unified approach to gear designers.
A cycloidal gearbox is a high-precision gearbox that is used in heavy-duty machines. It has a large reduction ratio, which makes it necessary to have a very large input speed. Cycloid gears have high accuracy, but they are susceptible to vibration issues. In this article, the authors describe how a cycloidal gearbox works and how vibrations are measured. They also show how this gearbox can be used to detect faults.
The gearbox is used in positioners, multi-axis robots, and heavy-duty machines. The main characteristics of this gearbox are the high accuracy, the overload capacity, and the large reduction ratio.
There is little documentation on vibrations and condition monitoring of cycloidal gearboxes. The authors describe their approach to the problem, using a cycloidal gearbox and a testing bench. Their approach involves measuring the frequency of the gearbox with different input speeds.
The results show a good separation between the healthy and damaged states. Fault frequencies show up in the lower orders of frequencies. Faults can be detected using binning, which eliminates the need for a tachometer. In addition, binning is combined with Principal Component Analysis to determine the state of the gearbox.
This method is compared to traditional techniques. In addition, the results show how binning can be used to calculate the defect frequencies of the bearings. It is also used to determine the frequencies of the components.
The signals from the test bench are acquired using four sensors. These sensors are medium sensitivity 100 mV/g accelerometers. The signals are then processed using different signal processing techniques. The results show that the vibration signals are correlated with the internal motion of the gearbox. This information is used to identify the internal frequency of the transmission.
The frequency analysis of vibration signals is performed in cyclostationary and noncyclostationary conditions. The signals are then analyzed to determine the magnitude of the gear meshing frequency.
Design
Using precision gearboxes, servomotors can now control heavy loads at high speed. Unlike cam indexing devices, cycloidal gears provide extremely accurate positioning and high torque. They also provide excellent torsional stiffness and shock load capacity.
Cycloid gears are specially designed to minimize vibration at high RPM. Unlike involute gears, they are not stacked, which reduces friction and forces experienced by each tooth. In addition, cycloidal gears have lower Hertzian contact stress.
Cycloid gears are often used in multi-axis robots for positioners. They can provide transmission ratios as high as 300:1 in a compact package. They are also used in first joints in heavy machines. However, they require extremely accurate manufacturing. They are also more difficult to produce than involute gears.
A cycloidal gearbox is a type of planetary gearbox. Cycloid gears are specially designed for high gear ratios. They also have the ability to provide a large reduction ratio in a single stage. They are increasingly used in first joints in heavy machines. They are also becoming more common in robotics.
In order to achieve a large reduction ratio, the input speed of the gear must be very high. Generally, the input speed is between 500 rpm and 4500 rpm. However, in some cases, the input speed may be lower.
A cycloid is formed by rolling a rolling circle on a base circle. The ratio between the rolling circle diameter and the base circle diameter determines the shape of the cycloid. A hypocycloid is formed by rolling primarily on the inside of the base circle, while an epicycloid is formed by rolling primarily on the outside of the base circle.
Cycloid gears have a very small backlash, which minimizes the forces experienced by each tooth. These gears also have a good torsional stiffness, low friction, and shock load capacity. They also provide the best positioning accuracy.
The cycloidal gearbox was designed and built at Radom University. The design was based on three different cycloidal gears. The first pair had the external profile at the nominal dimension, while the second pair had the profile minus tolerance. The load plate had threaded screw holes arranged 15 mm away from the center.

editor by CX 2023-05-29
China Best Sales China Factory Wholesale Maintenance Free Long Life Steel Reducer Gearbox small cycloidal gearbox
Product Description
Product Description
China Factory wholesale maintenance free long life steel reducer Gearbox
HangZhou Fubao Electromechanical Technology Co., Ltd.WF series steel reducer Gearbox for 5 axis machining center developed and manufactured by WEITENSTAN together with German and ZheJiang technicians for many years.
High precision miniature cycloidal gearbox has the characteristics of smaller, ultra-thin, lightweight and high rigidity, anti-overload and high torque. With good deceleration performance, smooth operation and accurate positioning can be achieved. Integrated design, can be directly connected with the motor, to achieve high precision, high rigidity, high durability and other advantages. It is designed for high speed ratio, high geometric accuracy, low motion loss, large torque capacity and high stiffness applications. The compact design (minimum OD ≈40mm, currently the world’s smallest precision cycloidal pin-wheel reducer) allows it to be installed in limited Spaces.
The design of WEITENSTAN high-precision reducers is based on a new reduction principle and newly developed radial and axial output bearings. The result is a new generation of power transmission systems. The new drive concept allows WEITENSTAN gear units to be used directly in the gears of robot joints, rotary tables and various transport systems.
WEITENSTAN high-precision reducers are designed for applications requiring large speed ratios, high precision, low-loss motion, high torque capacity, and high rigidity. At the same time, they are compact in design, can be installed in limited spaces, and have small inertia.
Reducer drawings
Detailed Photos
Product Advantage
China Factory wholesale maintenance free long life steel reducer Gearbox
advantages:
1, fine precision cycloidal structure
Ultra flat shape is achieved through differential reduction mechanism and thin cross roller bearing, contributing to the compact size of the equipment. The combination of small size and unmatched superior parameters achieves the best combination of performance, price and size (high cost performance).
2. Excellent accuracy (transmission loss ≤1 arcmin)
Through the complex meshing of precision cycloid gear and high precision roller pin, higher transmission accuracy is achieved while maintaining small size and high speed ratio.
3, high rigidity
Increase the mesh rate to disperse the load, so the rigidity is high.
4. High overload capacity
It maintains trouble-free operation under abnormally low noise and vibration conditions while ensuring excellent overturning and torsional stiffness parameters. Integrated axial radial cross roller bearings, high load capacity and overload capacity of the reducer, can ensure users to provide a variety of temperature range of applications.
5, the motor installation is simple
Electromechanical integration design, can be directly connected with the motor, any brand of motor can be installed directly, without adding any device.
6. Maintenance free
Seal grease to achieve maintenance free. No refueling, no mounting direction restrictions.
7, stable performance
The manufacturing process of high wear-resistant materials and high precision parts has been certified by ISO9000 quality system, which guarantees the reliable operation of the reducer.
Product Classification
WF Series
High Precision Miniature Reducer
WF series is a high precision micro cycloidal reducer with flange, which has a wide range of applications. This series of reducers includes precise reduction mechanisms and radial – axial roller bearings. The unique design allows load to act directly on the output flange or housing without additional bearings. WF series reducer is characterized by module design, can be installed through the flange motor and reducer, belongs to the motor directly connected reducer.
WFH Series
High Precision Miniature Reducer
WFH series is a hollow form of high precision miniature cycloidal reducer, wire, compressed air pipeline, drive shaft can be through the hollow shaft, non-motor direct connection type reducer. The WFH series is fully sealed, full of grease and includes precise deceleration mechanism and radial – axial roller bearings. The unique design allows load to be acted directly on the output flange or housing without additional bearings.
WR Series
high-precision corner reducer
The WR series is a flange output corner reducer. Like the WF and WFH series, it is a high-precision reducer (backlash less than 1 arc.min), and the level 2 can also be within 1 arc.min, which is higher than other types. Corner type reducer. It can replace the harmonic drive reducer, and its life and rigidity are more than 3 times that of the harmonic.
Product Parameters
| Size | reduction ratio | Rated output moment | Allowable torque of start and stop | Instantaneous allowable moment | Rated input speed | Maximum input speed | Tilt stiffness | Torsional stiffness | No-load starting torque | Transmission accuracy | Error accuracy | Moment of inertia | Weight | |
| Axis rotation | Shell rotation | Nm | Nm | Nm | rpm | rpm | Nm/arcmin | Nm/arcmin | Nm | arcmin | arcmin | kg-m² | kg | |
| WF07 | 21 | 20 | 15 | 30 | 45 | 3000 | 6000 | 6 | 1.1 | 0.12 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | 0.52 | 0.42 |
| 41 | 40 | 0.11 | 0.47 | |||||||||||
| WF17 | 21 | 20 | 50 | 100 | 150 | 3000 | 6000 | 28 | 6 | 0.21 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | 0.88 | 0.85 |
| 41 | 40 | 0.18 | 0.72 | |||||||||||
| 61 | 60 | 0.14 | 0.69 | |||||||||||
| WF25 | 21 | 20 | 110 | 220 | 330 | 3000 | 5500 | 131 | 24 | 0.47 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | 6.12 | 2 |
| 31 | 30 | 0.41 | 5.67 | |||||||||||
| 41 | 40 | 0.38 | 4.9 | |||||||||||
| 51 | 50 | 0.35 | 4.56 | |||||||||||
| 81 | 80 | 0.31 | 4.25 | |||||||||||
| WF32 | 25 | 24 | 190 | 380 | 570 | 3000 | 4500 | 240 | 35 | 1.15 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | 11 | 4.2 |
| 31 | 30 | 1.1 | 10.8 | |||||||||||
| 51 | 50 | 0.77 | 9.35 | |||||||||||
| 81 | 80 | 0.74 | 8.32 | |||||||||||
| 101 | 100 | 0.6 | 7.7 | |||||||||||
| WF40 | 25 | 24 | 320 | 640 | 960 | 3000 | 4000 | 377 | 50 | 1.35 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | P1≤±1 P2≤±3 | 13.2 | 6.6 |
| 31 | 30 | 1.32 | 12.96 | |||||||||||
| 51 | 50 | 0.92 | 11.22 | |||||||||||
| 81 | 80 | 0.81 | 9.84 | |||||||||||
| 121 | 120 | 0.72 | 8.4 | |||||||||||
Installation Instructions
Company Profile
Q: Speed reducer grease replacement time
A: When sealing appropriate amount of grease and running reducer, the standard replacement time is 20000 hours according to the aging condition of the grease. In addition, when the grease is stained or used in the surrounding temperature condition (above 40ºC), please check the aging and fouling of the grease, and specify the replacement time.
Q: Delivery time
A: Fubao has 2000+ production base, daily output of 1000+ units, standard models within 7 days of delivery.
Q: Reducer selection
A: Fubao provides professional product selection guidance, with higher product matching degree, higher cost performance and higher utilization rate.
Q: Application range of reducer
A: Fubao has a professional research and development team, complete category design, can match any stepping motor, servo motor, more accurate matching.
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
| Application: | Motor, Machinery, Agricultural Machinery |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Horizontal Type |

A Mathematical Model of a Cycloid Gearbox
Having a gearbox with a cycloidal rotor is an ideal design for a car or any other vehicle, as the cycloidal design can reduce the amplitude of vibration, which is a key component in car performance. Using a cycloidal gearbox is also a great way to reduce the amount of friction between the gears in the gearbox, which can help to reduce noise and wear and tear. A cycloidal gearbox is also a very efficient design for a vehicle that needs to perform under high loads, as the gearbox can be very robust against shock loads.
Basic design principles
cycloidal gearboxes are used for precision gearing applications. Cycloidal drives are compact and robust and offer lower backlash, torsional stiffness and a longer service life. They are also suitable for applications involving heavy loads.
Cycloidal drives are compact in size and provide very high reduction ratios. They are also very robust and can handle shock loads. Cycloidal drives are ideally suited to a wide range of drive technologies. Cycloidal gears have excellent torsional stiffness and can provide a transmission ratio of 300:1. They can also be used in applications where stacking multiple gear stages is not desired.
In order to achieve a high reduction ratio, cycloidal gears must be manufactured extremely accurately. Cycloidal gears have a curved tooth profile that removes shear forces at any point of contact. This provides a positive fit for the gear disc. This profile can be provided on a separate outer bushing or as an internal gear profile insert.
Cycloidal drives are used in marine propulsion systems, where the load plate rotates around the X and Y axis. The plate is anchored by a threaded screw hole arranged 15mm away from the center.
A secondary carrier body is used in a cycloidal gearbox to support the load plate. The secondary carrier body is composed of a mounting carrier body and a secondary carrier disc.
Low friction
Several studies have been conducted to understand the static problems of gears. In this paper, we discuss a mathematical model of a low friction cycloidal gearbox. This model is designed to calculate various parameters that affect the performance of the gearbox during production.
The model is based on a new approach that includes the stiction effect and the nonlinear friction characteristic. These parameters are not covered by the conventional rule of thumb.
The stiction effect is present when the speed direction is changed. During this time, the input torque is required to prevail over the stiction effect to generate movement. The model also enables us to calculate the magnitude of the stiction effect and its breakaway speed.
The most important thing is that the model can be used to improve the dynamic behavior of a controlled system. In this regard, the model has a high degree of accuracy. The model is tested in several quadrants of the gearbox to find the optimum stiction breakaway speed. The simulation results of the model show that this model is effective in predicting the efficiency of a low friction cycloidal gearbox.
In addition to the stiction model, we also studied the efficiency of a low friction cycloidal reducer. The reduction ratio of this gearbox was estimated from the formula. It is found that the ratio approaches negative infinity when the motor torque is close to zero Nm.
Compact
Unlike standard planetary gears, cycloidal gearboxes are compact, low friction and feature virtually zero backlash. They also offer high reduction ratios, high load capacity and high efficiency. These features make them a viable option for a variety of applications.
Cycloid disks are driven by an eccentric input shaft. They are then driven by a stationary ring gear. The ring gear rotates the cycloidal disk at a higher rate. The input shaft rotates nine times to complete a full rotation. The ring gear is designed to correct the dynamic imbalance.
CZPT cycloidal gearheads are designed for precision and stable operation. These reducers are robust and can handle large translocations. They also offer high overload protection. They are suitable for shock wave therapy. CZPT gearheads are also well suited for applications with critical positioning accuracy. They also require low assembly and design costs. They are designed for long service life and low hysteresis loss.
CZPT cycloidal reducers are used in a variety of industrial applications, including CNC machining centers, robot positioners and manipulators. They offer a unique design that can handle high forces on the output axis, and are especially suitable for large translocations. These gearheads are highly efficient, reducing costs, and are available in a variety of sizes. They are ideal for applications that require millimetre accuracy.
High reduction ratios
Compared to other gearboxes, cycloidal gearboxes offer high reduction ratios and small backlash. They are also less expensive. Cycloid gearboxes can be used in a variety of industries. They are suitable for robotic applications. They also have high efficiency and load capacity.
A cycloidal gearbox works by rotating a cycloidal disc. This disc contains holes that are bigger than the pins on the output shaft. When the disc is rotated, the output pins move in the holes to generate a steady output shaft rotation. This type of gearbox does not require stacking stages.
Cycloid gearboxes are usually shorter than planetary gearboxes. Moreover, they are more robust and can transmit higher torques.
Cycloid gearboxes have an eccentric cam that drives the cycloidal disc. The cycloidal disc advances in 360deg/pivot/roller steps. It also rotates in an eccentric pattern. It meshes with the ring-gear housing. It also engages the internal teeth of the ring-gear housing.
The number of lobes on the cycloidal disc is not sufficient to generate a good transmission ratio. In fact, the number of lobes must be less than the number of pins surrounding the cycloidal disc.
The cycloidal disc is rotated by an eccentric cam that extends from the base shaft. The cam also spins inside the cycloidal disc. The eccentric motion of the cam helps the cycloidal disc rotate around the pins of the ring-gear housing.
Reducing amplitude of the vibration
Various approaches to reducing amplitude of the vibration in a cycloidal gearbox have been studied. These approaches are based on the kinematic analysis of gearbox.
A cycloidal gearbox is a gearbox that consists of bearings, gears, and an eccentric bearing that drives a cycloidal disc. This gearbox has a high reduction ratio, which is achieved by a series of output shaft pins that drive the output shaft as the disc rotates.
The test bench used in the studies has four sensors. Each sensor acquires signals with different signal processing techniques. In addition, there is a tachometer that acquires variations in rotational velocity at the input side.
The kinematic study of the robotic gearbox was performed to understand the frequency of vibrations and to determine whether the gearbox is faulty. It was found that the gearbox is in healthy operation when the amplitude of the x and y is low. However, when the amplitude is high, it is indicative of a malfunctioning element.
The frequency analysis of vibration signals is performed for both cyclostationary and noncyclostationary conditions. The frequencies that are selected are those that appear in both types of conditions.
Robust against shock loads
Compared to traditional gearboxes, cycloidal gearboxes have significant benefits when it comes to shock loads. These include high shock-load capacity, high efficiency, reduced cost, lower weight, lower friction, and better positioning accuracy.
Cycloid gears can be used to replace traditional planetary gears in applications where inertia is important, such as the transportation of heavy loads. They have a lighter design and can be manufactured to a more compact size, which helps reduce cost and installation expense. Cycloid gears are also able to provide transmission ratios of up to 300:1 in a small package.
Cycloid gears are also suitable for applications where a long service life is essential. Their radial clamping ring reduces inertia by up to 39%. Cycloid gears have a torsional stiffness that is five times higher than that of conventional planetary gears.
Cycloid gearboxes can provide significant improvements in concrete mixers. They are a highly efficient design, which allows for important innovations. They are also ideal for servo applications, machine tools, and medical technology. They feature user-friendly screw connections, effective corrosion protection, and effective handling.
Cycloid gears are especially useful for applications with critical positioning accuracy. For example, in the control of large parabolic antennas, high shock load capacity is required to maintain accuracy. Cycloid gears can withstand shock loads up to 500% of their rated torque.
Inertial effects
Various studies have been conducted to investigate the static problems of gears. However, there is still a need for a proper model to investigate the dynamic behaviour of a controlled system. For this, a mathematical model of a cycloidal gearbox has been developed. The presented model is a simple model that can be used as the basis for a more complex mechanical model.
The mathematical model is based on the cycloidal gearbox’s mechanical construction and has a nonlinear friction characteristic. The model is able to reproduce the current peaks and breaks at standstill. It also considers the stiction effect. However, it does not cover backlash or torsional stiffness.
This model is used to calculate the torque generating current and the inertia of the motor. These values are then compared with the real system measurement. The results show that the simulation results are very close to the real system measurement.
Several parameters are considered in the model to improve its dynamic behaviour. These parameters are calculated from the harmonic drive system analysis. These are torque-generating current, inertia, and the contact forces of the rotating parts.
The model has a high level of accuracy and can be used for motor control. It is also able to reproduce the dynamic behaviour of a controlled system.

editor by CX 2023-05-26